Gypsum screed offers faster drying times and superior smoothness compared to cement screed, making it ideal for indoor flooring where speed and finish quality are essential. It provides better thermal insulation and soundproofing properties, enhancing overall comfort in living spaces. However, cement screed is more durable and suitable for external or heavy-load areas due to its higher strength and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
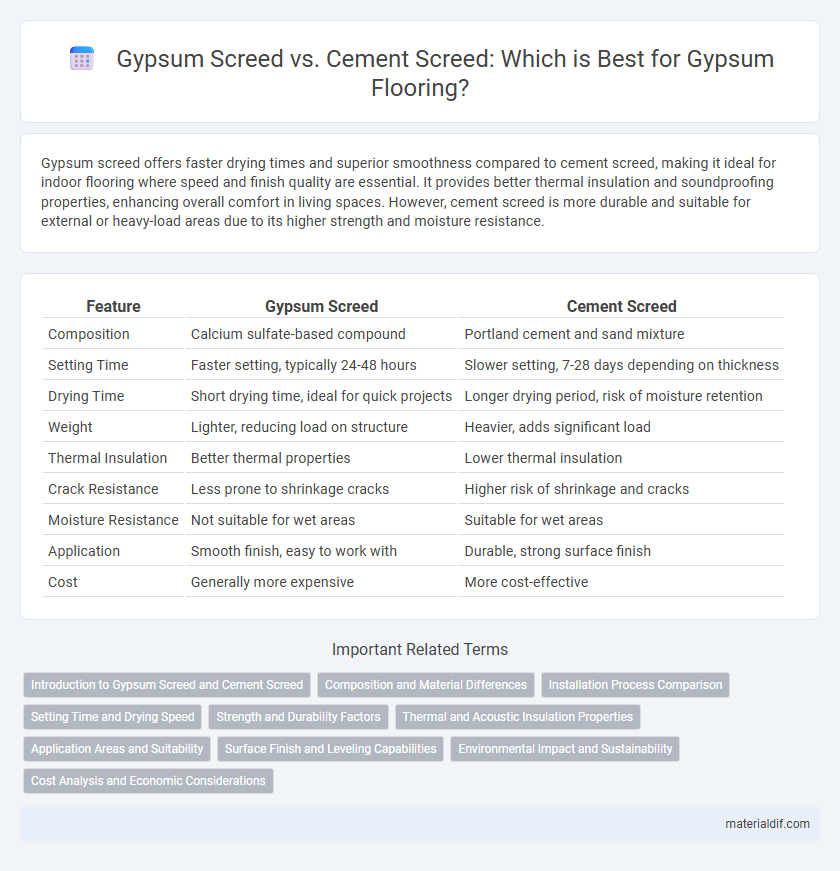
| Feature | Gypsum Screed | Cement Screed |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium sulfate-based compound | Portland cement and sand mixture |
| Setting Time | Faster setting, typically 24-48 hours | Slower setting, 7-28 days depending on thickness |
| Drying Time | Short drying time, ideal for quick projects | Longer drying period, risk of moisture retention |
| Weight | Lighter, reducing load on structure | Heavier, adds significant load |
| Thermal Insulation | Better thermal properties | Lower thermal insulation |
| Crack Resistance | Less prone to shrinkage cracks | Higher risk of shrinkage and cracks |
| Moisture Resistance | Not suitable for wet areas | Suitable for wet areas |
| Application | Smooth finish, easy to work with | Durable, strong surface finish |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Gypsum Screed and Cement Screed
Gypsum screed is a lightweight, fast-setting floor leveling material composed primarily of calcium sulfate, offering excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties for interior applications. Cement screed, made from a mixture of cement, sand, and water, provides high compressive strength and moisture resistance, suitable for both indoor and outdoor floors. Choosing between gypsum and cement screed depends on project requirements such as drying time, load-bearing capacity, and environmental conditions.
Composition and Material Differences
Gypsum screed consists primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, offering a lighter and more flexible composition compared to the traditional cement screed made from Portland cement, sand, and water. The gypsum base allows for faster drying times and better moisture regulation, while cement screeds provide higher compressive strength and moisture resistance due to their dense, cementitious matrix. These material differences impact the choice of screed depending on application requirements like load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions.
Installation Process Comparison
Gypsum screed offers faster installation times due to its lighter weight and self-leveling properties, reducing labor effort and drying periods compared to cement screed. Cement screed requires more water, longer curing times, and precise mixing, making the installation process more labor-intensive and time-consuming. Gypsum screed's installation benefits include minimal shrinkage and improved surface smoothness, ideal for underfloor heating systems, whereas cement screed provides higher compressive strength for heavy-duty applications.
Setting Time and Drying Speed
Gypsum screed offers a significantly faster setting time compared to cement screed, typically setting within 1 to 3 hours, which accelerates project timelines on construction sites. The drying speed of gypsum screed is also superior, usually achieving readiness for final floor covering within 7 days, whereas cement screed requires up to 28 days to fully dry. This rapid drying capability reduces labor costs and minimizes delays in subsequent flooring installation phases.
Strength and Durability Factors
Gypsum screed offers faster drying times and smooth finishes but has lower compressive strength, typically around 15-20 MPa, making it less durable under heavy loads compared to cement screed, which usually reaches compressive strengths of 25-40 MPa. Cement screed provides superior hardness and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for areas subjected to frequent wear or moisture exposure. The choice between gypsum and cement screed depends on project requirements, with cement screed favored for long-term durability and strength in high-traffic or wet environments.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Gypsum screed offers superior thermal insulation compared to cement screed due to its lower thermal conductivity, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. The porous structure of gypsum screed also provides better acoustic insulation by effectively dampening sound transmission through floors. In contrast, cement screed's higher density results in lower insulation performance, making gypsum screed preferable for applications requiring improved thermal comfort and noise reduction.
Application Areas and Suitability
Gypsum screed offers excellent suitability for interior applications, especially in residential and commercial flooring, due to its quick drying time and lightweight properties, making it ideal for situations requiring rapid installation and reduced structural load. Cement screed is more appropriate for heavy-duty areas such as industrial floors, exterior spaces, or locations exposed to moisture because of its superior durability, water resistance, and mechanical strength. Choosing between gypsum and cement screeds depends on environmental conditions and load requirements, with gypsum preferred for dry, controlled environments and cement favored for robust, moisture-prone applications.
Surface Finish and Leveling Capabilities
Gypsum screed offers a smoother surface finish with excellent self-leveling properties, making it ideal for achieving flat and even floors with minimal effort. Cement screed, while durable and strong, often requires more manual leveling and can result in a rougher texture that may need further smoothing. The superior workability and fine texture of gypsum screed enhance surface aesthetics and reduce preparation time for floor coverings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum screed offers a lower carbon footprint compared to cement screed, as its production releases significantly less CO2 and consumes less energy. Its recyclability and ability to enhance indoor air quality through moisture regulation contribute to superior sustainability. Cement screeds, while durable, involve higher environmental costs due to extensive raw material extraction and higher greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Gypsum screed typically offers lower material and labor costs compared to cement screed due to faster drying times and ease of application, reducing overall project timelines and associated expenses. Cement screed, while generally more expensive in installation, provides higher durability and moisture resistance, which may result in lower long-term maintenance costs in high-traffic or damp environments. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including initial investment and lifecycle expenses, is essential for accurate economic considerations between gypsum and cement screeds.
Gypsum screed vs Cement screed Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com