Gypsum board offers excellent fire resistance, easy installation, and smooth finishing, making it ideal for indoor walls and ceilings in dry environments. Cement board provides superior moisture resistance, durability, and mold prevention, which is essential for wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Choosing between gypsum board and cement board depends on the specific requirements of the space, especially regarding moisture exposure and structural strength.
Table of Comparison
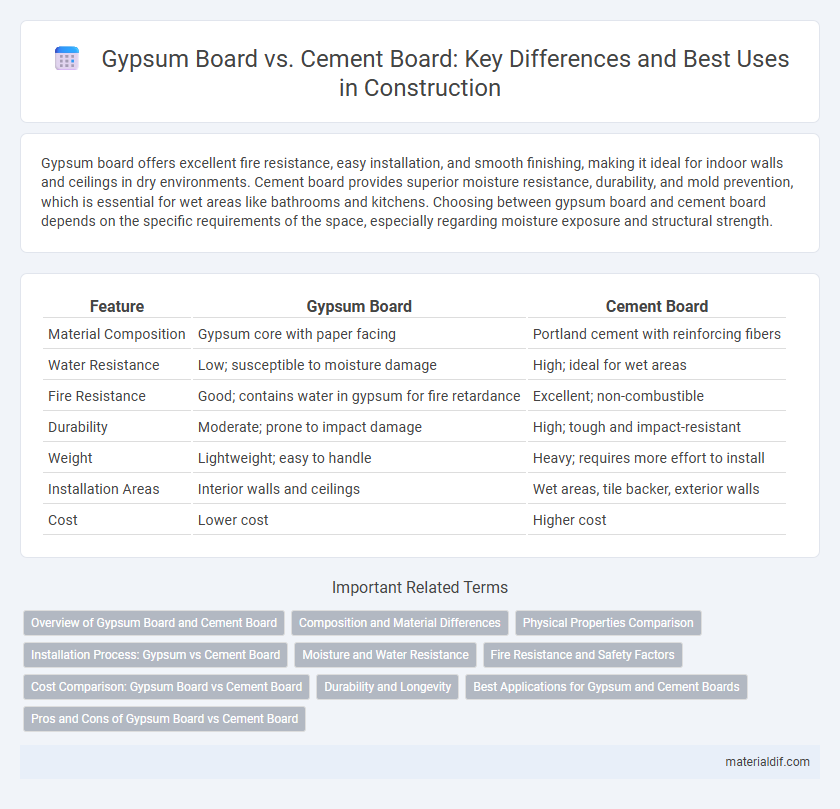
| Feature | Gypsum Board | Cement Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Gypsum core with paper facing | Portland cement with reinforcing fibers |
| Water Resistance | Low; susceptible to moisture damage | High; ideal for wet areas |
| Fire Resistance | Good; contains water in gypsum for fire retardance | Excellent; non-combustible |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to impact damage | High; tough and impact-resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight; easy to handle | Heavy; requires more effort to install |
| Installation Areas | Interior walls and ceilings | Wet areas, tile backer, exterior walls |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Overview of Gypsum Board and Cement Board
Gypsum board, composed of a gypsum core sandwiched between layers of paper, provides excellent fire resistance and soundproofing, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Cement board consists of a cement and fiberglass mesh core, offering superior durability and moisture resistance, which suits wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Both materials ensure strong, stable wall systems but differ significantly in application based on environmental exposure and performance needs.
Composition and Material Differences
Gypsum board is primarily composed of a core of gypsum plaster sandwiched between layers of paper, offering lightweight and fire-resistant properties ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Cement board consists of cement reinforced with glass fibers or other aggregates, providing superior moisture resistance and durability suited for exterior applications and wet areas. The fundamental material distinction lies in gypsum's softness and ease of installation compared to the rigid, water-resistant nature of cement board, affecting their respective performance in construction environments.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gypsum board features lightweight composition and excellent fire resistance, with a typical density of 600-900 kg/m3 and thermal conductivity around 0.17-0.25 W/m*K, whereas cement board is significantly heavier, usually 1400-1800 kg/m3, offering higher moisture resistance and superior structural strength. Cement board demonstrates greater impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for exterior applications and wet areas, while gypsum board excels in ease of installation and sound insulation for interior walls and ceilings. Both materials exhibit different bending strengths, with gypsum board averaging 4-7 MPa and cement board ranging between 10-20 MPa, influencing their respective suitability for various construction environments.
Installation Process: Gypsum vs Cement Board
Gypsum board offers a quicker and easier installation process due to its lightweight nature and compatibility with standard drywall tools, allowing for fast cutting and screwing. Cement board, being denser and heavier, requires more specialized tools such as carbide-tipped blades for cutting and corrosion-resistant fasteners, which can lengthen installation time. Moisture resistance in cement boards also necessitates careful sealing at joints to prevent water ingress, unlike gypsum boards that typically require additional waterproofing treatments in wet areas.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Gypsum board offers limited moisture resistance and is prone to damage in high humidity or direct water exposure, making it unsuitable for wet areas. Cement board features superior water resistance and durability, allowing it to withstand prolonged contact with moisture without deteriorating. This makes cement board the preferred choice for bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior applications where water exposure is frequent.
Fire Resistance and Safety Factors
Gypsum board offers excellent fire resistance due to its chemically bound water releasing steam when exposed to heat, slowing fire spread and maintaining structural integrity. Cement board, composed of cement and reinforcing fibers, provides superior durability and moisture resistance but generally has lower fire resistance compared to gypsum board. For safety-critical applications requiring heightened fire protection, gypsum board remains the preferred material, while cement board excels in environments prone to moisture and physical impact.
Cost Comparison: Gypsum Board vs Cement Board
Gypsum board typically costs between $10 to $15 per 4x8-foot sheet, making it a more economical choice for interior walls and ceilings compared to cement board, which ranges from $15 to $30 per sheet due to its durability and moisture resistance. Labor costs can also differ, with gypsum board being easier and faster to install, reducing overall project expenses. Cement board's higher upfront cost is often justified in areas exposed to moisture, such as bathrooms or exterior walls, where its long-term durability can lower maintenance and replacement costs.
Durability and Longevity
Gypsum board offers moderate durability, suitable for interior walls and ceilings but vulnerable to moisture and impact damage, which limits its lifespan in high-humidity or high-traffic areas. Cement board is highly durable, resistant to water, mold, and physical damage, making it ideal for wet environments like bathrooms and exterior applications, significantly extending the lifespan of wall and flooring systems. Comparing longevity, cement board typically outperforms gypsum board by maintaining structural integrity over decades under harsh conditions while gypsum board may require more frequent replacement or repairs.
Best Applications for Gypsum and Cement Boards
Gypsum board excels in interior wall and ceiling applications due to its lightweight nature, ease of installation, and excellent fire resistance, especially in dry environments such as residential and commercial buildings. Cement board is best suited for wet or high-moisture areas like bathrooms, kitchens, and exterior wall substrates, offering superior durability, mold resistance, and support for tile installations. Choosing gypsum board optimizes indoor air quality and finish smoothness, while cement board provides structural stability and moisture protection in demanding conditions.
Pros and Cons of Gypsum Board vs Cement Board
Gypsum board offers superior fire resistance, ease of installation, and a smoother finish, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings in dry environments, but it is less durable and moisture-resistant compared to cement board. Cement board provides excellent water resistance and structural strength, suitable for wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens, but it is heavier, more difficult to cut, and typically requires additional finishing work. Choosing between gypsum board and cement board depends on the specific application, with gypsum board favored for aesthetic and fire-rated needs and cement board preferred for moisture-prone and high-impact areas.
Gypsum Board vs Cement Board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com