Gypsum sheets are a specific type of drywall made from gypsum plaster pressed between two thick sheets of paper, providing excellent fire resistance and moisture control compared to traditional drywall. Drywall serves as a general term for panels used to create walls and ceilings, but gypsum sheets are preferred for their durability and soundproofing properties. Choosing gypsum sheets over standard drywall enhances structural integrity and long-term performance in both residential and commercial construction.
Table of Comparison
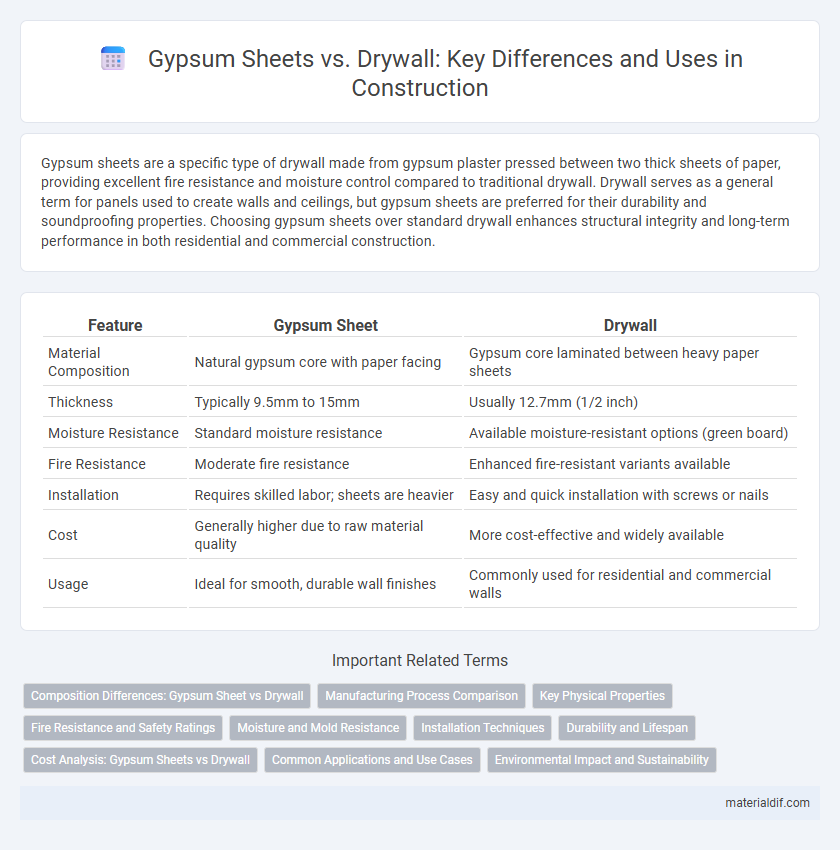
| Feature | Gypsum Sheet | Drywall |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural gypsum core with paper facing | Gypsum core laminated between heavy paper sheets |
| Thickness | Typically 9.5mm to 15mm | Usually 12.7mm (1/2 inch) |
| Moisture Resistance | Standard moisture resistance | Available moisture-resistant options (green board) |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance | Enhanced fire-resistant variants available |
| Installation | Requires skilled labor; sheets are heavier | Easy and quick installation with screws or nails |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material quality | More cost-effective and widely available |
| Usage | Ideal for smooth, durable wall finishes | Commonly used for residential and commercial walls |
Composition Differences: Gypsum Sheet vs Drywall
Gypsum sheets consist primarily of a solid gypsum core encased in a dense paper facing, providing enhanced moisture resistance compared to standard drywall. Drywall typically features a gypsum core with paper facings but may include additives and varying thicknesses optimized for different applications such as fire resistance or soundproofing. The compositional differences between gypsum sheets and drywall influence their durability, installation processes, and suitability for specific environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Gypsum sheets and drywall are commonly used building materials manufactured through distinct processes that impact their properties and applications. Gypsum sheets are produced by mixing calcined gypsum with water and additives, then casting the slurry onto a mat before drying, resulting in a dense, smooth panel ideal for finishing surfaces. Drywall manufacturing involves layering gypsum plaster between two sheets of paper, followed by drying and cutting, which provides a lightweight, affordable, and easy-to-install wallboard solution.
Key Physical Properties
Gypsum sheets and drywall both consist primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, but gypsum sheets typically offer higher density and improved moisture resistance compared to standard drywall panels. The key physical properties distinguishing gypsum sheets include enhanced fire resistance due to their uniform thickness and a denser core composition, which increases durability and load-bearing capacity. Drywall, while widely used for interior wall construction, often exhibits lower impact resistance and is more susceptible to moisture damage, making gypsum sheets a preferred choice in environments requiring superior structural integrity and moisture control.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Gypsum sheets offer superior fire resistance compared to standard drywall due to their higher chemical composition of calcium sulfate dihydrate, which releases water vapor when exposed to heat, slowing fire spread. Fire ratings for gypsum sheets can reach up to 1- or 2-hour protection periods, making them ideal for building codes requiring enhanced safety standards. In contrast, traditional drywall provides basic fire resistance but generally falls short in environments demanding stringent fire safety performance.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Gypsum sheets offer superior moisture and mold resistance compared to traditional drywall due to their denser composition and enhanced additives that inhibit water absorption. Mold-resistant gypsum boards incorporate special coatings and fiberglass mats, reducing the risk of fungal growth in humid environments. These properties make gypsum sheets an ideal choice for bathrooms, basements, and other moisture-prone areas.
Installation Techniques
Gypsum sheets are typically heavier and thicker than drywall, requiring specialized fastening techniques using screws or nails to ensure secure attachment to framing. Drywall installation prioritizes quick mounting with standardized screw spacing and taping the joints with joint compound for a smooth finish. Both materials demand precise cutting tools and proper handling to prevent damage during installation and maintain surface integrity.
Durability and Lifespan
Gypsum sheets offer higher durability and longer lifespan compared to traditional drywall due to their denser composition and enhanced resistance to moisture and impact. Unlike regular drywall, gypsum sheets are less prone to cracking, sagging, and mold growth, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and humid environments. Their reinforced structure extends the lifespan by several years, reducing maintenance and replacement costs in commercial and residential applications.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Sheets vs Drywall
Gypsum sheets typically cost more upfront than traditional drywall due to their enhanced durability and moisture resistance, making them a cost-effective option for long-term projects. Drywall offers a lower initial installation expense but may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs over time, especially in damp environments where gypsum sheets excel. Budget planning should consider both immediate material costs and extended lifecycle expenses to optimize overall affordability.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Gypsum sheets are commonly used in interior wall and ceiling applications due to their moisture resistance and smooth finish, making them ideal for bathrooms and kitchens. Drywall, often made with gypsum core, is widely used in residential and commercial construction for partition walls and ceilings because of its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Both materials offer fire resistance, but gypsum sheets provide enhanced durability for high-humidity environments compared to standard drywall.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum sheets, made primarily from natural gypsum, offer higher environmental sustainability compared to traditional drywall due to their lower energy consumption during production and superior recyclability. Drywall, often containing synthetic additives and facing challenges in disposal and recycling, contributes more significantly to landfill waste and resource depletion. The eco-friendly attributes of gypsum sheets include reduced carbon footprint and enhanced potential for reuse in construction projects, promoting sustainable building practices.
Gypsum sheet vs Drywall Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com