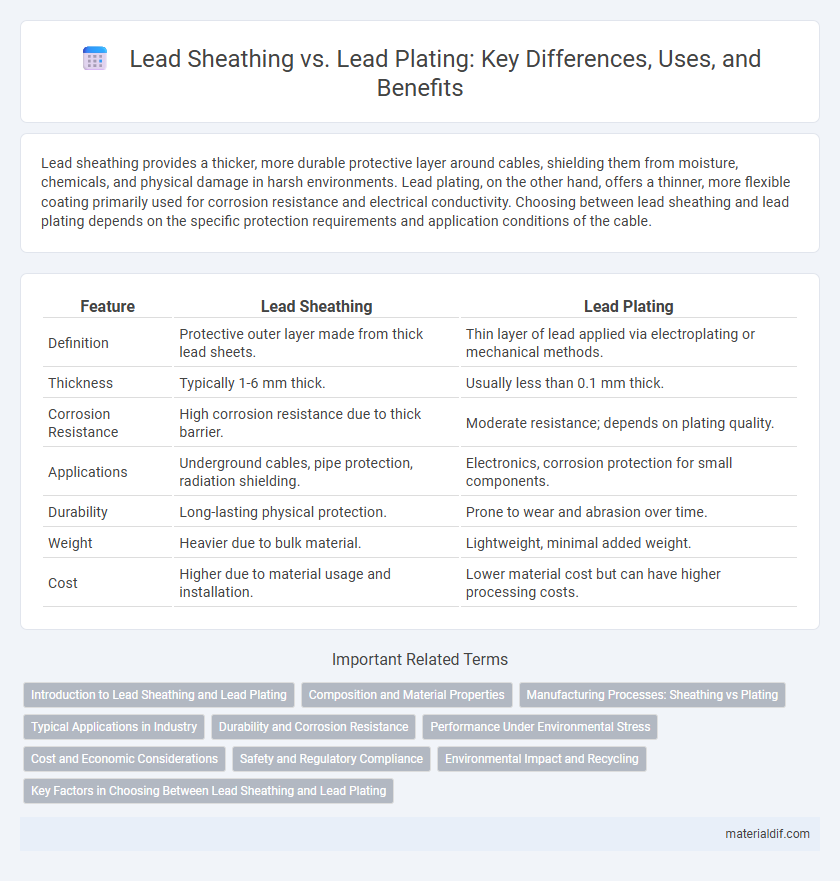
Lead sheathing provides a thicker, more durable protective layer around cables, shielding them from moisture, chemicals, and physical damage in harsh environments. Lead plating, on the other hand, offers a thinner, more flexible coating primarily used for corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Choosing between lead sheathing and lead plating depends on the specific protection requirements and application conditions of the cable.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Sheathing | Lead Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protective outer layer made from thick lead sheets. | Thin layer of lead applied via electroplating or mechanical methods. |
| Thickness | Typically 1-6 mm thick. | Usually less than 0.1 mm thick. |
| Corrosion Resistance | High corrosion resistance due to thick barrier. | Moderate resistance; depends on plating quality. |
| Applications | Underground cables, pipe protection, radiation shielding. | Electronics, corrosion protection for small components. |
| Durability | Long-lasting physical protection. | Prone to wear and abrasion over time. |
| Weight | Heavier due to bulk material. | Lightweight, minimal added weight. |
| Cost | Higher due to material usage and installation. | Lower material cost but can have higher processing costs. |
Introduction to Lead Sheathing and Lead Plating
Lead sheathing involves encasing pipes or cables with a protective layer of lead to prevent corrosion and environmental damage, commonly used in underground or underwater applications. Lead plating, on the other hand, refers to the electrochemical process of depositing a thin layer of lead onto a metal surface to enhance corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Both techniques optimize lead's durability and protective properties in industrial and construction settings.
Composition and Material Properties
Lead sheathing consists of thick, pure lead sheets designed for corrosion resistance and protection in applications like cable insulation and pipe covering. Lead plating involves a thin layer of lead deposited onto another metal surface, combining lead's corrosion resistance with the base metal's structural strength. Pure lead sheathing offers superior malleability and density, whereas lead plating provides enhanced durability and cost efficiency through minimal lead usage.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheathing vs Plating
Lead sheathing involves encasing cables or pipes with a thick layer of lead through extrusion or wrapping methods, providing durable corrosion resistance and mechanical protection. Lead plating, on the other hand, applies a thin layer of lead onto metal surfaces via electroplating, offering surface-level protection primarily against corrosion and oxidation. Sheathing requires more material and labor-intensive processes, while plating is more suitable for intricate components needing minimal lead coverage.
Typical Applications in Industry
Lead sheathing is commonly used in the cable and piping industry to provide corrosion resistance and mechanical protection in harsh environments such as underground or underwater installations. Lead plating is typically applied in the electronics and automotive sectors to enhance surface durability and improve conductivity in components like connectors and battery terminals. Both methods utilize lead's unique properties but differ in application techniques and industry-specific requirements.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Lead sheathing offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead plating due to its thicker and more uniform protective layer, effectively shielding underlying materials from environmental factors. Lead plating, while thinner and more cost-effective, is prone to wear and corrosion over time, reducing its effectiveness in harsh conditions. The robustness of lead sheathing makes it ideal for applications requiring long-term protection against moisture, chemicals, and mechanical damage.
Performance Under Environmental Stress
Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance in marine and underground environments, effectively protecting pipelines from moisture and chemical exposure. Lead plating, while thinner, provides a uniform protective layer ideal for electrical applications where flexibility and minimal weight are critical. Performance under environmental stress favors lead sheathing for long-term durability, whereas lead plating excels in controlled settings requiring precise conductivity and surface protection.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Lead sheathing offers a cost-effective solution for corrosion protection in underground pipelines due to its simpler installation and lower material expenses compared to lead plating. Lead plating involves a more complex process requiring electrochemical equipment, resulting in higher initial costs and maintenance expenses. Evaluating long-term economic benefits, lead sheathing typically provides better value for large-scale projects requiring durable, low-maintenance protection.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Lead sheathing offers superior safety by providing a robust barrier against chemical corrosion and mechanical damage, essential for protecting cables in hazardous environments. Regulatory compliance often favors lead sheathing due to its proven durability and effectiveness in meeting stringent environmental and occupational health standards. In contrast, lead plating may pose higher risks of lead exposure over time, making it less favorable in applications where long-term safety and compliance are critical.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Lead sheathing involves applying a thick layer of lead for corrosion protection, resulting in higher lead consumption and more significant environmental disposal concerns due to its bulk. Lead plating uses a thin layer of lead deposited on a substrate, reducing material usage and minimizing toxic lead waste during recycling processes. Recycling lead-plated materials is more efficient and environmentally friendly, as less lead contamination occurs compared to bulk lead sheathed products.
Key Factors in Choosing Between Lead Sheathing and Lead Plating
Key factors in choosing between lead sheathing and lead plating include corrosion resistance, application environment, and cost-effectiveness. Lead sheathing offers superior protection in harsh underground or marine conditions due to its thickness and durability, while lead plating provides a thinner, more economical option ideal for electrical components requiring flexibility. Material compatibility and installation methods also influence the decision for optimal performance and longevity.
Lead sheathing vs Lead plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com