Gypsum panels are interior products designed for drywall applications, providing a smooth, fire-resistant surface for walls and ceilings. Gypsum sheathing, on the other hand, is used on exterior walls to offer structural strength, moisture resistance, and a base for weather barriers. While both enhance building safety, gypsum sheathing specifically protects against environmental elements, whereas gypsum panels focus on interior finish and fire protection.
Table of Comparison
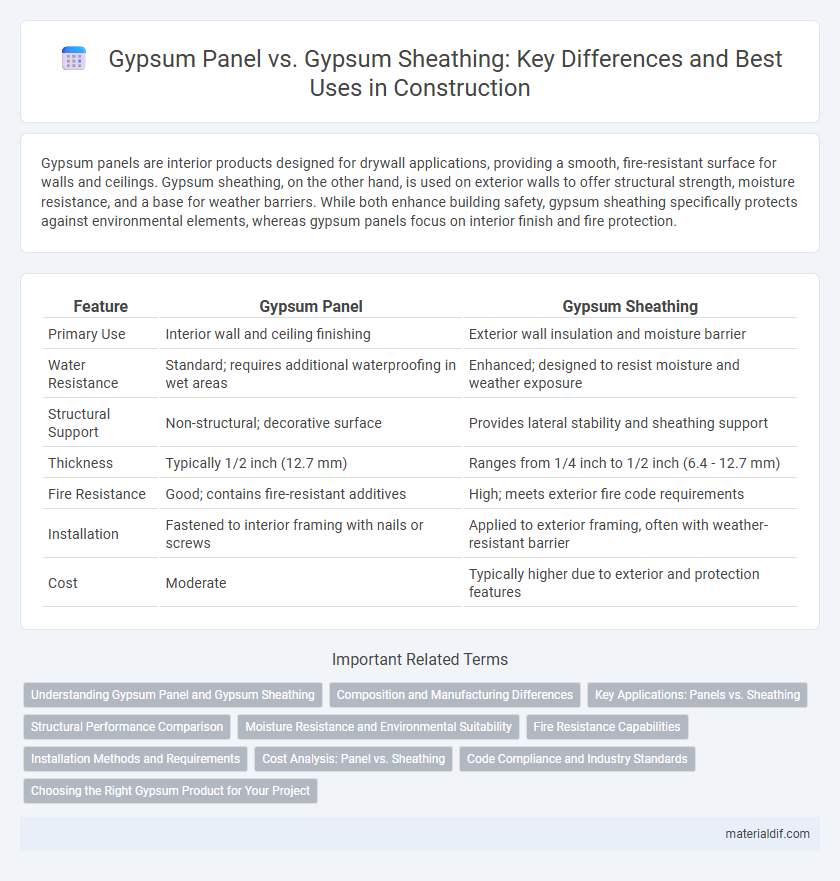
| Feature | Gypsum Panel | Gypsum Sheathing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Interior wall and ceiling finishing | Exterior wall insulation and moisture barrier |
| Water Resistance | Standard; requires additional waterproofing in wet areas | Enhanced; designed to resist moisture and weather exposure |
| Structural Support | Non-structural; decorative surface | Provides lateral stability and sheathing support |
| Thickness | Typically 1/2 inch (12.7 mm) | Ranges from 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch (6.4 - 12.7 mm) |
| Fire Resistance | Good; contains fire-resistant additives | High; meets exterior fire code requirements |
| Installation | Fastened to interior framing with nails or screws | Applied to exterior framing, often with weather-resistant barrier |
| Cost | Moderate | Typically higher due to exterior and protection features |
Understanding Gypsum Panel and Gypsum Sheathing
Gypsum panels, commonly known as drywall, are interior wall and ceiling materials made from gypsum plaster sandwiched between paper facings, primarily used for finishing interior spaces due to their fire resistance and ease of installation. Gypsum sheathing, on the other hand, serves as an exterior substrate in wall assemblies, providing structural support, moisture resistance, and a base for exterior finishes. Understanding the distinct roles of gypsum panels and sheathing helps optimize building performance, especially in moisture management and fire safety.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Gypsum panels consist of a gypsum core encased in paper facings, engineered primarily for interior wall applications, offering smooth surfaces ideal for painting or wallpaper. Gypsum sheathing features a gypsum core combined with weather-resistant facings, such as fiberglass mats or water-resistant coatings, designed for exterior wall protection against moisture and fire. Manufacturing processes for gypsum panels emphasize fine facings and consistent core density, whereas gypsum sheathing focuses on enhanced durability and resistance to environmental elements.
Key Applications: Panels vs. Sheathing
Gypsum panels are primarily used for interior wall and ceiling finishes, providing smooth surfaces ideal for painting or wallpapering, while gypsum sheathing is designed for exterior use as a substrate in wall assemblies, offering moisture and fire resistance. Gypsum panels improve indoor air quality and soundproofing in residential and commercial spaces, whereas gypsum sheathing protects structural framing from weather exposure and aids in energy efficiency. Selecting gypsum panels or sheathing depends on whether the application requires interior aesthetic enhancement or exterior structural protection.
Structural Performance Comparison
Gypsum panels offer enhanced fire resistance and soundproofing properties, making them ideal for interior wall assemblies, while gypsum sheathing provides superior moisture resistance and structural rigidity required for exterior wall applications. The core composition of gypsum panels is denser and designed for smooth finishing, whereas gypsum sheathing includes water-resistant additives and fiberglass mats to improve durability under environmental exposure. Structural performance differences arise from their specialized formulations, with gypsum sheathing contributing to lateral load support and impact resistance in building envelopes.
Moisture Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Gypsum panels offer enhanced moisture resistance due to their water-resistant core and treated paper facing, making them ideal for interior applications in damp environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. Gypsum sheathing, designed primarily for exterior use, incorporates a weather-resistant coating to protect structural elements from moisture infiltration while allowing vapor permeability to prevent mold growth. Environmental suitability of gypsum panels favors indoor sustainable building standards, whereas gypsum sheathing contributes to exterior wall durability and energy efficiency in commercial and residential construction.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum panels offer enhanced fire resistance due to their dense composition and integrated glass fibers, effectively slowing heat transfer in building interiors. Gypsum sheathing provides exterior wall fire protection with its water-resistant properties but generally has lower fire resistance compared to interior gypsum panels. Both materials contribute to fire safety, yet gypsum panels are preferred in applications demanding higher fire rating standards.
Installation Methods and Requirements
Gypsum panels are typically installed indoors using screws or nails directly onto wall studs or ceiling joists, requiring precise alignment and joint taping for a smooth finish. Gypsum sheathing, applied on exterior walls, demands weather-resistant barriers and requires fastening through structural framing with corrosion-resistant fasteners to ensure durability against moisture and wind. Proper sealing and flashing around gypsum sheathing are critical to prevent water infiltration and maintain building envelope integrity.
Cost Analysis: Panel vs. Sheathing
Gypsum panels generally offer a lower cost per square foot compared to gypsum sheathing due to reduced installation labor and faster application times. Gypsum sheathing, while more expensive upfront, provides additional moisture and fire resistance benefits that can lower long-term maintenance expenses. Evaluating the total project budget should consider both material costs and potential savings in durability and performance.
Code Compliance and Industry Standards
Gypsum panels and gypsum sheathing serve distinct functions in building construction, with gypsum panels primarily used for interior walls and ceilings, whereas gypsum sheathing is designed for exterior applications providing moisture resistance and fire protection. Code compliance for gypsum panels typically adheres to ASTM C1396 standards, ensuring fire resistance and structural performance, while gypsum sheathing must meet ASTM C1177 standards to qualify for exterior use, including resistance to weather elements. Industry standards mandate that gypsum sheathing be installed behind weather-resistant barriers to maintain building envelope integrity, whereas gypsum panels require proper framing and fastening to comply with local building codes focused on interior safety and finish quality.
Choosing the Right Gypsum Product for Your Project
Gypsum panels offer a smooth, paint-ready surface ideal for interior walls and ceilings, while gypsum sheathing provides structural strength and moisture resistance for exterior wall assemblies. Selecting the right gypsum product depends on project requirements such as location, exposure to elements, and desired finish durability. For optimal performance, interior applications benefit from gypsum panels, whereas exterior walls require gypsum sheathing with enhanced weather resistance and fire-rated properties.
Gypsum Panel vs Gypsum Sheathing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com