Gypsum fiber boards offer superior strength and enhanced impact resistance compared to paper-faced gypsum, making them ideal for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas. The fibrous composition improves durability and fire resistance, while paper-faced gypsum primarily relies on a paper layer that can weaken when exposed to moisture. Choosing gypsum fiber over paper-faced gypsum ensures longer-lasting performance and greater structural integrity in demanding building applications.
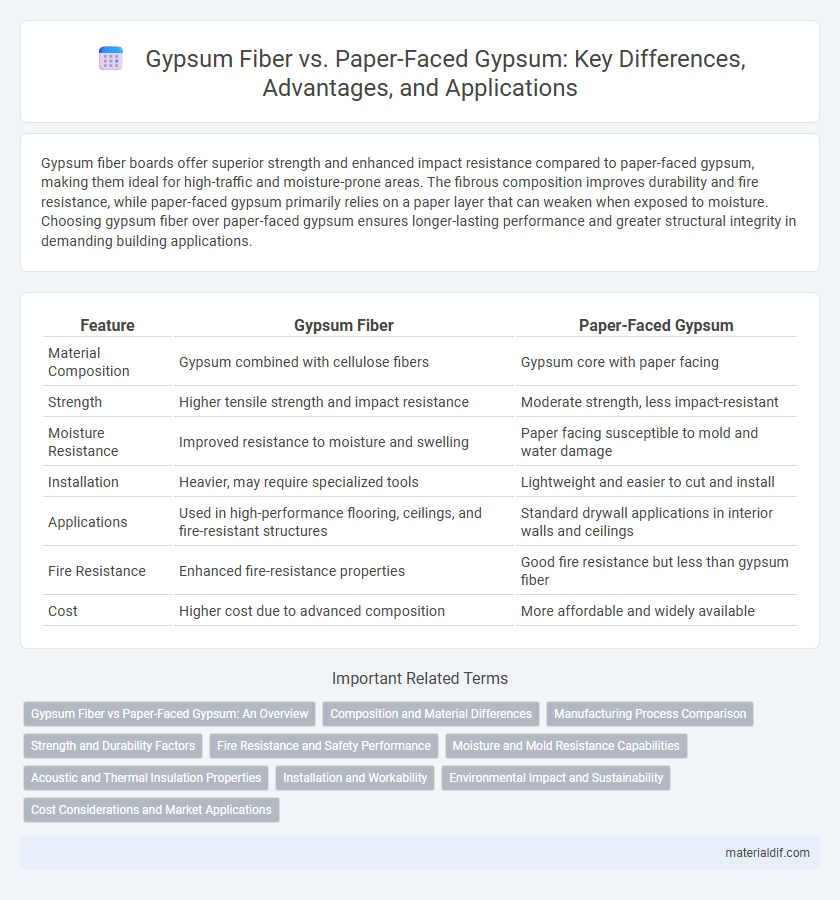
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Fiber | Paper-Faced Gypsum |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Gypsum combined with cellulose fibers | Gypsum core with paper facing |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate strength, less impact-resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | Improved resistance to moisture and swelling | Paper facing susceptible to mold and water damage |
| Installation | Heavier, may require specialized tools | Lightweight and easier to cut and install |
| Applications | Used in high-performance flooring, ceilings, and fire-resistant structures | Standard drywall applications in interior walls and ceilings |
| Fire Resistance | Enhanced fire-resistance properties | Good fire resistance but less than gypsum fiber |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced composition | More affordable and widely available |
Gypsum Fiber vs Paper-Faced Gypsum: An Overview
Gypsum fiber boards are composed of gypsum mixed with cellulose fibers, offering enhanced impact resistance, moisture durability, and improved fire performance compared to traditional paper-faced gypsum boards. Paper-faced gypsum consists of a gypsum core with a paper covering, which provides smooth surfaces but is more susceptible to water damage and less durable under heavy impact. The fiber reinforcement in gypsum fiber boards makes them suitable for demanding applications like commercial interiors and wet areas where strength and moisture resistance are critical.
Composition and Material Differences
Gypsum fiber boards consist of gypsum combined with cellulose fibers, providing enhanced strength and impact resistance, whereas paper-faced gypsum boards have a gypsum core covered with paper on both sides for surface finish and additional protection. The cellulose fibers in gypsum fiber boards improve durability and moisture resistance compared to the typically less robust paper facing, which can be susceptible to water damage. These material differences make gypsum fiber boards suitable for applications requiring higher structural integrity and moisture resilience, unlike standard paper-faced gypsum which is commonly used for interior wall and ceiling surfaces.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Gypsum fiber boards are manufactured by mixing finely ground gypsum with cellulose fibers, enhancing durability and moisture resistance through a wet-pressing process. Paper-faced gypsum boards consist of a gypsum core encased in specially treated paper sheets, produced by a continuous layering and drying method that ensures smooth surface finishing. The manufacturing of gypsum fiber involves integrating reinforcing fibers directly into the gypsum matrix, resulting in a composite material with improved mechanical performance compared to the layered structure of paper-faced gypsum.
Strength and Durability Factors
Gypsum fiber boards exhibit superior strength and durability compared to paper-faced gypsum due to their composite composition that includes cellulose fibers, enhancing impact resistance and load-bearing capacity. The fiber reinforcement in gypsum fiber boards improves moisture resistance and reduces susceptibility to surface damage, making them ideal for high-traffic and wet environments. In contrast, paper-faced gypsum relies on paper layers that are more prone to tearing and water absorption, limiting its long-term durability and structural performance.
Fire Resistance and Safety Performance
Gypsum fiber boards offer superior fire resistance compared to paper-faced gypsum due to their dense composition and non-combustible fibers that enhance structural integrity under high temperatures. Fire testing standards such as ASTM E84 demonstrate that gypsum fiber panels achieve lower flame spread and smoke development ratings, improving overall safety performance in building applications. Paper-faced gypsum, while providing easier finishing and installation, is more susceptible to burning and contributes to higher smoke toxicity, making gypsum fiber a preferred choice for fire-rated assemblies.
Moisture and Mold Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum fiber boards exhibit superior moisture and mold resistance compared to paper-faced gypsum due to their synthetic fiber reinforcement and non-organic surface, which limits water absorption and inhibits mold growth. Paper-faced gypsum is more susceptible to moisture damage as the paper facing provides a nutrient-rich environment for mold development when exposed to humidity or water. For applications in high-moisture or mold-prone areas, gypsum fiber offers enhanced durability and longevity.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Properties
Gypsum fiber boards offer superior acoustic insulation due to their higher density and porous composition, effectively reducing sound transmission compared to paper-faced gypsum boards. Thermal insulation is also enhanced in gypsum fiber panels as they provide better resistance to heat flow, contributing to improved energy efficiency in buildings. The enhanced mechanical strength of gypsum fiber supports durability while maintaining insulation properties superior to traditional paper-faced gypsum.
Installation and Workability
Gypsum fiber boards offer superior installation ease due to enhanced rigidity and resistance to sagging, allowing for quicker handling and fastening on walls and ceilings. Paper-faced gypsum boards, while lighter and easier to cut, may require more careful handling to prevent tearing of the paper surface during installation. The higher density and fibrous composition of gypsum fiber panels improve screw holding capacity and reduce joint cracking, contributing to overall improved workability on construction sites.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum fiber boards are manufactured using recycled gypsum and cellulose fibers, significantly reducing construction waste compared to traditional paper-faced gypsum boards. The paper-facing in conventional gypsum boards often involves coated paper, which is less biodegradable and contributes to landfill pollution, whereas gypsum fiber materials promote better recyclability and lower environmental toxicity. The enhanced durability and moisture resistance of gypsum fiber also extend product lifespan, minimizing resource consumption and supporting sustainable building practices.
Cost Considerations and Market Applications
Gypsum fiber boards generally incur higher initial costs than paper-faced gypsum due to their enhanced durability and fire resistance, justifying investment in commercial and industrial construction projects. Paper-faced gypsum remains the preferred choice in residential applications and interior partitions due to its lower price and ease of installation. Market demand favors gypsum fiber in high-traffic public spaces and moisture-prone environments, while paper-faced gypsum dominates standard wallboard applications for budget-sensitive projects.
Gypsum fiber vs Paper-faced gypsum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com