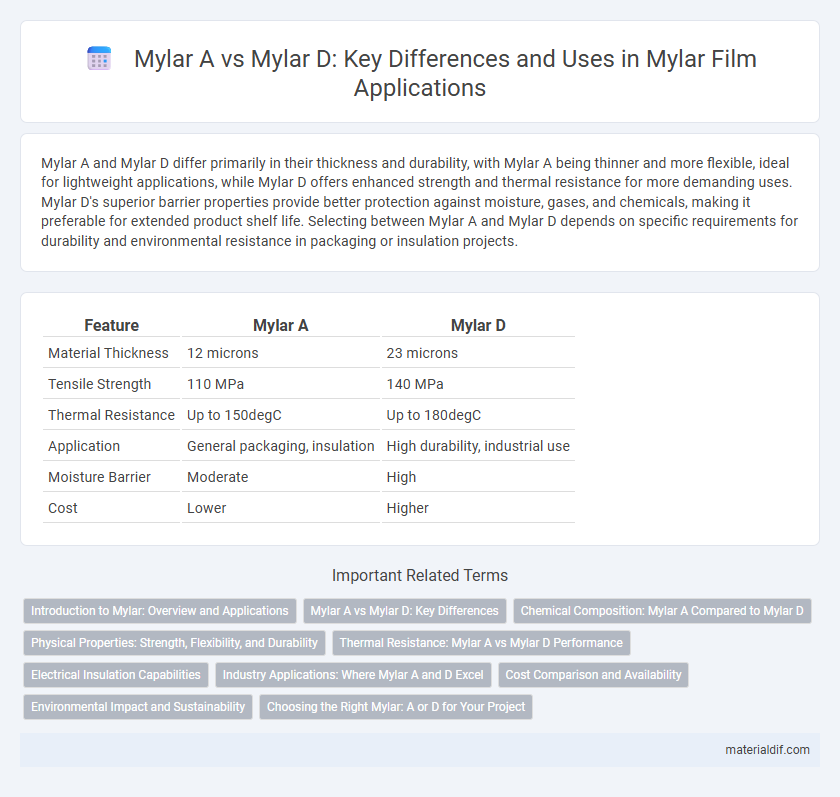
Mylar A and Mylar D differ primarily in their thickness and durability, with Mylar A being thinner and more flexible, ideal for lightweight applications, while Mylar D offers enhanced strength and thermal resistance for more demanding uses. Mylar D's superior barrier properties provide better protection against moisture, gases, and chemicals, making it preferable for extended product shelf life. Selecting between Mylar A and Mylar D depends on specific requirements for durability and environmental resistance in packaging or insulation projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mylar A | Mylar D |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | 12 microns | 23 microns |
| Tensile Strength | 110 MPa | 140 MPa |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 180degC |
| Application | General packaging, insulation | High durability, industrial use |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Mylar: Overview and Applications
Mylar A features a standard polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film known for its high tensile strength, dimensional stability, and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for packaging, insulation, and electronic applications. Mylar D incorporates a metallized layer, enhancing barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light, which significantly extends product shelf life in food packaging and pharmaceutical blister packs. The choice between Mylar A and Mylar D depends on specific application requirements involving durability, protection, and environmental resistance.
Mylar A vs Mylar D: Key Differences
Mylar A is a biaxially oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET) film known for its high tensile strength, superior clarity, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical insulation and packaging applications. Mylar D differs by incorporating a dielectric coating that enhances its electrical insulation properties and improves resistance to moisture and chemicals, which suits it for specialized industrial uses. The primary distinction lies in Mylar A's general-purpose versatility versus Mylar D's specialized dielectric performance.
Chemical Composition: Mylar A Compared to Mylar D
Mylar A is a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film with a standard one-side coating of ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) designed to enhance adhesion and durability, while Mylar D features a dual-side coating of EVA for improved chemical resistance and electrical insulation. The chemical composition of Mylar A includes a single EVA layer primarily for surface protection, whereas Mylar D's dual EVA layers offer enhanced resistance to moisture, solvents, and heat. These differences in coating chemistry directly impact the performance characteristics and suitability of each variant for specific industrial and electronic applications.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Mylar A exhibits higher tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring robust mechanical support, while Mylar D offers greater flexibility, suitable for conforming to complex shapes. Both variants provide excellent durability, though Mylar A demonstrates superior resistance to tearing and punctures under stress. These distinct physical properties influence their selection across industries such as electronics, packaging, and insulation.
Thermal Resistance: Mylar A vs Mylar D Performance
Mylar A exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to Mylar D, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, while Mylar D typically withstands around 125degC. The enhanced thermal stability of Mylar A makes it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to high heat. This performance difference is critical in electronics insulation and thermal barrier uses where temperature tolerance is essential.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Mylar A offers superior electrical insulation due to its high dielectric strength, typically around 5000 volts per mil, making it ideal for applications requiring robust voltage resistance. Mylar D, while still effective, features slightly lower dielectric properties but provides better thermal stability and mechanical flexibility. Both variants maintain excellent moisture resistance, ensuring reliable insulation performance in varying environmental conditions.
Industry Applications: Where Mylar A and D Excel
Mylar A excels in packaging applications due to its high tensile strength, excellent moisture barrier properties, and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for food and pharmaceutical industries. Mylar D is preferred in electrical insulation and industrial film applications because of its superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, ensuring reliable performance in motors, capacitors, and transformers. Both variants are key in manufacturing flexible printed circuits and solar panels, with Mylar A providing durability and Mylar D offering enhanced heat resistance.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Mylar A is generally more affordable and widely available due to its extensive use in packaging and insulation applications, making it a preferred choice for cost-sensitive projects. Mylar D, often used in specialized industrial and electronic applications, tends to be more expensive and may have limited availability depending on the supplier. Pricing variations between the two types are influenced by manufacturing processes and material properties, impacting overall project budgets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mylar A and Mylar D differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with Mylar D being a more eco-friendly option due to its enhanced recyclability and reduced carbon footprint during production. Mylar A often contains higher levels of non-recyclable additives, which contribute to greater landfill waste and slower degradation rates. Choosing Mylar D supports sustainable manufacturing practices and aligns better with circular economy principles.
Choosing the Right Mylar: A or D for Your Project
Choosing the right Mylar film depends on your specific project requirements, with Mylar A offering superior clarity and tensile strength ideal for high-precision applications such as photographic films and electronics insulation. Mylar D provides enhanced dimensional stability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for packaging, labeling, and applications exposed to varying environmental conditions. Assessing factors such as durability, environmental exposure, and clarity helps determine whether Mylar A or D best aligns with your project's performance needs.
Mylar A vs Mylar D Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com