Recycled iron offers significant environmental advantages over virgin iron by reducing the need for mining and lowering energy consumption in production processes. It maintains comparable strength and durability, making it an efficient and sustainable choice for manufacturing. Utilizing recycled iron supports circular economy practices, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources.
Table of Comparison
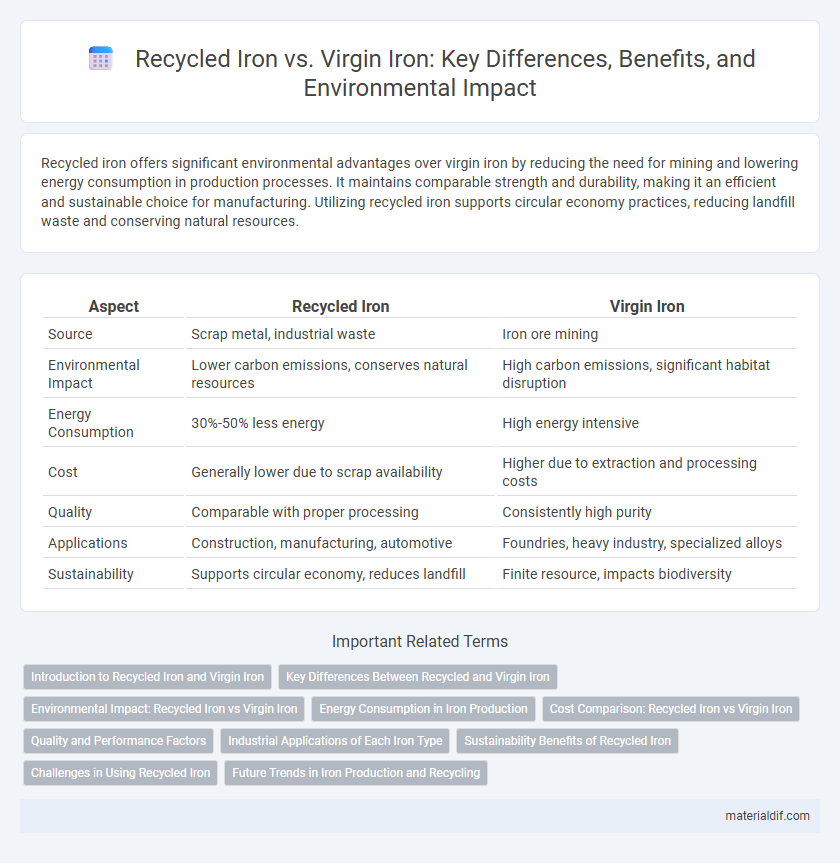
| Aspect | Recycled Iron | Virgin Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Scrap metal, industrial waste | Iron ore mining |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon emissions, conserves natural resources | High carbon emissions, significant habitat disruption |
| Energy Consumption | 30%-50% less energy | High energy intensive |
| Cost | Generally lower due to scrap availability | Higher due to extraction and processing costs |
| Quality | Comparable with proper processing | Consistently high purity |
| Applications | Construction, manufacturing, automotive | Foundries, heavy industry, specialized alloys |
| Sustainability | Supports circular economy, reduces landfill | Finite resource, impacts biodiversity |
Introduction to Recycled Iron and Virgin Iron
Recycled iron is derived from scrap metal that undergoes melting and refining processes to be reused in manufacturing, significantly reducing the need for raw material extraction and lowering carbon emissions. Virgin iron refers to iron produced directly from iron ore through blast furnaces or electric arc furnaces, involving mining, smelting, and refining to achieve high-quality metal. Both forms of iron serve critical roles in industries such as construction, automotive, and machinery, with recycled iron offering sustainability advantages while virgin iron ensures purity and strength for specialized applications.
Key Differences Between Recycled and Virgin Iron
Recycled iron is sourced from scrap metal that has been melted down and reprocessed, offering significant energy savings and reduced environmental impact compared to virgin iron, which is extracted directly from ore through mining and smelting. Virgin iron typically exhibits higher purity and consistency, making it preferred for applications requiring strict material standards, while recycled iron may contain trace impurities due to mixed scrap origins. The choice between recycled and virgin iron depends on factors like cost efficiency, sustainability goals, and the specific mechanical properties required in manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Iron vs Virgin Iron
Recycled iron significantly reduces the environmental impact compared to virgin iron by lowering energy consumption by up to 74% and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 58%. Mining virgin iron ore disrupts ecosystems, depletes natural resources, and increases carbon dioxide emissions through intensive extraction and processing methods. Utilizing recycled iron supports sustainable manufacturing practices, conserves natural reserves, and mitigates pollution, making it a crucial choice for eco-friendly steel production.
Energy Consumption in Iron Production
Recycled iron significantly reduces energy consumption compared to virgin iron production, using up to 75% less energy by avoiding the energy-intensive smelting process required for extracting iron from ores. The electric arc furnace method used for recycled iron melts scrap metal efficiently, lowering carbon emissions and operational costs. This energy efficiency contributes to sustainable iron production and supports global efforts to decrease industrial environmental impact.
Cost Comparison: Recycled Iron vs Virgin Iron
Recycled iron typically costs 20-40% less than virgin iron due to lower energy consumption and reduced raw material expenses in the smelting process. The production of virgin iron involves mining, refining, and higher energy input, resulting in increased operational costs and market prices. Cost efficiency in recycled iron makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers aiming to balance quality with budget constraints.
Quality and Performance Factors
Recycled iron often matches or exceeds the quality of virgin iron due to controlled processing that eliminates impurities and maintains alloy composition. Performance factors such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and malleability remain consistent, making recycled iron suitable for critical applications in construction and manufacturing. The use of recycled iron also reduces environmental impact without compromising durability or structural integrity.
Industrial Applications of Each Iron Type
Recycled iron excels in industrial applications such as construction, automotive manufacturing, and machinery production due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. Virgin iron, prized for its superior purity and strength, is essential in industries requiring high-grade materials like aerospace, heavy machinery, and specialized tool manufacturing. Both types of iron play critical roles in optimizing resource use and meeting specific performance standards across diverse industrial sectors.
Sustainability Benefits of Recycled Iron
Recycled iron significantly reduces energy consumption by up to 75% compared to producing virgin iron from ore, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. The process conserves natural resources by minimizing the need for mining raw iron ore, which helps to protect ecosystems and reduce land degradation. Utilizing recycled iron supports circular economy principles, promoting material reuse and reducing waste in steel production industries.
Challenges in Using Recycled Iron
Recycled iron faces challenges such as contamination from impurities like rust, paint, and non-metallic inclusions, which can reduce its mechanical properties and affect product quality. Variability in composition and inconsistent supply sources complicate processing and require advanced sorting and refining technologies to meet industry standards. Furthermore, energy-intensive extraction of residual impurities can increase production costs, making recycled iron less economically competitive compared to virgin iron.
Future Trends in Iron Production and Recycling
Future trends in iron production emphasize increasing the use of recycled iron due to its lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions compared to virgin iron. Advances in scrap sorting technologies and electric arc furnace efficiency are expected to further enhance the quality and availability of recycled iron. Industry projections suggest a significant shift towards circular economy practices, reducing reliance on virgin iron mining and supporting sustainable steel manufacturing.
Recycled Iron vs Virgin Iron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com