Foil-backed gypsum offers enhanced moisture resistance and improved thermal insulation compared to plain gypsum, making it ideal for use in environments prone to humidity and temperature fluctuations. The reflective foil layer acts as a vapor barrier, preventing moisture penetration and reducing energy costs by reflecting heat. In contrast, plain gypsum lacks these protective features, providing only basic fire resistance and structural support without the added benefits of moisture control or insulation.
Table of Comparison
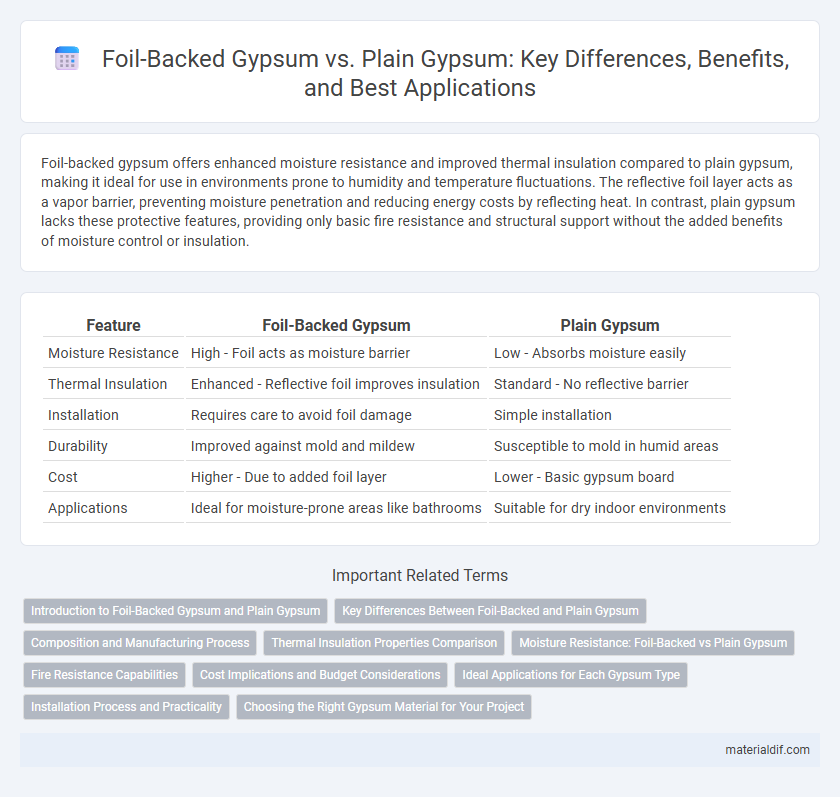
| Feature | Foil-Backed Gypsum | Plain Gypsum |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | High - Foil acts as moisture barrier | Low - Absorbs moisture easily |
| Thermal Insulation | Enhanced - Reflective foil improves insulation | Standard - No reflective barrier |
| Installation | Requires care to avoid foil damage | Simple installation |
| Durability | Improved against mold and mildew | Susceptible to mold in humid areas |
| Cost | Higher - Due to added foil layer | Lower - Basic gypsum board |
| Applications | Ideal for moisture-prone areas like bathrooms | Suitable for dry indoor environments |
Introduction to Foil-Backed Gypsum and Plain Gypsum
Foil-backed gypsum consists of a gypsum core bonded to a reflective foil facing, enhancing moisture resistance and thermal insulation compared to plain gypsum, which is a standard drywall material without additional facings. The foil facing in foil-backed gypsum improves durability in humid environments and provides a vapor barrier, making it suitable for areas prone to moisture exposure. Plain gypsum offers a smooth surface for finishing applications but lacks the enhanced protective properties inherent in foil-backed variants.
Key Differences Between Foil-Backed and Plain Gypsum
Foil-backed gypsum features a metallic foil layer that enhances moisture resistance and thermal insulation compared to plain gypsum, which lacks this protective layer. The foil backing acts as a vapor barrier, making foil-backed panels ideal for high-humidity environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. Plain gypsum is more cost-effective and easier to install but offers less protection against moisture and heat.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Foil-backed gypsum consists of a standard gypsum core laminated with a reflective aluminum foil facing, enhancing moisture resistance and fire retardant properties during manufacturing. Plain gypsum is composed solely of a calcined gypsum core without any additional surface treatment, produced by hydrating dehydrated calcium sulfate. The lamination process in foil-backed gypsum involves bonding the aluminum foil to the gypsum board under heat and pressure, differentiating it from the straightforward drying and setting processes used for plain gypsum boards.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Foil-backed gypsum offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to plain gypsum due to its reflective foil layer that reduces radiant heat transfer. While plain gypsum primarily provides basic thermal resistance through its density and thickness, foil-backed gypsum enhances energy efficiency by reflecting heat away, leading to improved temperature regulation in buildings. This makes foil-backed gypsum a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced thermal performance and energy savings.
Moisture Resistance: Foil-Backed vs Plain Gypsum
Foil-backed gypsum significantly enhances moisture resistance compared to plain gypsum due to its reflective foil layer that acts as a vapor barrier, preventing moisture infiltration and reducing mold growth. Plain gypsum lacks this protective layer, making it more prone to water absorption and damage in high-humidity environments. This makes foil-backed gypsum ideal for areas such as bathrooms and kitchens where moisture control is critical.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Foil-backed gypsum enhances fire resistance by integrating a reflective foil layer that acts as a radiant heat barrier, reducing heat transfer in comparison to plain gypsum. Plain gypsum relies solely on the inherent fire-resistant properties of calcium sulfate dihydrate, which slows the spread of flames but lacks additional thermal reflection. The foil backing improves overall performance in fire-rated assemblies by providing an extra measure of protection against high temperatures, making it preferable in environments with stringent fire safety requirements.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Foil-backed gypsum typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to plain gypsum due to its integrated moisture and vapor barrier properties, which can reduce the need for additional materials and labor in damp environments. Budget considerations should factor in long-term savings associated with improved durability and reduced maintenance expenses when using foil-backed gypsum. Plain gypsum offers a lower initial investment, making it suitable for dry, budget-constrained projects where moisture protection is not a primary concern.
Ideal Applications for Each Gypsum Type
Foil-backed gypsum is ideal for areas requiring enhanced moisture resistance and thermal insulation, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior walls. Plain gypsum suits interior spaces with low humidity levels, offering cost-effective fire resistance and soundproofing in bedrooms and living rooms. Choosing the appropriate gypsum type optimizes durability and performance tailored to specific environmental conditions and building requirements.
Installation Process and Practicality
Foil-backed gypsum boards offer enhanced moisture resistance and thermal insulation, making them ideal for installation in areas prone to humidity such as bathrooms and kitchens. The installation process of foil-backed gypsum requires careful handling to avoid damaging the reflective foil layer, and often involves using specialized fasteners or adhesives to maintain the board's integrity. Plain gypsum boards are easier to install due to their simpler composition but lack the added moisture protection, which may necessitate additional waterproofing measures during construction.
Choosing the Right Gypsum Material for Your Project
Foil-backed gypsum offers enhanced moisture resistance and improved thermal insulation, making it ideal for areas prone to humidity or temperature fluctuations. Plain gypsum, while cost-effective and easy to install, suits dry environments where moisture exposure is minimal. Selecting the right gypsum material depends on project-specific factors such as environmental conditions, budget constraints, and performance requirements.
Foil-Backed Gypsum vs Plain Gypsum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com