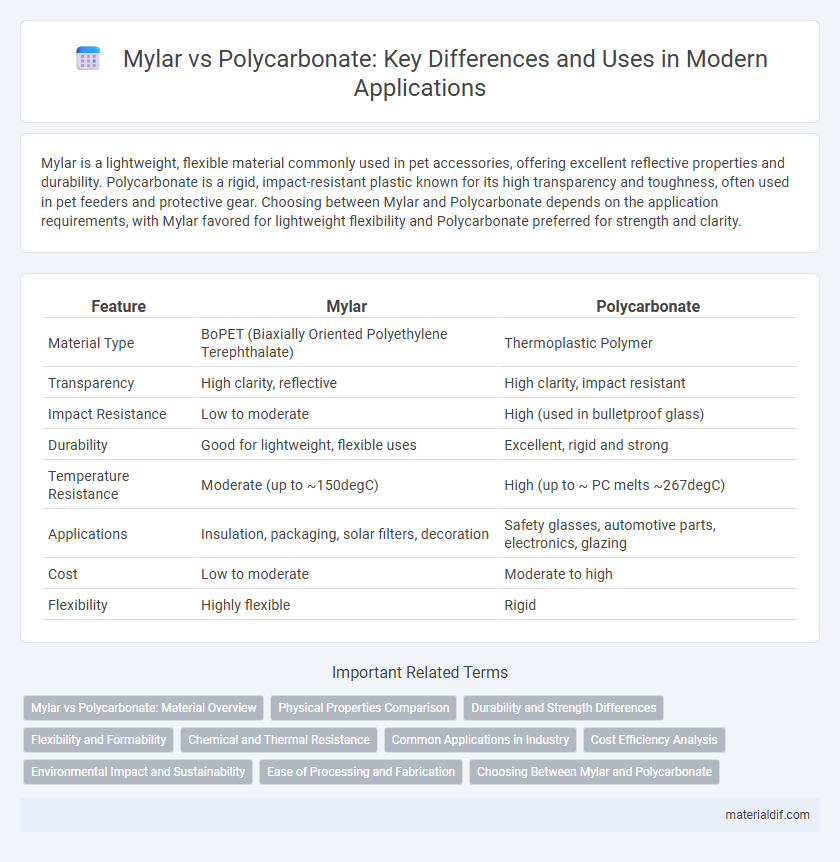
Mylar is a lightweight, flexible material commonly used in pet accessories, offering excellent reflective properties and durability. Polycarbonate is a rigid, impact-resistant plastic known for its high transparency and toughness, often used in pet feeders and protective gear. Choosing between Mylar and Polycarbonate depends on the application requirements, with Mylar favored for lightweight flexibility and Polycarbonate preferred for strength and clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mylar | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Transparency | High clarity, reflective | High clarity, impact resistant |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | High (used in bulletproof glass) |
| Durability | Good for lightweight, flexible uses | Excellent, rigid and strong |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate (up to ~150degC) | High (up to ~ PC melts ~267degC) |
| Applications | Insulation, packaging, solar filters, decoration | Safety glasses, automotive parts, electronics, glazing |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible | Rigid |
Mylar vs Polycarbonate: Material Overview
Mylar is a polyester film known for its excellent tensile strength, chemical stability, and high electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic characterized by its impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance, often used in safety glasses and electronics. Compared to polycarbonate, Mylar offers superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance, while polycarbonate provides better impact toughness and heat resistance for structural uses.
Physical Properties Comparison
Mylar exhibits superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and elasticity. Polycarbonate offers higher impact resistance and better heat resistance, suitable for protective gear and thermal insulation. The choice between Mylar and polycarbonate depends on balancing flexibility, strength, and thermal stability requirements.
Durability and Strength Differences
Mylar exhibits superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to impact, making it highly durable against tears and punctures in various applications. Polycarbonate, while also strong, offers greater impact resistance and shatterproof qualities, providing enhanced protection under heavy mechanical stress. The choice between Mylar and Polycarbonate depends on specific durability needs, with Mylar excelling in flexibility and chemical resistance, and Polycarbonate outperforming in toughness and structural strength.
Flexibility and Formability
Mylar exhibits superior flexibility and formability compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for applications requiring thin, bendable films. Polycarbonate offers greater rigidity and impact resistance but lacks the same degree of pliability as Mylar, limiting its use in flexible or curved designs. The lightweight and stretchable nature of Mylar supports complex shaping without cracking, unlike polycarbonate which tends to resist deformation.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Mylar exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polycarbonate, as it withstands exposure to solvents, oils, and various chemicals without degrading. Thermal resistance of Mylar is notable, with a stable operating range typically between -70degC to 150degC, whereas polycarbonate softens around 147degC, limiting its high-temperature applications. These characteristics make Mylar preferable for environments requiring durable chemical and thermal stability.
Common Applications in Industry
Mylar is predominantly used in flexible packaging, electrical insulation, and solar control window films, leveraging its excellent tensile strength and dimensional stability. Polycarbonate finds widespread application in impact-resistant windows, automotive headlamp lenses, and electronic device enclosures due to its superior toughness and optical clarity. Industrial sectors favor Mylar for lightweight, moisture-resistant films, while polycarbonate is preferred where durability and shatter resistance are critical.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Mylar film offers a highly cost-efficient solution compared to polycarbonate sheets, primarily due to its lower material and production expenses. While polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance, Mylar's affordability and ease of manufacturing make it ideal for large-scale applications requiring budget-conscious materials. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, Mylar minimizes upfront investment without significantly compromising performance in light-duty uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mylar, a polyester film made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), offers a lower environmental footprint compared to polycarbonate due to its recyclability and reduced energy consumption during production. Polycarbonate manufacturing involves bisphenol A (BPA), which poses ecological and health concerns, whereas Mylar's chemical stability minimizes harmful emissions and leaching. Mylar's potential for reuse and recycling enhances its sustainability profile, making it preferable for eco-conscious applications over polycarbonate.
Ease of Processing and Fabrication
Mylar offers superior ease of processing and fabrication compared to polycarbonate due to its thin, flexible film structure, which allows for effortless cutting, heat sealing, and lamination. Polycarbonate requires higher temperatures and specialized equipment for molding and shaping, making it less user-friendly in rapid prototyping or small-scale fabrication. The lightweight and dimensional stability of Mylar streamline production workflows, especially in applications like insulation, packaging, and flexible electronics.
Choosing Between Mylar and Polycarbonate
Mylar offers exceptional clarity, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and durable films. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and higher temperature tolerance, suited for demanding environments and structural uses. When choosing between Mylar and Polycarbonate, consider Mylar for insulation, packaging, and graphics, while Polycarbonate fits protective gear, lenses, and architectural components.
Mylar vs Polycarbonate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com