Gypsum drywall offers faster installation and smoother surfaces compared to traditional lath and plaster, significantly reducing labor costs and construction time. It provides superior fire resistance and moisture control, enhancing durability in modern buildings. Unlike lath and plaster, drywall is easier to repair and modify, making it a practical choice for contemporary interior walls.
Table of Comparison
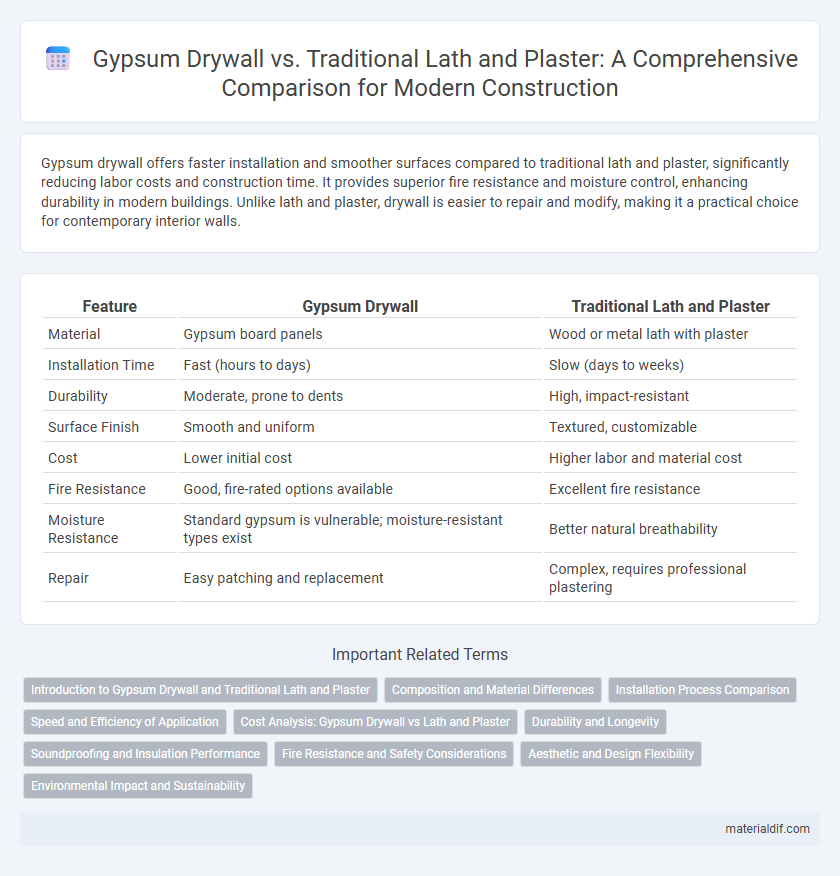
| Feature | Gypsum Drywall | Traditional Lath and Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Gypsum board panels | Wood or metal lath with plaster |
| Installation Time | Fast (hours to days) | Slow (days to weeks) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | High, impact-resistant |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and uniform | Textured, customizable |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher labor and material cost |
| Fire Resistance | Good, fire-rated options available | Excellent fire resistance |
| Moisture Resistance | Standard gypsum is vulnerable; moisture-resistant types exist | Better natural breathability |
| Repair | Easy patching and replacement | Complex, requires professional plastering |
Introduction to Gypsum Drywall and Traditional Lath and Plaster
Gypsum drywall consists of gypsum plaster pressed between two thick sheets of paper, providing a faster and cleaner installation compared to traditional lath and plaster, which involves applying multiple layers of wet plaster over wooden or metal laths. Drywall offers better moisture resistance, uniform surface finish, and simplified repair processes, while lath and plaster is valued for its superior soundproofing and durability in historic or high-end construction. The shift from lath and plaster to gypsum drywall began in the mid-20th century, driven by gypsum drywall's cost efficiency and ease of use.
Composition and Material Differences
Gypsum drywall consists primarily of a core of gypsum plaster sandwiched between paper facings, providing a lightweight and uniform surface. Traditional lath and plaster relies on wooden or metal laths covered with multiple layers of plaster, which often include lime, sand, and cement for strength. The key material difference lies in gypsum drywall's pre-manufactured panels versus the on-site application and curing of wet plaster mixtures in lath and plaster systems.
Installation Process Comparison
Gypsum drywall installation significantly reduces labor time by using large, pre-manufactured sheets that can be quickly attached to framing with screws or nails, compared to traditional lath and plaster which requires multiple labor-intensive steps including mounting wooden lath, applying several coats of plaster, and lengthy drying times. Drywall taping and mudding streamline finishing, while lath and plaster demands skilled artisans to achieve smooth surfaces through successive plaster layers. The drywall process offers faster construction schedules and lower costs, while lath and plaster provide superior soundproofing and durability at the expense of longer installation periods.
Speed and Efficiency of Application
Gypsum drywall offers significantly faster installation compared to traditional lath and plaster due to its large, pre-manufactured panels that cover more surface area quickly. The ready-to-finish surface of drywall reduces the need for multiple labor-intensive steps like wet plaster application and drying time associated with lath and plaster. This efficiency in application makes gypsum drywall the preferred choice for modern construction projects aiming to reduce labor costs and accelerate timelines.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Drywall vs Lath and Plaster
Gypsum drywall offers a significantly lower installation cost compared to traditional lath and plaster due to faster application times and reduced labor requirements. Material expenses for gypsum drywall are generally less, with sheets being mass-produced and widely available, while lath and plaster demand skilled artisans and more intensive labor. Repair and maintenance costs also favor gypsum drywall, which can be easily patched, whereas plaster often requires professional refinishing that increases long-term expenses.
Durability and Longevity
Gypsum drywall offers enhanced durability compared to traditional lath and plaster due to its resistance to cracking and shrinkage, ensuring a longer lifespan in residential and commercial construction. Traditional lath and plaster is more labor-intensive to install and prone to damage from moisture, making gypsum drywall a superior choice for environments requiring greater longevity. Modern gypsum drywall also incorporates mold and fire-resistant additives, contributing to sustained structural integrity over time.
Soundproofing and Insulation Performance
Gypsum drywall offers superior soundproofing and insulation performance compared to traditional lath and plaster due to its dense gypsum core and the ability to incorporate sound-dampening materials like resilient channels and insulation batts. The uniform surface and tighter seams of drywall reduce sound transmission and thermal bridging, enhancing both acoustic and thermal insulation efficiency. Traditional lath and plaster, while durable, typically allows more sound and heat transfer because of its heterogeneous structure and lack of integrated insulation.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Gypsum drywall offers superior fire resistance compared to traditional lath and plaster due to its chemically bound water content, which slows heat transfer and reduces fire spread. This inherent fire-resistant property makes gypsum drywall a preferred choice in building safety codes and enhances occupant protection during fires. Traditional lath and plaster, while durable, lacks the same fire retardant benefits and may require additional treatments to meet modern safety standards.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Gypsum drywall offers smoother surfaces and consistent texture compared to traditional lath and plaster, enabling modern design trends such as seamless walls and intricate patterns. Its plasticity allows for easier installation of curved walls, niches, and integrated lighting features, enhancing aesthetic versatility in interior spaces. Unlike the labor-intensive plastering process, gypsum drywall supports quicker modifications and diverse finishes, catering to dynamic design requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum drywall generates less construction waste and requires less water and energy in production compared to traditional lath and plaster, reducing its environmental footprint. The drywall's ability to be recycled and its use of natural gypsum, a plentiful mineral, enhance its sustainability credentials. In contrast, traditional lath and plaster involve more labor-intensive processes and materials like wood lath, which can contribute to resource depletion and higher emissions.
Gypsum drywall vs Traditional lath and plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com