Gypsum sheathing offers excellent fire resistance and moisture durability, making it ideal for interior walls and exterior applications where water exposure is limited. Fiber cement sheathing provides superior strength and impact resistance, excelling in environments prone to harsh weather and physical damage. Both materials contribute to structural integrity, but fiber cement sheathing is preferred for exterior walls due to its enhanced weatherproofing and longevity.
Table of Comparison
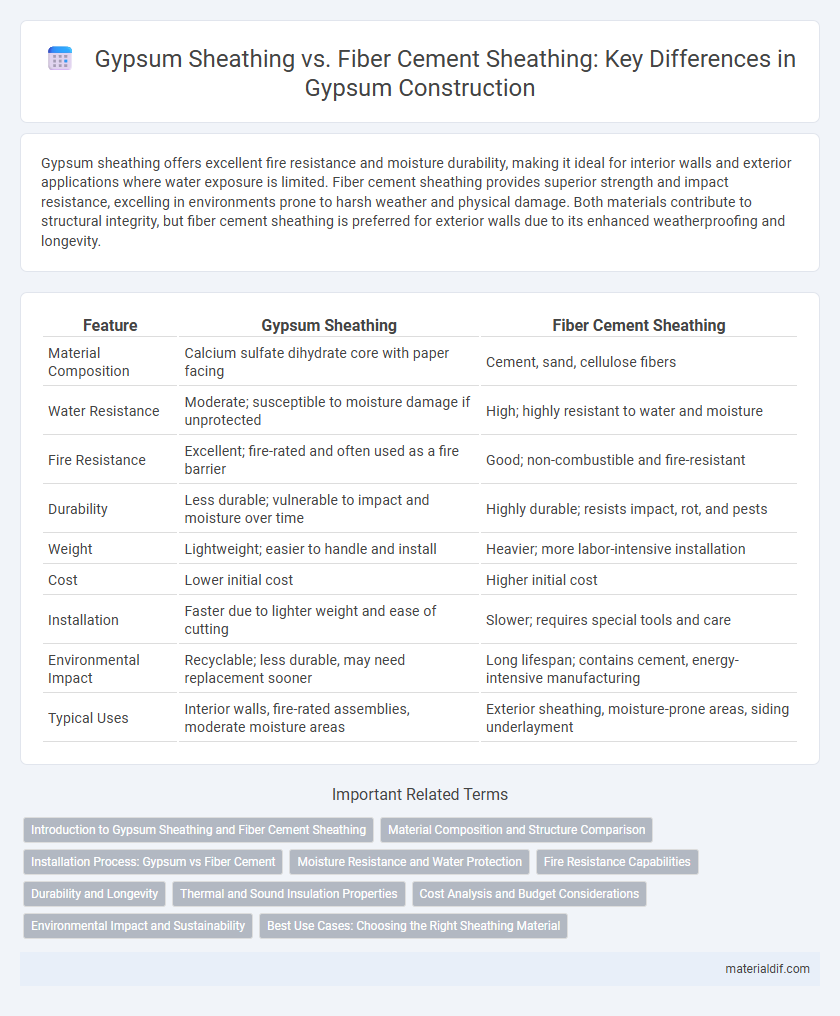
| Feature | Gypsum Sheathing | Fiber Cement Sheathing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate core with paper facing | Cement, sand, cellulose fibers |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; susceptible to moisture damage if unprotected | High; highly resistant to water and moisture |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent; fire-rated and often used as a fire barrier | Good; non-combustible and fire-resistant |
| Durability | Less durable; vulnerable to impact and moisture over time | Highly durable; resists impact, rot, and pests |
| Weight | Lightweight; easier to handle and install | Heavier; more labor-intensive installation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Installation | Faster due to lighter weight and ease of cutting | Slower; requires special tools and care |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable; less durable, may need replacement sooner | Long lifespan; contains cement, energy-intensive manufacturing |
| Typical Uses | Interior walls, fire-rated assemblies, moderate moisture areas | Exterior sheathing, moisture-prone areas, siding underlayment |
Introduction to Gypsum Sheathing and Fiber Cement Sheathing
Gypsum sheathing is a moisture-resistant panel made from core gypsum and protective facers, designed to improve fire resistance and provide a smooth substrate for exterior finishes. Fiber cement sheathing consists of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offering enhanced durability, resistance to rot, and high impact strength for exterior wall systems. Both materials serve as essential components in modern building envelopes, balancing structural performance and weather resistance.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Gypsum sheathing consists primarily of a core of gypsum plaster, reinforced with fiberglass mats, offering fire resistance and mold resistance due to its inorganic core. Fiber cement sheathing combines cellulose fibers with cement and silica, providing superior durability, moisture resistance, and impact strength due to its dense, cementitious matrix. The structural differences result in gypsum being lighter and easier to cut, while fiber cement sheathing delivers enhanced longevity in harsh environments.
Installation Process: Gypsum vs Fiber Cement
Gypsum sheathing offers a lightweight and easy-to-cut installation process, often requiring fewer specialized tools compared to fiber cement sheathing, which demands power tools and dust suppression measures due to its dense composition. Gypsum panels can be quickly secured with nails or screws and typically allow faster wall assembly, while fiber cement sheathing requires more labor-intensive handling and the use of corrosion-resistant fasteners. The reduced installation time of gypsum sheathing can lead to lower labor costs, whereas fiber cement provides enhanced durability and moisture resistance critical for certain building envelope applications.
Moisture Resistance and Water Protection
Gypsum sheathing offers moderate moisture resistance but can degrade when exposed to prolonged wet conditions, making it less effective for water protection compared to fiber cement sheathing. Fiber cement sheathing provides superior water resistance due to its dense, non-porous composition, preventing water infiltration and reducing the risk of mold and structural damage. In construction applications where moisture exposure is frequent or high, fiber cement sheathing is preferred for its durability and long-term protection against water intrusion.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum sheathing offers superior fire resistance due to its high moisture content and chemically bound water, which helps slow heat transfer and prevents flame spread. Fiber cement sheathing provides moderate fire resistance but lacks the inherent fire-retardant properties found in gypsum, making it less effective in extreme fire exposure. Building codes often prefer gypsum sheathing in fire-rated assemblies for enhanced safety and compliance.
Durability and Longevity
Gypsum sheathing offers moderate durability with resistance to fire and mold but may degrade when exposed to prolonged moisture. Fiber cement sheathing provides superior longevity and enhanced durability due to its robust composition, resisting moisture, impact, and pests effectively. Buildings utilizing fiber cement sheathing generally experience lower maintenance costs and enhanced structural integrity over time compared to gypsum alternatives.
Thermal and Sound Insulation Properties
Gypsum sheathing provides moderate thermal insulation with an R-value typically around 0.45 per inch, effectively reducing heat transfer in building envelopes. Fiber cement sheathing offers superior sound insulation due to its dense composition, significantly dampening airborne noise compared to gypsum. While gypsum excels in fire resistance and moisture regulation, fiber cement is more durable under harsh environmental conditions, impacting overall insulation performance.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Gypsum sheathing typically offers a lower initial cost compared to fiber cement sheathing, making it a budget-friendly option for projects with tight financial constraints. However, fiber cement sheathing provides greater durability and resistance to moisture and fire, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Careful evaluation of upfront savings against lifecycle costs is essential for accurate budget planning in construction applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum sheathing is composed primarily of naturally occurring calcium sulfate, offering recyclability and lower embodied energy compared to fiber cement sheathing, which contains cement and cellulose fibers with higher CO2 emissions during production. Fiber cement sheathing provides superior durability and moisture resistance but involves energy-intensive manufacturing and the extraction of raw materials that contribute to environmental degradation. Choosing gypsum sheathing supports sustainability goals by minimizing carbon footprint and promoting safer disposal practices, while fiber cement excels in long-term performance but with greater environmental costs.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Sheathing Material
Gypsum sheathing is best suited for interior walls and ceilings due to its fire-resistant properties and ease of installation, offering excellent moisture resistance when treated. Fiber cement sheathing excels in exterior applications where durability against weather, impact resistance, and mold prevention are critical, making it ideal for high-humidity or coastal environments. Selecting the right sheathing material depends on balancing factors like fire rating, moisture exposure, structural support, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Gypsum sheathing vs Fiber cement sheathing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com