Foil-backed gypsum offers superior moisture resistance and thermal insulation compared to paper-faced gypsum, making it ideal for areas prone to humidity or temperature fluctuations. Unlike paper-faced gypsum, the foil backing acts as a vapor barrier, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth. This durability and enhanced protection make foil-backed gypsum a preferred choice for bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
Table of Comparison
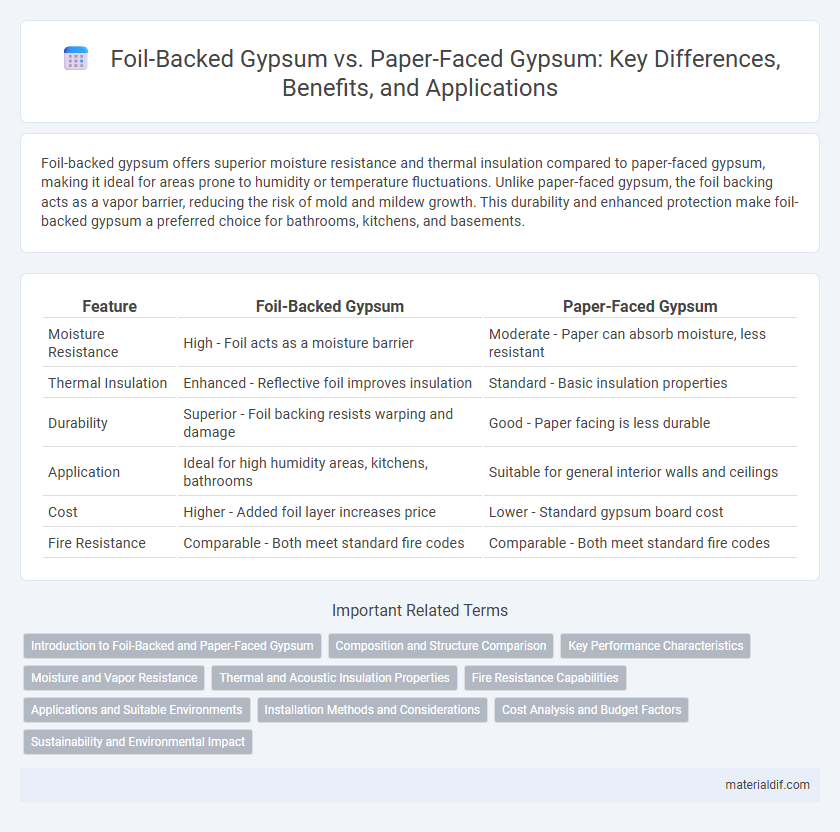
| Feature | Foil-Backed Gypsum | Paper-Faced Gypsum |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | High - Foil acts as a moisture barrier | Moderate - Paper can absorb moisture, less resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Enhanced - Reflective foil improves insulation | Standard - Basic insulation properties |
| Durability | Superior - Foil backing resists warping and damage | Good - Paper facing is less durable |
| Application | Ideal for high humidity areas, kitchens, bathrooms | Suitable for general interior walls and ceilings |
| Cost | Higher - Added foil layer increases price | Lower - Standard gypsum board cost |
| Fire Resistance | Comparable - Both meet standard fire codes | Comparable - Both meet standard fire codes |
Introduction to Foil-Backed and Paper-Faced Gypsum
Foil-backed gypsum features a layer of reflective foil that enhances moisture resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-humidity environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. Paper-faced gypsum, coated with a paper surface, offers easy paint adhesion and is commonly used in standard interior wall and ceiling applications. The choice between foil-backed and paper-faced gypsum depends on specific environmental requirements and desired durability characteristics.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Foil-backed gypsum board features a core of gypsum plaster combined with a thin layer of aluminum foil on one side, enhancing moisture resistance and reflecting radiant heat. Paper-faced gypsum board consists of a gypsum core sandwiched between two layers of heavy paper, providing structural strength and ease of finishing but lower moisture resistance. The foil layer in foil-backed gypsum creates a vapor barrier, making it ideal for high-humidity areas, while paper-faced gypsum relies on paint or other coatings for moisture protection.
Key Performance Characteristics
Foil-backed gypsum boards offer superior moisture resistance and enhanced thermal insulation compared to paper-faced gypsum, making them ideal for high-humidity environments and exterior applications. Paper-faced gypsum provides better soundproofing qualities and ease of finishing due to its smooth surface and flexibility in interior settings. Both types deliver fire resistance, but foil-backed gypsum excels in vapor barrier properties, contributing to improved energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Moisture and Vapor Resistance
Foil-backed gypsum offers superior moisture and vapor resistance compared to paper-faced gypsum, making it ideal for high-humidity environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. The foil layer acts as a vapor barrier, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth by preventing water vapor infiltration. In contrast, paper-faced gypsum is more susceptible to moisture damage and is best suited for dry interior spaces.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Foil-backed gypsum boards provide enhanced thermal insulation due to the reflective foil layer that reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency in buildings. Paper-faced gypsum boards offer superior acoustic insulation by absorbing sound waves effectively, making them ideal for noise control in interior spaces. Choosing between foil-backed and paper-faced gypsum depends on prioritizing either thermal resistance or soundproofing based on specific construction requirements.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Foil-backed gypsum boards offer superior fire resistance compared to paper-faced gypsum due to their aluminum foil layer, which acts as a heat reflector and moisture barrier, slowing heat transfer during a fire. Paper-faced gypsum provides basic fire resistance but lacks the additional protection against heat and moisture, making it less effective in high-temperature scenarios. Fire ratings for foil-backed gypsum often exceed those of standard paper-faced boards, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced safety measures.
Applications and Suitable Environments
Foil-backed gypsum is ideal for moisture-prone areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements due to its enhanced water resistance and vapor barrier properties. Paper-faced gypsum is commonly used in standard interior walls and ceilings where moisture exposure is minimal, offering ease of finishing and painting. Selecting foil-backed gypsum improves durability in high-humidity environments, while paper-faced gypsum remains the economical choice for dry, controlled conditions.
Installation Methods and Considerations
Foil-backed gypsum boards require careful handling to avoid tearing the reflective foil during installation, with fastening methods such as screws or nails needing to ensure secure attachment without compromising the moisture barrier. Paper-faced gypsum panels have standard installation practices emphasizing proper taping and joint compound application to prevent cracking and ensure a smooth finish. Both types necessitate attention to environmental conditions, as foil-backed boards offer superior moisture resistance, while paper-faced gypsum is more prone to damage in high-humidity areas.
Cost Analysis and Budget Factors
Foil-backed gypsum boards typically cost 15-25% more than paper-faced gypsum due to the added moisture and vapor barrier properties, which enhance durability in humid environments. Budget considerations should include long-term savings on maintenance and mold remediation, as foil-backed options reduce potential damage and replacement costs. Choosing between the two depends on project requirements, but foil-backed gypsum offers greater value in moisture-prone areas despite higher upfront expenses.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Foil-backed gypsum boards offer enhanced moisture resistance and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing landfill waste, contributing positively to sustainability efforts. Paper-faced gypsum, typically recycled and biodegradable, provides an eco-friendly alternative with lower embodied energy but is more susceptible to water damage, potentially increasing waste over time. Choosing between foil-backed and paper-faced gypsum depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements in specific construction environments.
Foil-backed gypsum vs Paper-faced gypsum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com