Gypsum is a naturally occurring mineral widely used in construction, offering better fire resistance and sound insulation compared to Plaster of Paris (POP), which is a processed form primarily used for decorative purposes. Gypsum provides superior durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for wall partitions and ceilings in humid environments, whereas POP is more prone to cracking and damage when exposed to water. Choosing gypsum over POP ensures enhanced structural integrity and a longer-lasting finish in both residential and commercial buildings.
Table of Comparison
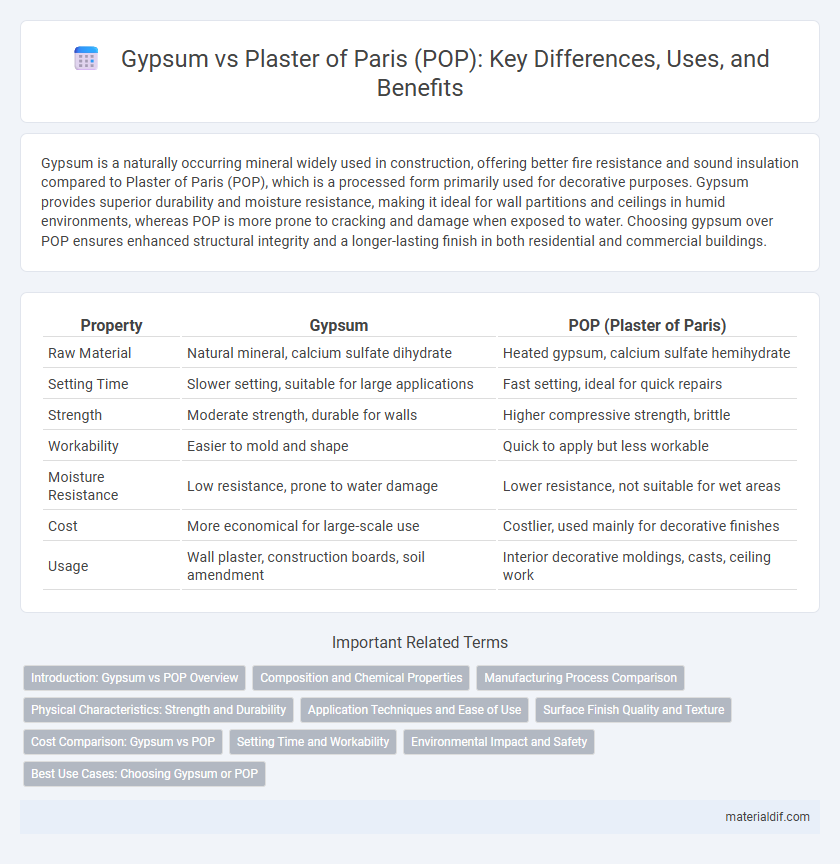
| Property | Gypsum | POP (Plaster of Paris) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Natural mineral, calcium sulfate dihydrate | Heated gypsum, calcium sulfate hemihydrate |
| Setting Time | Slower setting, suitable for large applications | Fast setting, ideal for quick repairs |
| Strength | Moderate strength, durable for walls | Higher compressive strength, brittle |
| Workability | Easier to mold and shape | Quick to apply but less workable |
| Moisture Resistance | Low resistance, prone to water damage | Lower resistance, not suitable for wet areas |
| Cost | More economical for large-scale use | Costlier, used mainly for decorative finishes |
| Usage | Wall plaster, construction boards, soil amendment | Interior decorative moldings, casts, ceiling work |
Introduction: Gypsum vs POP Overview
Gypsum is a natural mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, widely used in construction for wall finishes and molding due to its durability and moisture resistance. Plaster of Paris (POP) is a quick-setting material derived from gypsum by heating, commonly used for decorative work and fine detailing in interiors. While both materials originate from gypsum, gypsum boards offer better fire resistance and moisture control compared to the more brittle and less moisture-resistant POP.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Gypsum consists primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O), while Plaster of Paris (POP) is obtained by heating gypsum to remove water, resulting in calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4* 1/2H2O). The chemical transformation alters their properties, with gypsum being stable and hydrated, and POP being more reactive and setting rapidly upon mixing with water. This difference in composition and chemical state impacts their applications, durability, and workability in construction and decorative finishes.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Gypsum is processed by heating natural mineral to remove water content, resulting in a fine powder called calcined gypsum, while Plaster of Paris (POP) is produced through the calcination of pure gypsum at high temperatures around 150degC to 180degC, partially dehydrating it. The manufacturing of gypsum involves grinding and heating raw gypsum minerals, whereas POP manufacturing requires controlled drying to achieve quick setting properties suitable for casting and construction. Both processes focus on dehydration but differ in temperature control and purity requirements, affecting the final product's setting time and strength.
Physical Characteristics: Strength and Durability
Gypsum exhibits higher compressive strength and enhanced durability compared to Plaster of Paris (POP), making it more suitable for structural applications and long-lasting finishes. Its naturally crystalline structure provides superior resistance to cracking and moisture damage, whereas POP is more brittle and prone to deterioration over time. These physical characteristics make gypsum a preferred choice for environments requiring robustness and longevity in building materials.
Application Techniques and Ease of Use
Gypsum boards offer a faster installation process with larger panels that reduce jointing and finishing time compared to POP, which requires multiple layers and longer drying periods. Gypsum is more versatile for wall linings and ceilings with consistent quality, while POP demands skilled workmanship for intricate designs and smooth finishes. The ease of use of gypsum boards, including superior fire resistance and moisture control, makes them ideal for modern construction, whereas POP is often favored for detailed ornamental work.
Surface Finish Quality and Texture
Gypsum provides a smoother and more consistent surface finish compared to Plaster of Paris (POP), resulting in finer texture ideal for high-quality wall finishes. The crystalline structure of gypsum ensures better adhesion and reduces the occurrence of cracks and uneven surfaces commonly seen in POP applications. Gypsum's natural moisture-resistant properties also contribute to a more durable and aesthetically pleasing finish over time.
Cost Comparison: Gypsum vs POP
Gypsum is generally more cost-effective than Plaster of Paris (POP) due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious construction projects. While POP requires higher energy consumption during production, gypsum slabs offer easier installation and reduced labor costs, further enhancing overall savings. The long-term durability and reduced maintenance of gypsum also contribute to lower lifecycle costs compared to POP.
Setting Time and Workability
Gypsum sets slower than Plaster of Paris (POP), allowing for extended workability and ease of application in detailed molding. POP typically sets within 5 to 10 minutes, which is ideal for rapid projects but limits adjustment time. Gypsum's longer setting time, often ranging from 20 to 30 minutes, provides greater flexibility, making it suitable for complex or large-scale plastering work.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Gypsum offers a more sustainable option than Plaster of Paris (POP) due to its lower carbon footprint and biodegradability, reducing environmental pollution during manufacturing and disposal. Unlike POP, gypsum production consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to eco-friendly construction practices. Gypsum also poses fewer health risks, as it releases minimal dust and lacks the chemical additives found in POP, enhancing indoor air quality and worker safety.
Best Use Cases: Choosing Gypsum or POP
Gypsum boards excel in large-scale construction projects due to their fire resistance, sound insulation, and moisture control, making them ideal for walls and ceilings in residential and commercial buildings. Plaster of Paris (POP) is preferred for detailed ornamental work, rapid setting times, and smooth finishes in interior decoration and repair tasks. Selecting between gypsum and POP hinges on project requirements for durability, aesthetics, and application speed, with gypsum suited for structural elements and POP favored for artistic detailing.
Gypsum vs POP (Plaster of Paris) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com