Mylar insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic components in pet-related devices. Kapton insulation provides superior heat tolerance and chemical stability, suitable for high-temperature environments and flexible circuit applications in pet technology. Choosing between Mylar and Kapton depends on the specific thermal and mechanical demands of the pet product design.
Table of Comparison
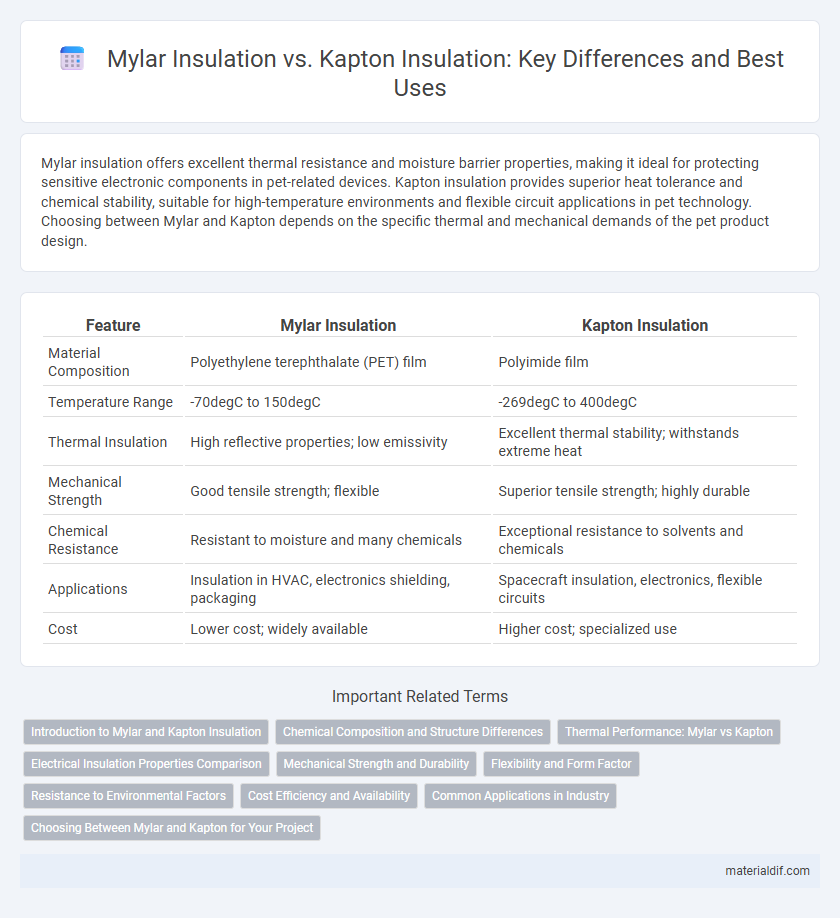
| Feature | Mylar Insulation | Kapton Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film | Polyimide film |
| Temperature Range | -70degC to 150degC | -269degC to 400degC |
| Thermal Insulation | High reflective properties; low emissivity | Excellent thermal stability; withstands extreme heat |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength; flexible | Superior tensile strength; highly durable |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to moisture and many chemicals | Exceptional resistance to solvents and chemicals |
| Applications | Insulation in HVAC, electronics shielding, packaging | Spacecraft insulation, electronics, flexible circuits |
| Cost | Lower cost; widely available | Higher cost; specialized use |
Introduction to Mylar and Kapton Insulation
Mylar insulation, made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film, offers excellent thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for aerospace and electronic applications. Kapton insulation, derived from polyimide film, provides superior heat resistance up to 400degC and electrical insulation properties, which are critical in high-temperature and space environments. Both Mylar and Kapton serve as flexible insulation materials but differ significantly in temperature tolerance and chemical stability, influencing their specific use cases.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Mylar insulation is primarily composed of biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), a polyester film known for its high tensile strength, chemical stability, and reflective properties. Kapton insulation consists of polyimide, a polymer characterized by aromatic rings and imide linkages, providing exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation. The fundamental structural difference lies in Mylar's polyester backbone versus Kapton's polyimide chains, which significantly influences their respective temperature tolerances and chemical resistances in insulation applications.
Thermal Performance: Mylar vs Kapton
Mylar insulation offers excellent thermal reflective properties, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer through radiation in low-temperature environments. Kapton insulation, however, provides superior thermal stability and can withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -269degC to over 400degC without degradation. For applications requiring high thermal resilience and electrical insulation under harsh conditions, Kapton outperforms Mylar, while Mylar is preferable for lightweight, cost-effective thermal insulation in moderate temperature ranges.
Electrical Insulation Properties Comparison
Mylar insulation exhibits excellent dielectric strength of approximately 7,000 volts per mil, providing effective electrical insulation in various applications, while Kapton insulation offers superior thermal stability alongside a dielectric strength around 3,620 volts per mil. Mylar's polyethylene terephthalate composition ensures high tensile strength and moisture resistance, whereas Kapton's polyimide structure enables it to maintain electrical properties under extreme temperatures (-269degC to 400degC). The choice between Mylar and Kapton insulation depends on specific electrical requirements, environmental conditions, and thermal endurance needs in electronic and aerospace industries.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Mylar insulation exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Kapton, making it more resistant to tearing and punctures in demanding applications. Its durability under environmental stressors such as moisture and UV exposure ensures extended lifespan in insulation systems. In contrast, Kapton offers excellent thermal stability but generally has lower mechanical robustness, limiting its use in high-abrasion settings.
Flexibility and Form Factor
Mylar insulation offers superior flexibility compared to Kapton insulation, making it ideal for applications requiring tight bends and intricate shapes. While Kapton provides excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation, Mylar's thinner form factor and higher pliability allow for easier integration into compact electronic assemblies. This enhanced flexibility and slim profile enable Mylar to conform better to complex surfaces, optimizing space and improving overall device performance.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Mylar insulation offers superior resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for outdoor and high-humidity environments. Kapton insulation excels in thermal stability and withstands extreme temperatures up to 400degC, but it is less resistant to UV degradation and moisture penetration compared to Mylar. Mylar's enhanced durability in harsh environmental conditions ensures longer lifespan and reliability in insulation applications exposed to varied elements.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Mylar insulation offers a more cost-efficient solution compared to Kapton insulation, making it ideal for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects. Readily available in various thicknesses and roll sizes, Mylar ensures easy procurement and faster deployment in manufacturing processes. Kapton insulation, while premium and high-performance, typically involves higher costs and limited availability due to specialized production requirements.
Common Applications in Industry
Mylar insulation is widely used in electronics, packaging, and aerospace for its excellent dielectric properties and moisture resistance, making it ideal for circuit boards and flexible printed circuits. Kapton insulation is preferred in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and automotive industries due to its exceptional thermal stability and electrical insulation performance. Common industrial applications of Mylar include insulation layers in transformers and capacitors, while Kapton is often applied in flexible heaters and insulation for wiring in extreme heat conditions.
Choosing Between Mylar and Kapton for Your Project
Mylar insulation offers excellent tensile strength and moisture resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and environmental protection. Kapton insulation excels at high-temperature resistance up to 400degC, suitable for aerospace and electronics projects needing thermal stability. Choosing between Mylar and Kapton depends on your project's thermal demands and environmental exposure, with Mylar preferred for general insulation and Kapton for extreme heat environments.
Mylar Insulation vs Kapton Insulation Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com