Kevlar offers superior strength and flexibility compared to fiberglass, making it more resistant to impact and wear, especially in pet accessories like collars and harnesses. While fiberglass is lightweight and cost-effective, Kevlar's durability ensures longer-lasting protection and enhanced safety for pets in demanding environments. Choosing Kevlar over fiberglass provides a balance of toughness and comfort, ideal for active pets needing resilient gear.
Table of Comparison
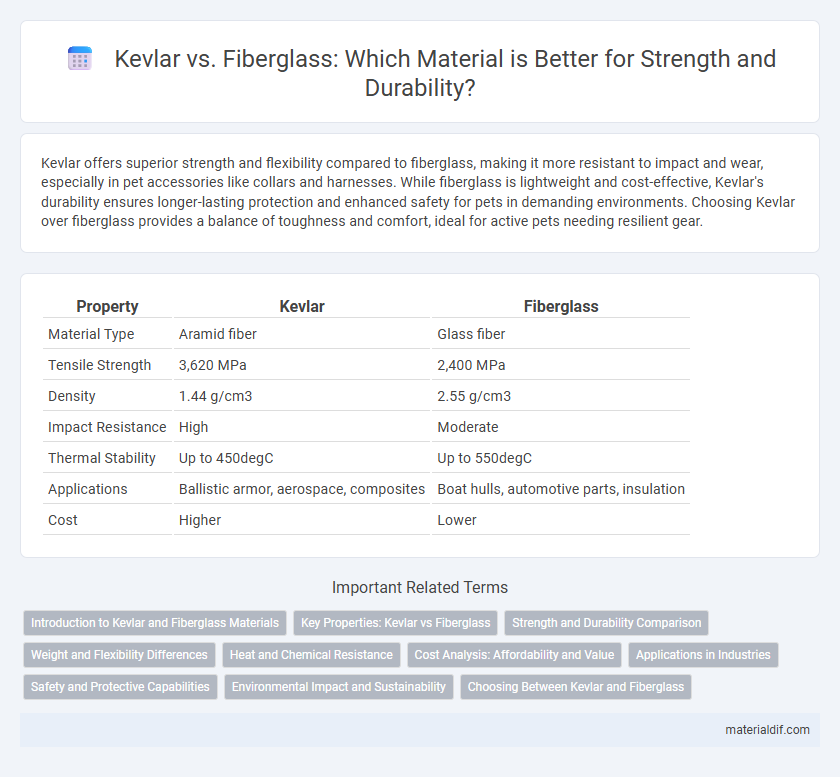
| Property | Kevlar | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aramid fiber | Glass fiber |
| Tensile Strength | 3,620 MPa | 2,400 MPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 2.55 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 550degC |
| Applications | Ballistic armor, aerospace, composites | Boat hulls, automotive parts, insulation |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Kevlar and Fiberglass Materials
Kevlar is a high-strength synthetic fiber known for its exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for ballistic and impact-resistant applications. Fiberglass consists of fine glass fibers woven into a composite material prized for its durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties. Both materials are widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, with Kevlar offering superior crack resistance and fiberglass providing cost-effective structural reinforcement.
Key Properties: Kevlar vs Fiberglass
Kevlar exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to fiberglass, making it highly effective in ballistic applications and protective gear. Fiberglass offers greater stiffness and better resistance to compression, which benefits structural uses such as in construction and automotive components. Both materials have distinct advantages in weight, durability, and flexibility, with Kevlar being lighter and more flexible, while fiberglass provides enhanced rigidity and cost-effectiveness.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Kevlar exhibits superior tensile strength, often exceeding 3,620 MPa, compared to fiberglass's typical range of 2,400 MPa, making it more resistant to impact and abrasion. Its molecular structure provides exceptional durability, maintaining integrity under repeated stress and harsh environmental conditions, whereas fiberglass tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and fatigue. These properties position Kevlar as the preferred material for applications requiring long-term strength and high resistance to wear.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Kevlar is significantly lighter than fiberglass, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it ideal for applications requiring reduced weight without compromising durability. Kevlar's flexibility surpasses that of fiberglass, allowing it to absorb and distribute impact more effectively, enhancing performance in protective gear and flexible composite materials. Fiberglass tends to be stiffer and heavier, limiting its use where lightweight and flexible properties are critical.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar offers superior heat resistance compared to fiberglass, withstanding temperatures up to 450degC before degrading, whereas fiberglass typically tolerates around 370degC. Chemically, Kevlar exhibits excellent resistance to organic solvents and oils but can degrade in strong acids and bases, while fiberglass shows higher resistance to chemical corrosion in acidic and alkaline environments. These properties make Kevlar ideal for applications requiring high thermal stability and moderate chemical exposure, outperforming fiberglass in thermal durability but with specific chemical limitations.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Kevlar offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to fiberglass, making it a premium choice with higher upfront costs but greater long-term value due to durability and performance. Fiberglass is more affordable initially, suitable for budget-sensitive projects where extreme strength is less critical. The cost analysis favors Kevlar in applications demanding high impact resistance and longevity, while fiberglass remains cost-effective for lower-stress environments.
Applications in Industries
Kevlar offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to fiberglass, making it the preferred material in aerospace, military, and automotive industries for bulletproof vests, helmets, and high-performance tires. Fiberglass is widely used in construction, marine, and wind energy sectors due to its cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding into large structural components. Both materials fulfill critical roles, with Kevlar excelling in safety and protective gear, while fiberglass dominates in insulation, boat hulls, and fiberglass-reinforced plastics.
Safety and Protective Capabilities
Kevlar offers superior impact resistance and energy absorption compared to fiberglass, making it a preferred choice for bulletproof vests and helmets designed to enhance personal safety. Its exceptional tensile strength and flexibility allow Kevlar to withstand high-velocity impacts without shattering, unlike fiberglass which tends to be more brittle under stress. These protective capabilities make Kevlar a critical material in applications requiring reliable ballistic protection and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kevlar demonstrates a lower environmental impact compared to fiberglass due to its superior durability and longer lifespan, which reduces the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Kevlar production consumes less energy and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions relative to fiberglass manufacturing, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Furthermore, Kevlar's recyclability potential enhances sustainability by allowing material recovery and reuse in various industrial applications.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Fiberglass
Kevlar offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet durable materials, such as body armor and high-performance composites. Fiberglass provides greater rigidity and higher heat resistance at a more affordable cost, often preferred in marine, automotive, and construction industries. Selecting between Kevlar and fiberglass depends on the balance of strength, weight, thermal stability, and budget constraints for specific use cases.
Kevlar vs Fiberglass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com