Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, offers superior strength and toughness compared to grey cast iron due to its spherical graphite inclusions that enhance machinability and resistance to impact. Grey cast iron contains flake graphite, which causes brittleness but provides excellent vibration damping and thermal conductivity. Choosing between nodular iron and grey cast iron depends on the specific application requirements such as load-bearing capacity, wear resistance, and machinability.
Table of Comparison
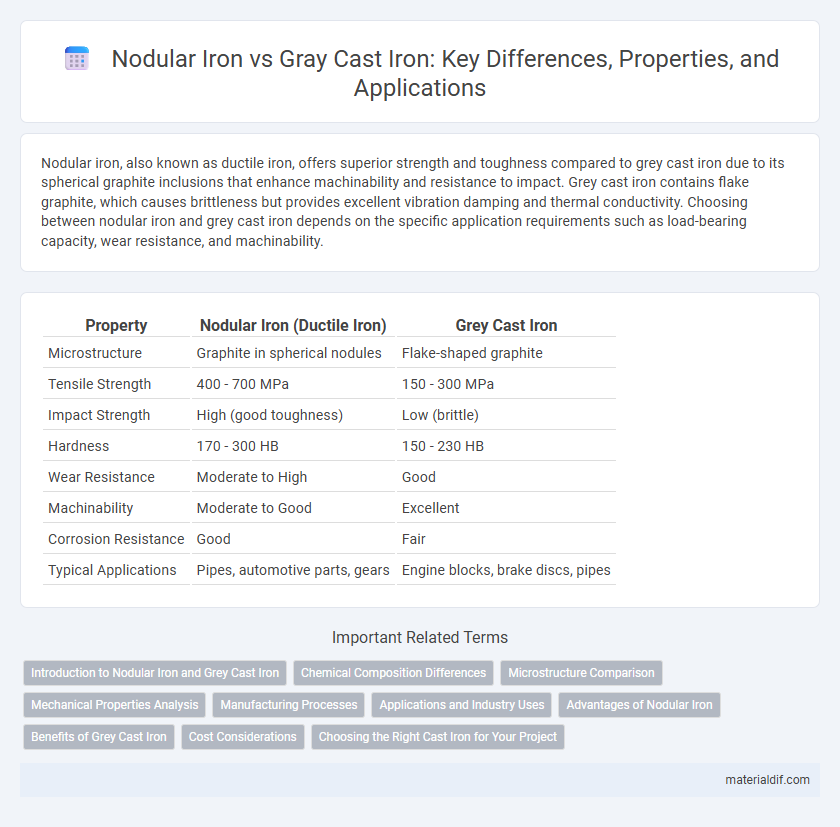
| Property | Nodular Iron (Ductile Iron) | Grey Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Microstructure | Graphite in spherical nodules | Flake-shaped graphite |
| Tensile Strength | 400 - 700 MPa | 150 - 300 MPa |
| Impact Strength | High (good toughness) | Low (brittle) |
| Hardness | 170 - 300 HB | 150 - 230 HB |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate to High | Good |
| Machinability | Moderate to Good | Excellent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Fair |
| Typical Applications | Pipes, automotive parts, gears | Engine blocks, brake discs, pipes |
Introduction to Nodular Iron and Grey Cast Iron
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, features spherical graphite inclusions that enhance its strength and ductility compared to grey cast iron, which contains flake-like graphite structures leading to higher brittleness. Grey cast iron is commonly used for its excellent machinability and vibration damping properties, while nodular iron is preferred in applications requiring higher tensile strength and impact resistance. Both materials are widely utilized in automotive, construction, and heavy machinery industries, with nodular iron often selected for more demanding mechanical components.
Chemical Composition Differences
Nodular iron contains higher levels of magnesium and cerium, which promote the formation of spherical graphite nodules, enhancing ductility and toughness. Grey cast iron has a higher carbon content and silicon, leading to flake graphite structures that improve vibration damping but reduce tensile strength. The presence of these distinct alloying elements fundamentally influences the microstructure and mechanical properties of each iron type.
Microstructure Comparison
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, features a microstructure with spherical graphite nodules that enhance its strength and ductility, compared to grey cast iron, which contains flaky graphite flakes that create stress concentration points leading to brittleness. The graphite morphology in nodular iron promotes better mechanical properties by minimizing crack initiation, whereas the flaky graphite in grey cast iron results in a more brittle fracture behavior. Both microstructures influence thermal conductivity and machinability, making nodular iron preferable for applications demanding higher toughness and fatigue resistance.
Mechanical Properties Analysis
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to grey cast iron due to its spherical graphite microstructure, which enhances tensile strength, ductility, and impact resistance. Grey cast iron features flake-shaped graphite that induces stress concentration points, resulting in lower tensile strength and reduced resistance to fracture. The tensile strength of nodular iron typically ranges from 400 to 600 MPa, whereas grey cast iron usually falls between 150 to 350 MPa, highlighting nodular iron's suitability for applications requiring enhanced toughness and fatigue resistance.
Manufacturing Processes
Nodular iron undergoes a unique casting process involving the addition of magnesium or cerium to molten iron, which alters the graphite structure from flakes to spheroids, significantly enhancing ductility and strength. Grey cast iron is produced by pouring molten iron into a mold where graphite forms in flakes during solidification, imparting excellent vibration damping but lower tensile strength. Controlled cooling rates and careful alloying differentiate the manufacturing processes, resulting in distinct microstructures tailored for specific engineering applications.
Applications and Industry Uses
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, is extensively used in automotive components, pipes, and heavy machinery due to its superior tensile strength and impact resistance. Grey cast iron is preferred in manufacturing engine blocks, machine bases, and cookware because of its excellent vibration damping and thermal conductivity. Both materials serve critical roles in construction, transportation, and industrial manufacturing industries, with nodular iron favored for structural applications and grey cast iron for wear-resistant, vibration-absorbing parts.
Advantages of Nodular Iron
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to grey cast iron, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Its graphite structure, in spherical nodules rather than flakes, reduces stress concentration and enhances machinability and fatigue resistance. This combination of mechanical properties allows nodular iron to outperform grey cast iron in automotive parts, pipes, and heavy-duty machinery components.
Benefits of Grey Cast Iron
Grey cast iron offers superior machinability due to its graphite microstructure, which acts as a lubricant during cutting, reducing tool wear and production costs. Its excellent damping capacity minimizes vibration, making it ideal for automotive engine blocks and machinery bases. Grey cast iron also boasts better thermal conductivity, enhancing heat dissipation in industrial applications.
Cost Considerations
Nodular iron typically exhibits higher manufacturing costs due to its complex alloying and heat treatment processes compared to grey cast iron, which is cheaper to produce because of its simpler graphite structure. The enhanced mechanical properties of nodular iron justify its increased expense for applications demanding superior strength and toughness. Grey cast iron remains a cost-effective choice for components where rigidity and vibration damping are prioritized over tensile strength.
Choosing the Right Cast Iron for Your Project
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to grey cast iron, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and toughness. Grey cast iron features excellent machinability and vibration damping but is more brittle, which suits applications needing good wear resistance without heavy mechanical stress. Selecting the right cast iron depends on the project's mechanical demands, balancing nodular iron's robustness against grey cast iron's thermal conductivity and surface finish.
Nodular Iron vs Grey Cast Iron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com