Gypsum powder offers superior workability and faster setting times compared to lime powder, making it ideal for plastering and finishing applications. Unlike lime powder, gypsum provides better moisture resistance and reduces cracking in construction materials. Its chemical composition also enhances the strength and smoothness of surfaces, outperforming lime in most building projects.
Table of Comparison
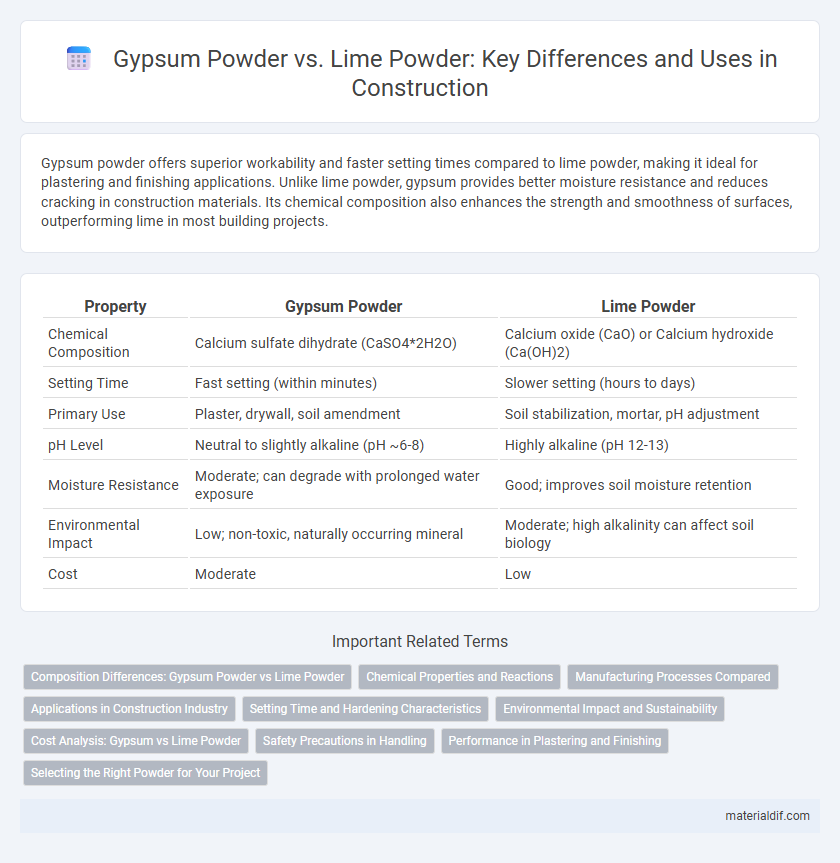
| Property | Gypsum Powder | Lime Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O) | Calcium oxide (CaO) or Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) |
| Setting Time | Fast setting (within minutes) | Slower setting (hours to days) |
| Primary Use | Plaster, drywall, soil amendment | Soil stabilization, mortar, pH adjustment |
| pH Level | Neutral to slightly alkaline (pH ~6-8) | Highly alkaline (pH 12-13) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate; can degrade with prolonged water exposure | Good; improves soil moisture retention |
| Environmental Impact | Low; non-toxic, naturally occurring mineral | Moderate; high alkalinity can affect soil biology |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Composition Differences: Gypsum Powder vs Lime Powder
Gypsum powder primarily consists of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O), which offers moderate solubility and a neutral pH, making it ideal for soil amendment and construction. Lime powder is composed mainly of calcium oxide (CaO) or calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), known for its high alkalinity and strong reactivity with acidic soils. The distinct chemical compositions of gypsum and lime powders result in differing effects on soil pH, nutrient availability, and structural properties in building materials.
Chemical Properties and Reactions
Gypsum powder primarily consists of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O), which releases water molecules upon heating, making it ideal for controlled setting and hardness in construction. Lime powder, composed mainly of calcium oxide (CaO), reacts exothermically with water to form calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), facilitating faster setting and increased alkalinity. The contrasting chemical behaviors influence their applications: gypsum supports moderate pH environments and slow hydration, while lime induces rapid carbonation and elevated pH levels.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Gypsum powder is produced by heating natural gypsum rock at approximately 150degC to remove water content, resulting in calcium sulfate hemihydrate, while lime powder is manufactured through calcination of limestone at higher temperatures around 900-1000degC to form calcium oxide. The gypsum process involves controlled dehydration and calcination that preserves sulfate content, whereas lime production requires more intense thermal decomposition, releasing carbon dioxide. These distinct manufacturing parameters significantly affect the physical and chemical properties, making gypsum powder suitable for plaster and drywall applications, and lime powder ideal for soil stabilization and water treatment.
Applications in Construction Industry
Gypsum powder is extensively used in the construction industry for creating smooth interior wall finishes, plasterboards, and as a component in cement to improve workability and reduce setting time. Lime powder is primarily utilized for soil stabilization, mortar preparation, and as a key ingredient in traditional plaster and whitewashing due to its high alkalinity and binding properties. The choice between gypsum powder and lime powder depends on specific construction requirements such as setting time, moisture resistance, and surface finish quality.
Setting Time and Hardening Characteristics
Gypsum powder exhibits faster setting time and more predictable hardening characteristics compared to lime powder, which typically sets slower due to its hydration process. The calcium sulfate in gypsum reacts rapidly with water, forming interlocking crystals that enhance early strength development and surface hardness. Lime powder requires carbonation over time to fully harden, resulting in prolonged curing periods and increased flexibility during initial stages.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum powder production generates lower carbon emissions compared to lime powder, as it requires less energy-intensive processing and releases fewer greenhouse gases. Lime powder manufacturing involves calcination at high temperatures, leading to significant CO2 emissions and higher environmental impact. Gypsum's ability to improve soil structure without altering pH makes it a more sustainable choice for agricultural applications, while lime's strong alkalinity can disrupt soil ecosystems and require careful management.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum vs Lime Powder
Gypsum powder generally costs more than lime powder due to its higher purity and specialized processing requirements, impacting overall project budgets in construction and agriculture. Lime powder, being more abundant and easier to produce, offers a cost-effective alternative with a lower price per ton but may require larger quantities to achieve similar results. The choice between gypsum and lime powder depends on balancing initial material costs with long-term benefits such as soil conditioning efficiency and setting time in plaster applications.
Safety Precautions in Handling
Gypsum powder requires careful handling to avoid respiratory irritation due to its fine particulate nature, so using protective masks and ensuring adequate ventilation is essential in workspaces. Lime powder, being more caustic, demands strict safety precautions such as wearing gloves, goggles, and long-sleeved clothing to prevent skin burns and eye damage during application or mixing. Both substances should be stored in dry, well-ventilated areas to maintain stability and minimize health risks for workers.
Performance in Plastering and Finishing
Gypsum powder offers superior workability and faster setting times compared to lime powder, making it ideal for smooth plastering and fine finishing. Its excellent adhesion and minimal shrinkage enhance surface durability and reduce cracking risks. Lime powder, while eco-friendly and breathable, generally requires longer curing periods and may result in a coarser finish.
Selecting the Right Powder for Your Project
Gypsum powder offers superior workability and faster setting times compared to lime powder, making it ideal for interior plastering and smooth finishes in construction projects. Lime powder provides better breathability and alkali resistance, suitable for outdoor applications and historic restoration where moisture management is crucial. Selecting between gypsum and lime powder depends on project requirements such as drying speed, surface finish, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal durability and aesthetics.
Gypsum powder vs Lime powder Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com