Gypsum sheathing offers a durable, weather-resistant exterior layer specifically designed for wall assemblies, providing superior moisture protection compared to standard exterior gypsum board. Exterior gypsum board, while primarily used for interior walls and ceilings, lacks the enhanced water-resistant properties necessary for reliable exterior applications. Choosing gypsum sheathing ensures improved structural integrity and long-term performance in building envelopes exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
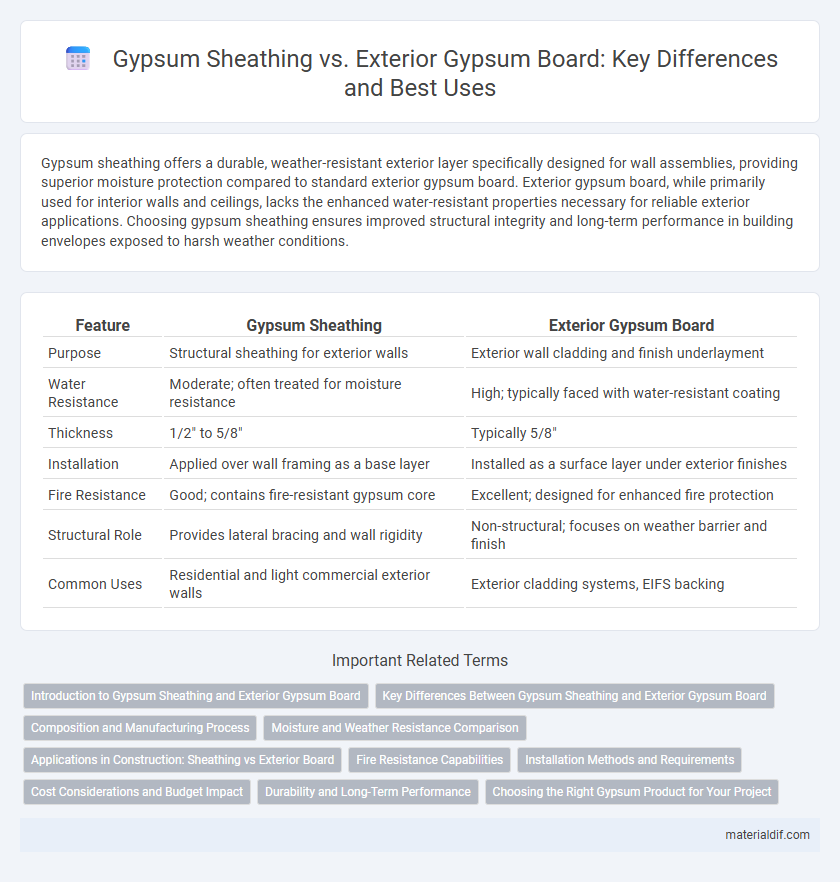
| Feature | Gypsum Sheathing | Exterior Gypsum Board |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Structural sheathing for exterior walls | Exterior wall cladding and finish underlayment |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; often treated for moisture resistance | High; typically faced with water-resistant coating |
| Thickness | 1/2" to 5/8" | Typically 5/8" |
| Installation | Applied over wall framing as a base layer | Installed as a surface layer under exterior finishes |
| Fire Resistance | Good; contains fire-resistant gypsum core | Excellent; designed for enhanced fire protection |
| Structural Role | Provides lateral bracing and wall rigidity | Non-structural; focuses on weather barrier and finish |
| Common Uses | Residential and light commercial exterior walls | Exterior cladding systems, EIFS backing |
Introduction to Gypsum Sheathing and Exterior Gypsum Board
Gypsum sheathing is a moisture-resistant, non-structural building panel used on exterior walls to provide a durable substrate for siding materials and enhance fire resistance. Exterior gypsum board, often integrated with fiberglass mats, serves as a weather-resistant barrier that improves the wall's thermal and moisture control properties. Both products are essential in modern construction for improving building envelope performance, with gypsum sheathing focusing on structural backing and exterior gypsum board emphasizing enhanced durability and weather protection.
Key Differences Between Gypsum Sheathing and Exterior Gypsum Board
Gypsum sheathing is a rigid panel used primarily as an exterior wall covering that provides structural support and moisture resistance, commonly installed beneath siding materials. Exterior gypsum board, while also designed for outdoor applications, typically offers enhanced water-resistant properties and fire protection, often utilized in multi-layer wall assemblies to improve building envelope performance. The key differences lie in their core formulations, with gypsum sheathing focusing on structural durability, whereas exterior gypsum board emphasizes weather resistance and fire safety.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gypsum sheathing and exterior gypsum board both consist primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, but their manufacturing processes and compositions differ significantly to meet distinct performance requirements. Gypsum sheathing incorporates fiberglass mat facings bonded to a core of gypsum plaster, enhancing moisture resistance and structural integrity for exterior wall applications. Exterior gypsum board typically features a water-resistant core treated with additives and a fiberglass mat to provide durability against weather exposure while maintaining fire resistance and ease of installation.
Moisture and Weather Resistance Comparison
Gypsum sheathing offers superior moisture resistance compared to traditional exterior gypsum board due to its enhanced water-repellent properties and specialized coatings designed for exterior use. Exterior gypsum board, while providing fire resistance and rigidity, tends to absorb moisture more readily, making it less suitable for prolonged exposure to weather conditions without additional protective barriers. The increased durability and weather resistance of gypsum sheathing reduce the risk of mold growth and structural damage in exterior applications.
Applications in Construction: Sheathing vs Exterior Board
Gypsum sheathing is primarily used as an exterior wall underlayment to provide a moisture-resistant barrier and structural support in wood and steel frame construction, enhancing wall durability and fire resistance. Exterior gypsum board, often treated with water-resistant additives, serves as an exterior cladding substrate that offers improved weather protection and contributes to the building envelope's thermal performance. Both materials facilitate air barrier systems but differ in their application scope, with sheathing focused on structural integrity and exterior boards emphasizing weather resistance and finishing compatibility.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum sheathing and exterior gypsum board both provide fire resistance, but gypsum sheathing typically offers enhanced protection due to its thicker composition and additives designed to improve fire retardancy. Exterior gypsum board, while also fire-resistant, is often used as a substrate for exterior cladding systems and may have additional water-resistant properties to withstand outdoor exposure. Fire resistance ratings for gypsum sheathing commonly achieve one to two hours of fire protection, making it suitable for structural applications requiring higher safety standards.
Installation Methods and Requirements
Gypsum sheathing requires fastening directly to exterior framing with corrosion-resistant fasteners, typically spaced at 6 to 12 inches, while exterior gypsum board installation demands precise joint treatment using fiberglass mesh tape and water-resistant compounds to enhance durability and moisture resistance. Both materials necessitate proper weather barriers and flashing integration to prevent moisture infiltration, but exterior gypsum board often requires additional layering or coatings for exterior exposure. Installation also involves strict adherence to manufacturer guidelines and local building codes to ensure fire resistance and structural integrity.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Gypsum sheathing typically offers a more cost-effective option compared to exterior gypsum board due to its thinner profile and simpler installation requirements, resulting in lower material and labor costs. Exterior gypsum board, while often more expensive upfront, provides enhanced moisture resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses and improving overall building performance. Budget impact analysis should weigh initial expenditures against lifecycle costs, considering project-specific factors such as climate conditions and structural requirements.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Gypsum sheathing offers enhanced moisture resistance and structural rigidity compared to exterior gypsum board, making it more durable for exterior wall applications. Its water-resistant core and fiberglass mat facings improve long-term performance by minimizing mold growth and deterioration under fluctuating weather conditions. Exterior gypsum board, while effective as an interior substrate, lacks these protective features, resulting in reduced durability when exposed to prolonged moisture.
Choosing the Right Gypsum Product for Your Project
Gypsum sheathing offers enhanced moisture resistance and structural durability, making it ideal for exterior wall assemblies exposed to harsh weather conditions. Exterior gypsum board provides fire-resistant properties and contributes to thermal insulation, suitable for various exterior cladding systems. Selecting the right gypsum product depends on project-specific requirements such as environmental exposure, fire codes, and installation method to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Gypsum Sheathing vs Exterior Gypsum Board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com