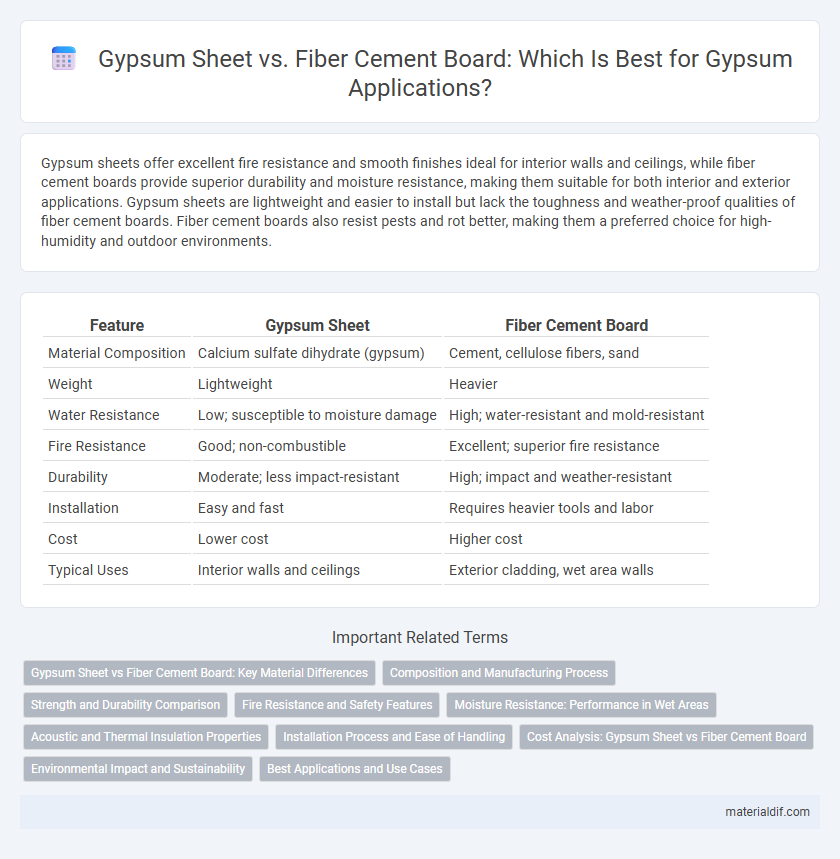
Gypsum sheets offer excellent fire resistance and smooth finishes ideal for interior walls and ceilings, while fiber cement boards provide superior durability and moisture resistance, making them suitable for both interior and exterior applications. Gypsum sheets are lightweight and easier to install but lack the toughness and weather-proof qualities of fiber cement boards. Fiber cement boards also resist pests and rot better, making them a preferred choice for high-humidity and outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Sheet | Fiber Cement Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) | Cement, cellulose fibers, sand |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Water Resistance | Low; susceptible to moisture damage | High; water-resistant and mold-resistant |
| Fire Resistance | Good; non-combustible | Excellent; superior fire resistance |
| Durability | Moderate; less impact-resistant | High; impact and weather-resistant |
| Installation | Easy and fast | Requires heavier tools and labor |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Uses | Interior walls and ceilings | Exterior cladding, wet area walls |
Gypsum Sheet vs Fiber Cement Board: Key Material Differences
Gypsum sheets are composed primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, offering lightweight and easy installation with excellent fire resistance, while fiber cement boards consist of cement mixed with cellulose fibers, providing superior moisture resistance and structural strength. Gypsum sheets typically have smooth surfaces ideal for indoor walls and ceilings but are less durable in wet environments compared to fiber cement boards, which are suitable for exterior applications due to their water and weather resistance. The choice between gypsum sheets and fiber cement boards depends on the specific requirements for moisture resistance, fire protection, and structural durability in construction projects.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gypsum sheets are primarily composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O) and produced by drying gypsum slurry between paper facings. Fiber cement boards consist of cement, cellulose fibers, and sand, created through a process of mixing, formed by extrusion or pressing, and then curing under controlled conditions. The manufacturing of gypsum sheets emphasizes setting and drying, whereas fiber cement boards undergo curing and steam treatment to develop strength and durability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gypsum sheets offer moderate strength suitable for interior walls but are prone to damage from moisture and impact, making them less durable in harsh environments. Fiber cement boards exhibit superior strength due to a dense composite of cement and cellulose fibers, providing exceptional resistance to water, fire, and physical impact. This durability makes fiber cement boards ideal for exterior applications and areas requiring long-lasting, robust construction materials.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Gypsum sheets offer excellent fire resistance due to their calcium sulfate dihydrate content, which releases water vapor when exposed to heat, slowing flame spread and maintaining structural integrity. Fiber cement boards provide superior impact resistance and durability but have comparatively lower fire resistance than gypsum sheets, though they still meet standard fire safety requirements. Both materials contribute to fire safety, with gypsum sheets being preferred in applications demanding enhanced fire protection and fiber cement boards favored for areas requiring toughness and moisture resistance.
Moisture Resistance: Performance in Wet Areas
Gypsum sheets have limited moisture resistance, making them less suitable for wet areas compared to fiber cement boards, which are engineered for high durability in damp environments. Fiber cement boards resist water absorption, mold, and mildew, ensuring long-term structural integrity in bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior applications. This superior moisture resistance positions fiber cement boards as the preferred choice for installations exposed to consistent moisture.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Properties
Gypsum sheets provide excellent sound absorption and thermal insulation due to their porous structure, making them ideal for interior partition walls and ceilings. Fiber cement boards offer superior durability and moisture resistance but generally have lower acoustic and thermal insulation properties compared to gypsum sheets. For projects prioritizing noise reduction and energy efficiency, gypsum sheets are a more effective choice than fiber cement boards.
Installation Process and Ease of Handling
Gypsum sheets are lightweight and easy to cut, making their installation faster with standard tools and less labor intensity compared to fiber cement boards. Fiber cement boards require specialized tools due to their density and hardness, resulting in a more time-consuming installation process and greater handling difficulty. The ease of handling gypsum sheets reduces installation costs and improves worker safety on-site.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Sheet vs Fiber Cement Board
Gypsum sheets generally offer lower initial costs compared to fiber cement boards, making them a budget-friendly option for interior walls and ceilings. Fiber cement boards, while more expensive upfront, provide superior durability, moisture resistance, and fire protection, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Cost-effectiveness depends on the specific application, environmental exposure, and desired lifespan of the material in construction projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum sheets have a lower carbon footprint during production due to the abundance of natural gypsum and lower energy consumption, whereas fiber cement boards require more energy-intensive processes involving cement and silica, increasing their environmental impact. Fiber cement boards offer greater durability and resistance to moisture and pests, extending building lifespan and reducing material waste, which supports sustainability despite higher initial emissions. Recycling and disposal practices vary, with gypsum sheets being more biodegradable and fiber cement boards often needing specialized handling to prevent environmental contamination.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Gypsum sheets excel in interior applications such as wall partitions, ceilings, and decorative features due to their lightweight, fire-resistant, and easy-to-install properties. Fiber cement boards are ideal for exterior use, offering superior moisture resistance, durability, and resistance to termites, making them perfect for cladding, soffits, and wet areas. Selecting gypsum sheets for dry interior environments and fiber cement boards for high-exposure or moisture-prone locations ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Gypsum sheet vs Fiber cement board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com