Lead glass contains a lower percentage of lead oxide, typically between 18-30%, making it sturdy and suitable for decorative items and industrial uses. Lead crystal has a higher lead oxide content, often above 24%, enhancing its brilliance, clarity, and weight, which makes it ideal for fine glassware and luxury ornaments. The increased lead content in lead crystal also allows for easier cutting and engraving, resulting in intricate designs and a sparkling finish.
Table of Comparison
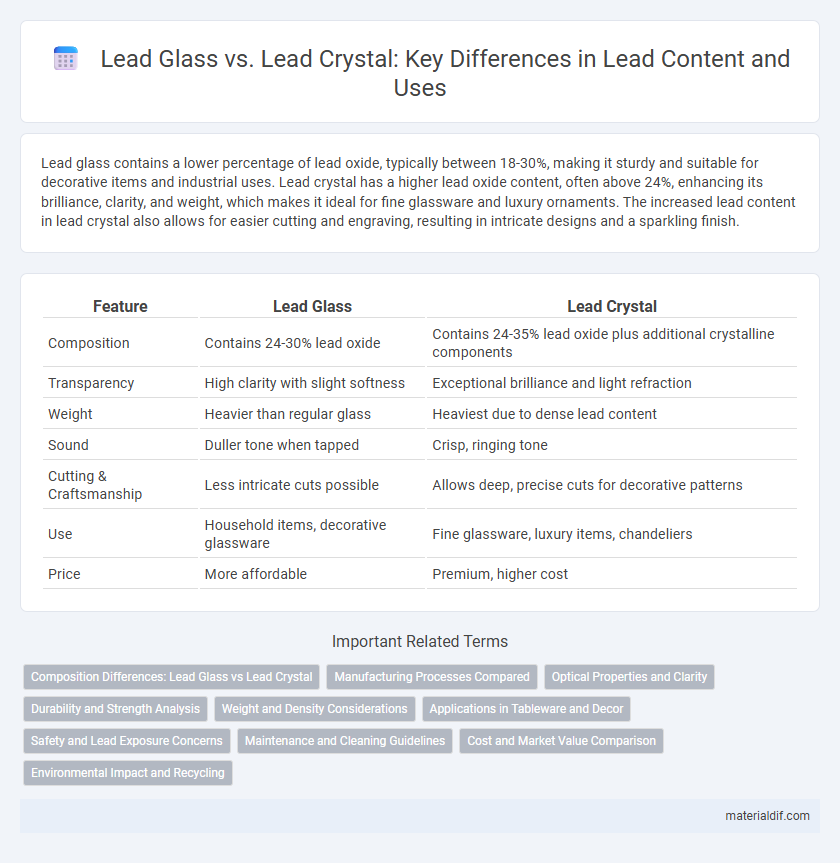
| Feature | Lead Glass | Lead Crystal |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains 24-30% lead oxide | Contains 24-35% lead oxide plus additional crystalline components |
| Transparency | High clarity with slight softness | Exceptional brilliance and light refraction |
| Weight | Heavier than regular glass | Heaviest due to dense lead content |
| Sound | Duller tone when tapped | Crisp, ringing tone |
| Cutting & Craftsmanship | Less intricate cuts possible | Allows deep, precise cuts for decorative patterns |
| Use | Household items, decorative glassware | Fine glassware, luxury items, chandeliers |
| Price | More affordable | Premium, higher cost |
Composition Differences: Lead Glass vs Lead Crystal
Lead glass contains a minimum of 18% lead oxide, enhancing its refractive index and density, while lead crystal typically contains at least 24% lead oxide, resulting in superior brilliance and weight. The higher lead content in lead crystal also improves its workability and resonance, making it ideal for fine glassware and decorative objects. Both compositions alter the glass structure, but lead crystal's elevated lead oxide percentage significantly affects its optical clarity and craftsmanship quality.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Lead glass is produced by adding lead oxide to molten glass, increasing its refractive index and weight while maintaining a relatively simpler manufacturing process. Lead crystal involves a more refined process that includes reheating and hand-cutting to enhance clarity and brilliance, often requiring skilled craftsmanship. The manufacturing of lead crystal emphasizes precision and aesthetic quality, distinguishing it from the more industrial and straightforward lead glass production.
Optical Properties and Clarity
Lead glass contains lead oxide, which enhances its refractive index, resulting in superior brilliance and light dispersion compared to ordinary glass. Lead crystal, typically containing at least 24% lead oxide, offers exceptional clarity and a higher density that increases its sparkle and prism-like effects. The increased lead content in crystal improves optical properties by amplifying light reflection and refraction, making it favored for fine glassware and decorative items.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Lead glass contains lower lead oxide content, resulting in moderate durability and strength suitable for everyday use, while lead crystal features higher lead oxide levels (at least 24%), enhancing its density and brilliance but making it more prone to scratching and chipping under impact. The increased lead content in lead crystal improves refractive qualities but compromises tensile strength compared to lead glass, affecting its resistance to mechanical stress. In applications requiring robust durability, lead glass is preferable, whereas lead crystal is favored for ornamental purposes where aesthetic brilliance outweighs strength considerations.
Weight and Density Considerations
Lead glass typically contains lower lead oxide content, resulting in a lighter weight and lower density compared to lead crystal. Lead crystal, often containing 24% or more lead oxide, exhibits significantly higher density, giving it a heavier and more substantial feel. The increased lead content in lead crystal enhances its weight and density, making it ideal for fine glassware requiring brilliance and heft.
Applications in Tableware and Decor
Lead crystal contains a higher percentage of lead oxide, usually between 24% and 30%, resulting in enhanced brilliance and weight ideal for luxury tableware and decorative items. Lead glass, with lower lead content or alternative additives, offers durability and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for practical glassware and everyday decorative pieces. The superior refractive index and clarity of lead crystal make it the preferred choice for premium wine glasses, chandeliers, and ornate vases.
Safety and Lead Exposure Concerns
Lead glass contains a lower percentage of lead oxide, typically around 18-30%, compared to lead crystal which often contains 24-33% or more, raising greater concerns about lead exposure during use or breakage. Lead crystal, known for its brilliance and weight, poses higher risks of lead leaching, especially when used with acidic beverages, making safety precautions essential to minimize ingestion. Regulatory guidelines recommend limiting exposure and using lead-free alternatives where prolonged contact with consumables occurs to ensure health safety.
Maintenance and Cleaning Guidelines
Lead glass requires gentle cleaning with mild detergent and warm water to prevent surface damage, while lead crystal demands more careful handling due to its higher lead oxide content, avoiding abrasive cleaners and extreme temperature changes. Soft cloths should be used for drying both types to maintain their clarity and prevent scratches, with lead crystal often benefiting from occasional polishing with specialized products to preserve its brilliance. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan and visual appeal of lead-containing glassware, making adherence to cleaning guidelines essential.
Cost and Market Value Comparison
Lead glass generally has lower production costs due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower lead oxide content, making it more affordable in the market. Lead crystal, containing higher lead oxide percentages (typically 24%-30%), commands a premium price because of its enhanced clarity, brilliance, and craftsmanship, which are highly valued by collectors. Market value for lead crystal remains consistently higher, supported by its reputation as a luxury product and strong demand in high-end glassware and decorative items.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Lead glass typically contains lower lead oxide content compared to lead crystal, resulting in reduced environmental hazards during production and disposal. Lead crystal's higher lead concentration poses greater risks to ecosystems through potential leaching and complicates recycling processes due to the toxicity of lead compounds. Recycling lead glass is more feasible and environmentally friendly, as facilities can safely process lower lead levels, minimizing lead contamination in waste streams.
Lead glass vs Lead crystal Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com