Lead sinkers provide excellent weight and durability for fishing, making them ideal for deep-water or heavy current environments, but their toxicity raises environmental concerns. Steel sinkers offer a non-toxic alternative that is lighter and less prone to corrosion, promoting sustainability while still maintaining sufficient weight for most fishing conditions. Choosing between lead and steel sinkers depends on balancing performance needs with ecological responsibility.
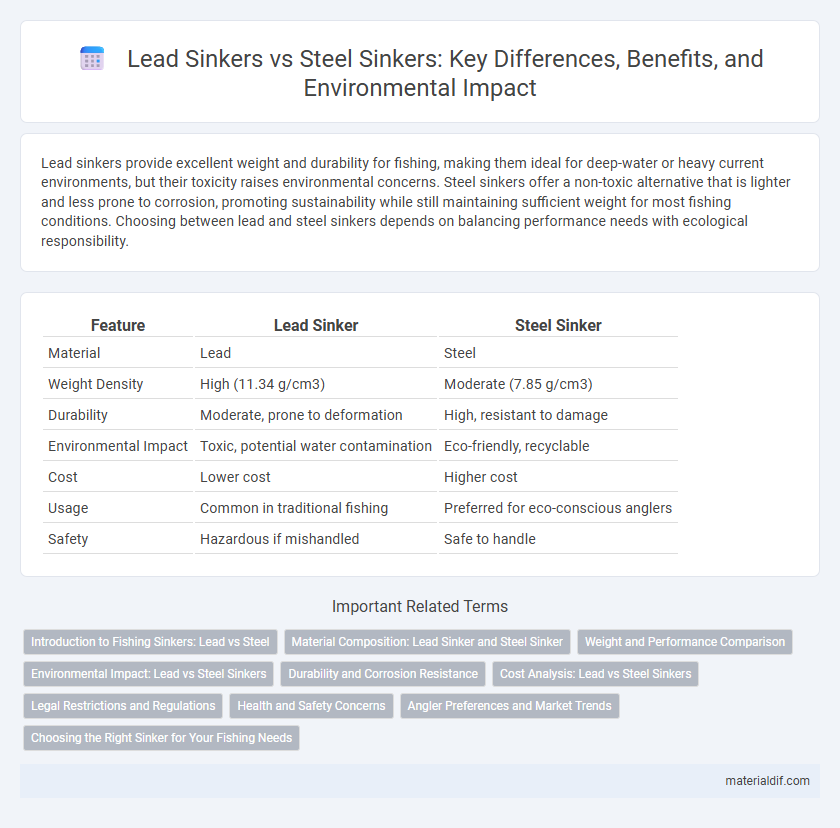
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Sinker | Steel Sinker |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Lead | Steel |
| Weight Density | High (11.34 g/cm3) | Moderate (7.85 g/cm3) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to deformation | High, resistant to damage |
| Environmental Impact | Toxic, potential water contamination | Eco-friendly, recyclable |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Usage | Common in traditional fishing | Preferred for eco-conscious anglers |
| Safety | Hazardous if mishandled | Safe to handle |
Introduction to Fishing Sinkers: Lead vs Steel
Fishing sinkers vary significantly between lead and steel in terms of density and environmental impact. Lead sinkers, favored for their high density, offer better casting distance and faster sinking, ideal for deep-water fishing. Steel sinkers provide a non-toxic alternative with lower density, reducing environmental pollution while delivering reliable weight for versatile fishing conditions.
Material Composition: Lead Sinker and Steel Sinker
Lead sinkers are composed primarily of lead, a dense and malleable metal that provides excellent weight for precise casting and stability in water currents. Steel sinkers, made from corrosion-resistant steel alloys, offer enhanced durability and are environmentally friendlier by avoiding lead toxicity. The choice between lead and steel sinkers depends on balancing weight density with environmental impact and longevity in fishing applications.
Weight and Performance Comparison
Lead sinkers typically offer higher density than steel sinkers, providing more weight in a smaller size, which allows for quicker sinking and better casting distance. Steel sinkers, while less dense, deliver improved durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for rugged fishing environments. Weight differences influence performance by affecting sink rate and sensitivity, with lead performing better for precise placements and steel favored for strength and environmental considerations.
Environmental Impact: Lead vs Steel Sinkers
Lead sinkers pose significant environmental risks due to their toxicity, which can contaminate water bodies and harm aquatic life upon deterioration. Steel sinkers offer a more eco-friendly alternative as they are less toxic and can be recycled, reducing pollution and long-term environmental damage. Choosing steel over lead sinkers helps minimize ecological harm while maintaining fishing effectiveness.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Lead sinkers offer excellent malleability but suffer from limited durability and significant corrosion over time, especially in saltwater environments. Steel sinkers provide superior durability and enhanced corrosion resistance, often coated or treated to withstand harsh conditions without degrading. Anglers seeking long-lasting performance typically prefer steel sinkers due to their resilience against rust and consistent weight retention.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Steel Sinkers
Lead sinkers are generally more affordable due to lower material and manufacturing costs compared to steel sinkers, making them a cost-effective choice for anglers. However, steel sinkers, while slightly more expensive upfront, offer greater durability and environmental benefits by reducing lead pollution and potential health risks. When evaluating overall value, the higher initial investment in steel sinkers can translate to long-term savings through increased longevity and reduced environmental impact fees.
Legal Restrictions and Regulations
Lead sinkers face increasing legal restrictions due to environmental concerns over lead poisoning in aquatic life, with many regions banning or limiting their use to protect water ecosystems. Steel sinkers are often promoted as a compliant alternative, meeting regulatory standards because they do not pose the same toxic risks. Anglers must verify local regulations, as legal allowances for lead and steel sinkers vary widely by country and state, influencing the choice of fishing tackle.
Health and Safety Concerns
Lead sinkers pose significant health risks due to lead's toxic properties, which can cause poisoning if ingested or handled improperly, affecting the nervous system and causing developmental issues. Steel sinkers offer a safer alternative, as steel is non-toxic and does not leach harmful substances into the environment or pose direct health hazards to anglers and wildlife. Choosing steel sinkers minimizes environmental contamination and reduces the risk of lead poisoning in aquatic ecosystems and fishing communities.
Angler Preferences and Market Trends
Angler preferences for lead sinkers remain strong due to their density and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for precise casting and sensitive bite detection. However, steel sinkers are increasingly favored in markets prioritizing environmental sustainability, as they are non-toxic and comply with regulations restricting lead use in fishing tackle. Market trends indicate a gradual shift towards steel sinkers in regions with strict lead bans, while traditional anglers continue to prefer lead for its proven performance.
Choosing the Right Sinker for Your Fishing Needs
Lead sinkers offer excellent weight and durability, making them ideal for maintaining bait stability in various water conditions. Steel sinkers provide an eco-friendly alternative, reducing environmental impact while offering comparable performance in corrosion resistance. Choosing the right sinker depends on factors like fishing environment, target species, and environmental considerations.
Lead Sinker vs Steel Sinker Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com