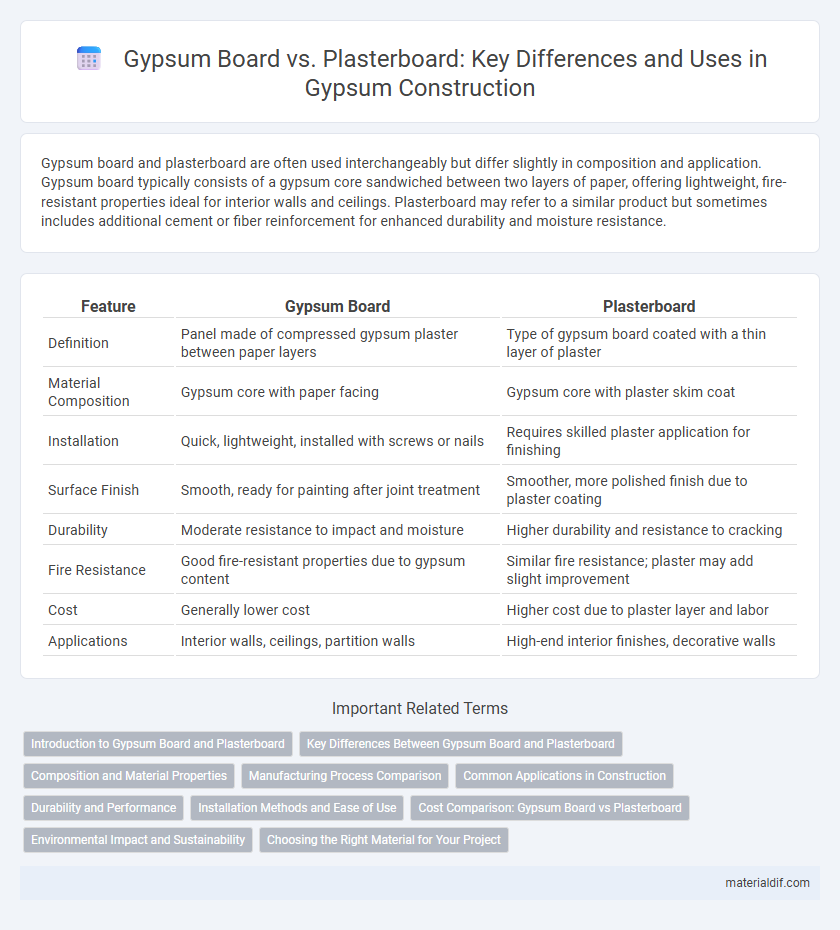
Gypsum board and plasterboard are often used interchangeably but differ slightly in composition and application. Gypsum board typically consists of a gypsum core sandwiched between two layers of paper, offering lightweight, fire-resistant properties ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Plasterboard may refer to a similar product but sometimes includes additional cement or fiber reinforcement for enhanced durability and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Board | Plasterboard |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Panel made of compressed gypsum plaster between paper layers | Type of gypsum board coated with a thin layer of plaster |
| Material Composition | Gypsum core with paper facing | Gypsum core with plaster skim coat |
| Installation | Quick, lightweight, installed with screws or nails | Requires skilled plaster application for finishing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ready for painting after joint treatment | Smoother, more polished finish due to plaster coating |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to impact and moisture | Higher durability and resistance to cracking |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire-resistant properties due to gypsum content | Similar fire resistance; plaster may add slight improvement |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to plaster layer and labor |
| Applications | Interior walls, ceilings, partition walls | High-end interior finishes, decorative walls |
Introduction to Gypsum Board and Plasterboard
Gypsum board, also known as drywall or plasterboard, consists of a core of gypsum plaster pressed between two thick sheets of paper, designed for interior wall and ceiling applications. Its ease of installation, fire resistance, and soundproofing qualities make it a popular choice in modern construction. Plasterboard specifically refers to gypsum board treated and finished to create smooth, paint-ready surfaces, often preferred for a seamless, high-quality finish.
Key Differences Between Gypsum Board and Plasterboard
Gypsum board and plasterboard are commonly used interior wall materials made from a core of gypsum plaster but differ in composition and application. Gypsum board typically includes a paper facing and is used for quick installation and fire resistance, while plasterboard often refers to traditional plaster applied over a lath base, providing a smoother finish. The key distinctions lie in gypsum board's prefab panel format versus plasterboard's on-site application method, affecting durability, texture, and labor requirements.
Composition and Material Properties
Gypsum board and plasterboard both consist primarily of gypsum, a soft sulfate mineral, sandwiched between layers of paper or fiberboard, but gypsum board often incorporates additives like glass fibers or polymers to enhance durability and moisture resistance. Plasterboard typically uses a more traditional gypsum core with paper facings, offering good fire resistance and soundproofing due to its dense composition. The differing formulations impact properties such as weight, strength, and insulation performance, with gypsum board generally favored for construction requiring enhanced mechanical and environmental resilience.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Gypsum board and plasterboard differ primarily in their manufacturing processes, where gypsum board is produced by sandwiching a core of gypsum plaster between two thick sheets of paper, ensuring a uniform, dense core for enhanced durability and fire resistance. Plasterboard manufacturing involves mixing gypsum with additives like starch and foam to create lighter, more flexible panels that are then coated with paper, optimizing moisture resistance and ease of cutting. These distinct production techniques influence their performance characteristics, with gypsum board favoring structural strength and plasterboard prioritizing versatility and installation speed.
Common Applications in Construction
Gypsum board, often interchangeable with plasterboard, is widely used in interior wall and ceiling construction for residential and commercial buildings due to its fire resistance and soundproofing qualities. Common applications include partition walls, ceiling linings, and backing for tiles, offering a smooth surface for painting or wallpapering. Variants such as moisture-resistant gypsum boards are preferred in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens, enhancing durability and performance.
Durability and Performance
Gypsum board typically offers enhanced durability compared to plasterboard due to its denser core, making it more resistant to dents, cracks, and moisture damage. Performance-wise, gypsum board provides superior fire resistance and soundproofing, which contributes to its widespread use in both residential and commercial construction. Plasterboard, while easier to install and more affordable, generally lacks the robustness and long-term resilience seen in gypsum board applications.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Gypsum board and plasterboard differ primarily in installation methods, with gypsum board designed for faster, screw-based attachment to studs, enabling quicker mounting and stability. Plasterboard typically requires additional steps, such as applying wet plaster layers over the board, making installation more labor-intensive and time-consuming. Gypsum board's lightweight, uniform panels simplify cutting and handling, enhancing ease of use compared to traditional plasterboard systems.
Cost Comparison: Gypsum Board vs Plasterboard
Gypsum board generally offers a lower cost per square foot compared to plasterboard due to its mass production and ease of installation, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects. Plasterboard, which requires more labor-intensive application and curing time, tends to incur higher labor costs and longer project timelines. Overall, gypsum board presents a more economical choice for cost-conscious construction without compromising essential performance characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum board and plasterboard both utilize gypsum as a core material, but gypsum board often incorporates recycled content and offers better recyclability, reducing landfill waste and environmental footprint. The production of gypsum board typically consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to traditional plasterboard manufacturing processes. Selecting gypsum board over plasterboard promotes sustainability through enhanced resource efficiency and reduced carbon emissions in construction.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Gypsum board and plasterboard both serve as popular wall and ceiling materials but differ in composition and application. Gypsum board comprises a gypsum core sandwiched between paper layers, offering ease of installation and moisture resistance, while plasterboard typically involves a gypsum base with a harder, smoother finish suitable for detailed architectural work. Selecting the right material depends on project requirements such as moisture exposure, desired finish quality, and installation complexity, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal.
Gypsum board vs Plasterboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com