Gypsum core drywall offers superior fire resistance and sound insulation compared to anhydrite core panels, making it ideal for residential and commercial interiors. Anhydrite core drywall provides enhanced moisture resistance and durability, suitable for environments prone to humidity and dampness. Choosing between gypsum and anhydrite cores depends on the specific requirements of the construction project, balancing fire protection, sound control, and moisture management.
Table of Comparison
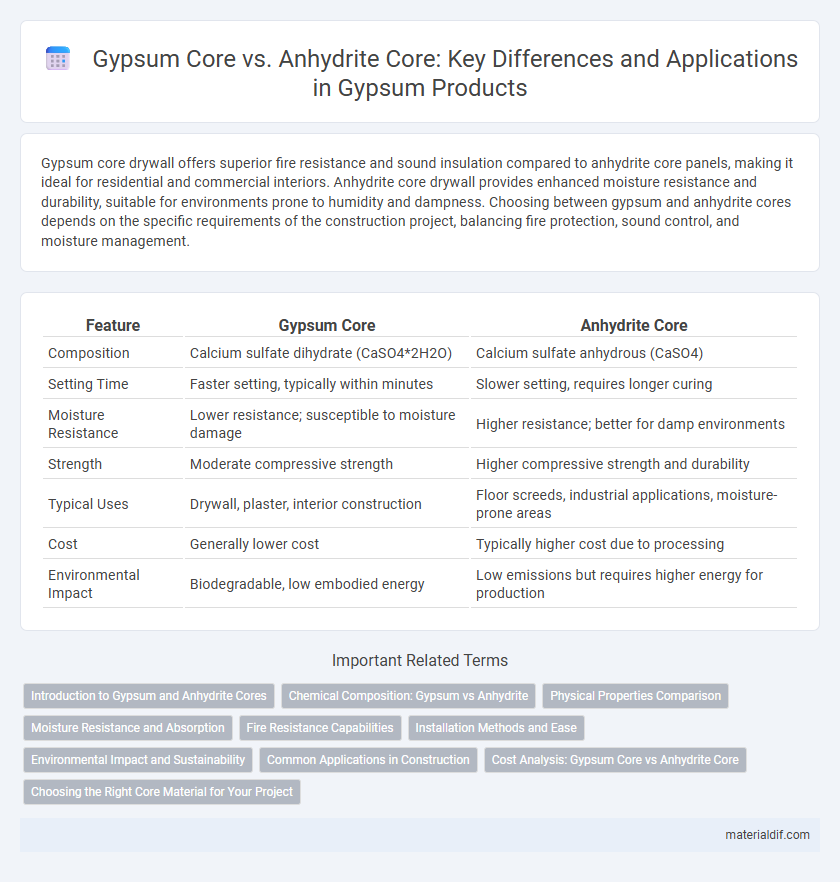
| Feature | Gypsum Core | Anhydrite Core |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O) | Calcium sulfate anhydrous (CaSO4) |
| Setting Time | Faster setting, typically within minutes | Slower setting, requires longer curing |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower resistance; susceptible to moisture damage | Higher resistance; better for damp environments |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength | Higher compressive strength and durability |
| Typical Uses | Drywall, plaster, interior construction | Floor screeds, industrial applications, moisture-prone areas |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to processing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low embodied energy | Low emissions but requires higher energy for production |
Introduction to Gypsum and Anhydrite Cores
Gypsum core consists primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, offering excellent fire resistance and sound insulation properties, making it ideal for drywall and ceiling applications. Anhydrite core is made from calcium sulfate anhydrous, providing higher compressive strength and improved moisture resistance compared to gypsum cores. Both cores are widely used in construction materials but are selected based on specific performance requirements such as durability and environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition: Gypsum vs Anhydrite
Gypsum core primarily consists of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O), whereas anhydrite core is composed of calcium sulfate anhydrate (CaSO4). The presence of water molecules in gypsum's chemical structure results in different physical properties compared to the anhydrite core, which lacks crystal water. These variations in chemical composition directly influence hardness, solubility, and industrial applications of gypsum and anhydrite cores.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gypsum core exhibits a lower density and higher porosity compared to anhydrite core, resulting in enhanced workability but reduced mechanical strength. Anhydrite core, with its denser microstructure and lower water absorption, offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring robust physical performance. The difference in mineral composition influences thermal conductivity, where anhydrite cores provide better insulation properties than gypsum cores.
Moisture Resistance and Absorption
Gypsum core drywall typically exhibits higher moisture absorption due to its porous structure, making it less suitable for wet or humid environments compared to anhydrite core drywall. Anhydrite core boards, derived from anhydrous calcium sulfate, offer superior moisture resistance and reduced water absorption, enhancing durability in areas prone to moisture exposure. These properties make anhydrite core drywall preferable for applications requiring enhanced mold resistance and long-term stability against humidity.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum core boards exhibit superior fire resistance due to their inherent water content, which releases steam under heat, slowing flame spread and maintaining structural integrity. Anhydrite core boards lack this chemically bound moisture, resulting in reduced fire-resistance performance and increased vulnerability to high temperatures. This fundamental difference makes gypsum core a preferred choice in fire-rated wall and ceiling assemblies for enhanced safety and compliance with building codes.
Installation Methods and Ease
Gypsum core offers faster installation due to its lighter weight and greater flexibility, allowing for easier cutting and shaping on-site compared to anhydrite core. Anhydrite core, being denser and more brittle, requires more careful handling and specialized tools, which can slow down the installation process. The moisture resistance of gypsum cores also enhances ease of use in varied environmental conditions, reducing potential delays caused by material damage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum core products typically have a lower environmental impact than anhydrite core counterparts due to the abundance and recyclability of naturally occurring gypsum, which reduces the need for energy-intensive processing. Anhydrite cores require higher temperatures for production, leading to greater CO2 emissions and energy consumption, which can challenge sustainability goals. The use of recycled gypsum in core manufacturing enhances resource efficiency and minimizes landfill waste, positioning gypsum cores as a more sustainable building material option.
Common Applications in Construction
Gypsum core is widely used in drywall and plaster products due to its excellent fire resistance and ease of installation, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Anhydrite core, derived from calcium sulfate without water, is preferred in flooring systems and cement applications for its superior hardness and quick setting properties. Both cores play essential roles in construction, with gypsum core dominating wall assemblies and anhydrite core enhancing floor durability.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Core vs Anhydrite Core
Gypsum core boards typically cost less than anhydrite core boards due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them more budget-friendly for standard construction projects. Anhydrite core boards, while more expensive, offer superior moisture resistance and durability, which can lead to reduced maintenance costs over time in high-humidity environments. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including initial investment and long-term performance, is crucial for selecting between gypsum and anhydrite cores in building applications.
Choosing the Right Core Material for Your Project
Gypsum core offers superior fire resistance and sound insulation, making it ideal for residential and commercial drywall applications where safety and comfort are priorities. Anhydrite core provides enhanced moisture resistance and structural strength, suited for humid environments and areas requiring higher durability. Selecting the right core material depends on specific project needs such as exposure conditions, load-bearing requirements, and desired finish quality.
Gypsum Core vs Anhydrite Core Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com