Acoustic gypsum board is specifically designed to enhance sound insulation by incorporating dense materials that reduce noise transmission between rooms, making it ideal for theaters, studios, and residential spaces. Fire-rated gypsum board contains non-combustible additives and reinforced core layers to provide increased fire resistance, helping to contain flames and prevent structural damage during fires. Selecting between acoustic and fire-rated gypsum boards depends on whether sound control or fire safety is the primary concern in a building project.
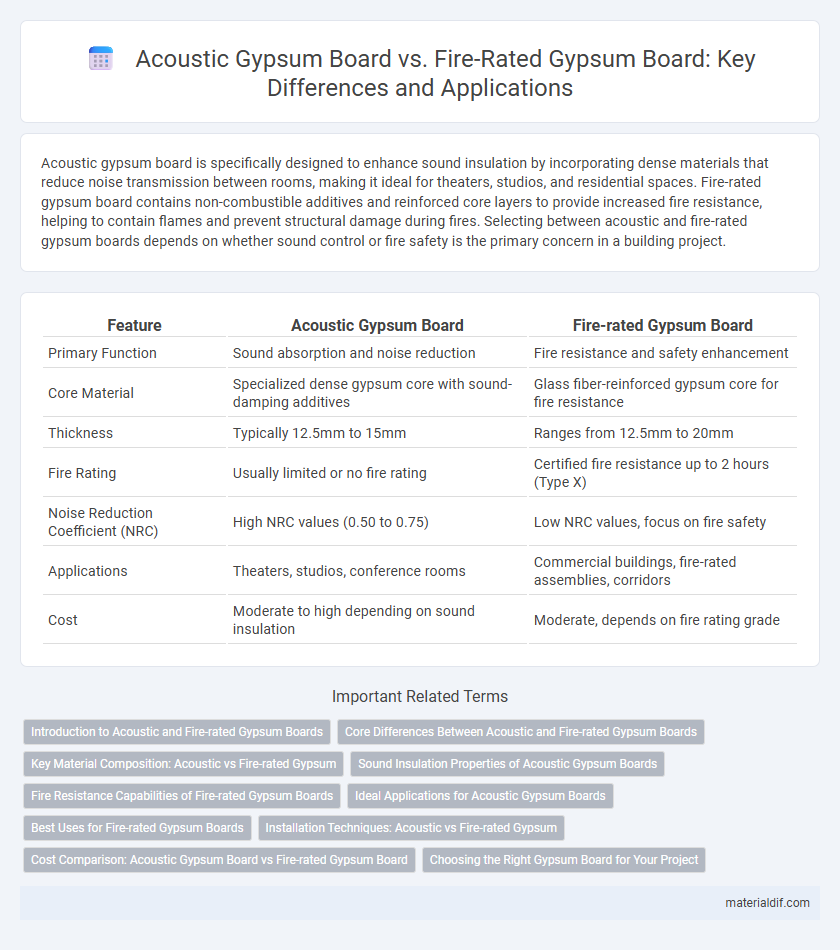
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Gypsum Board | Fire-rated Gypsum Board |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sound absorption and noise reduction | Fire resistance and safety enhancement |
| Core Material | Specialized dense gypsum core with sound-damping additives | Glass fiber-reinforced gypsum core for fire resistance |
| Thickness | Typically 12.5mm to 15mm | Ranges from 12.5mm to 20mm |
| Fire Rating | Usually limited or no fire rating | Certified fire resistance up to 2 hours (Type X) |
| Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) | High NRC values (0.50 to 0.75) | Low NRC values, focus on fire safety |
| Applications | Theaters, studios, conference rooms | Commercial buildings, fire-rated assemblies, corridors |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on sound insulation | Moderate, depends on fire rating grade |
Introduction to Acoustic and Fire-rated Gypsum Boards
Acoustic gypsum boards are designed with enhanced sound absorption properties, making them ideal for reducing noise transmission in residential and commercial buildings. Fire-rated gypsum boards contain additives and multiple layers to provide increased fire resistance, meeting specific building safety codes for fire protection. Both types maintain the core benefits of standard gypsum boards, such as durability and ease of installation, while catering to specialized needs in construction.
Core Differences Between Acoustic and Fire-rated Gypsum Boards
Acoustic gypsum boards are engineered with sound-dampening materials such as mineral fibers or vermiculite within the core to enhance noise reduction and improve room acoustics. Fire-rated gypsum boards contain non-combustible fibers and additives like glass mat facings to increase fire resistance, meeting specific fire safety standards and providing structural integrity under high temperatures. The core composition directly influences their performance, with acoustic boards prioritizing sound attenuation and fire-rated boards focusing on thermal protection and fire containment.
Key Material Composition: Acoustic vs Fire-rated Gypsum
Acoustic gypsum boards contain viscoelastic polymers and fiberglass additives to enhance sound absorption and reduce noise transmission, whereas fire-rated gypsum boards incorporate non-combustible fibers such as glass wool or vermiculite to improve fire resistance and thermal insulation. The core composition of acoustic gypsum is engineered to dampen vibrations, while fire-rated gypsum emphasizes fire retardant chemicals and denser formulations to withstand high temperatures. This specialized material differentiation directly impacts their performance in soundproofing versus fire protection applications.
Sound Insulation Properties of Acoustic Gypsum Boards
Acoustic gypsum boards are specifically engineered to enhance sound insulation by incorporating denser materials and specialized core compositions that effectively reduce airborne noise transmission. Compared to fire-rated gypsum boards, which prioritize fire resistance and maintain standard soundproofing capabilities, acoustic boards deliver superior noise control in environments requiring enhanced acoustic performance. Sound Transmission Class (STC) ratings for acoustic gypsum boards typically range from 45 to 60, significantly outperforming fire-rated gypsum boards in sound attenuation.
Fire Resistance Capabilities of Fire-rated Gypsum Boards
Fire-rated gypsum boards are engineered with specialized additives and denser compositions to enhance fire resistance, effectively delaying heat transfer and maintaining structural integrity during high-temperature exposure. These boards comply with stringent building codes and safety standards, offering superior protection against fire hazards compared to standard acoustic gypsum boards. Their fire resistance capabilities make them essential in fire-rated wall assemblies, shafts, and ceilings to prevent the spread of flame and smoke in residential and commercial buildings.
Ideal Applications for Acoustic Gypsum Boards
Acoustic gypsum boards are ideal for spaces requiring enhanced sound absorption and noise control, such as recording studios, conference rooms, and theaters. These boards contain specialized materials that reduce sound transmission, providing superior acoustic performance compared to fire-rated gypsum boards. Unlike fire-rated gypsum boards designed primarily for fire resistance in areas like stairwells and corridors, acoustic gypsum boards optimize speech clarity and privacy in noise-sensitive environments.
Best Uses for Fire-rated Gypsum Boards
Fire-rated gypsum boards offer enhanced fire resistance, making them ideal for use in walls, ceilings, and partitions where building codes require fire-rated assemblies to protect occupants and property. These boards are commonly installed in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and residential complexes to inhibit fire spread and maintain structural integrity during emergencies. Their effective performance in passive fire protection systems ensures compliance with safety standards and enhances overall building safety.
Installation Techniques: Acoustic vs Fire-rated Gypsum
Acoustic gypsum boards require careful sealing of joints and edges with acoustic sealants to maintain soundproofing integrity, while installation emphasizes staggered framing to minimize sound transmission paths. Fire-rated gypsum boards mandate the use of fire-resistant fasteners and tape coupled with specific thickness and layer configurations to meet fire safety codes. Proper alignment, fastening patterns, and compliance with manufacturer guidelines are critical for both to optimize performance in their respective applications.
Cost Comparison: Acoustic Gypsum Board vs Fire-rated Gypsum Board
Acoustic gypsum boards typically feature specialized materials designed to enhance soundproofing, resulting in higher manufacturing costs compared to standard gypsum products. Fire-rated gypsum boards incorporate additional fire-resistant additives and fiberglass cores, which increase their price but provide essential safety benefits for compliant building structures. While acoustic gypsum boards may be pricier due to sound attenuation properties, fire-rated gypsum boards usually command a premium price justified by their critical fire protection capabilities in commercial and residential construction.
Choosing the Right Gypsum Board for Your Project
Acoustic gypsum board is engineered to enhance sound insulation by incorporating dense core materials and specialized additives, making it ideal for spaces requiring noise control such as theaters or conference rooms. Fire-rated gypsum board contains glass fibers and other fire-resistant materials, providing extended fire protection and meeting building code requirements for fire safety in residential and commercial buildings. Selecting the right gypsum board depends on project priorities: prioritize acoustic gypsum for soundproofing needs and fire-rated gypsum for fire resistance compliance.
Acoustic Gypsum Board vs Fire-rated Gypsum Board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com