Gypsum sand offers superior moisture retention and nutrient release compared to silica sand, making it ideal for agricultural and horticultural applications. Silica sand excels in durability and drainage, preferred for construction and industrial uses where stability and abrasiveness are required. Selecting between gypsum sand and silica sand depends on the specific needs of soil amendment or structural support.
Table of Comparison
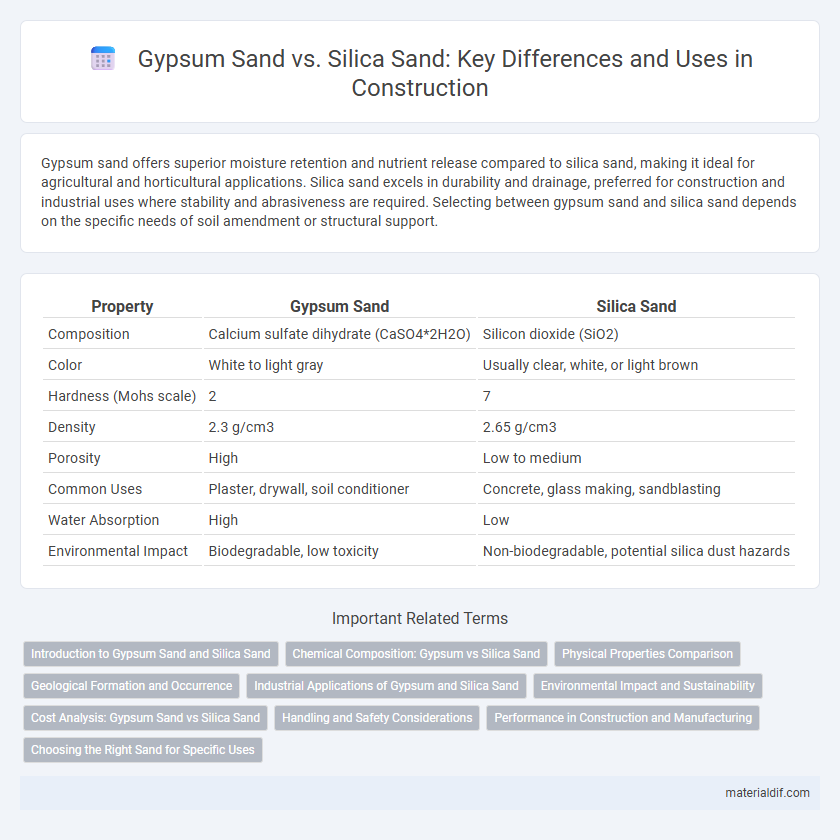
| Property | Gypsum Sand | Silica Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O) | Silicon dioxide (SiO2) |
| Color | White to light gray | Usually clear, white, or light brown |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 2 | 7 |
| Density | 2.3 g/cm3 | 2.65 g/cm3 |
| Porosity | High | Low to medium |
| Common Uses | Plaster, drywall, soil conditioner | Concrete, glass making, sandblasting |
| Water Absorption | High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity | Non-biodegradable, potential silica dust hazards |
Introduction to Gypsum Sand and Silica Sand
Gypsum sand, composed primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, is prized for its high solubility and use in soil conditioning and construction materials. Silica sand, rich in silicon dioxide (SiO2), is valued for its hardness and chemical stability, making it essential in glass manufacturing, filtration, and foundry applications. Both sands exhibit distinct mineralogical properties influencing their specific industrial roles and performance.
Chemical Composition: Gypsum vs Silica Sand
Gypsum primarily consists of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O), offering high solubility and beneficial properties for soil conditioning and construction applications. Silica sand is predominantly composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), providing exceptional hardness and chemical inertness crucial for industrial uses like glassmaking and foundry molds. The distinct chemical compositions significantly influence their physical characteristics and suitability across various sectors.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gypsum sand exhibits a softer texture with a Mohs hardness of 2, compared to silica sand's hardness of 7, making it easier to crush and reshape. The specific gravity of gypsum sand ranges from 2.3 to 2.4, lower than silica sand's typical specific gravity of 2.65, which affects sediment settling rates and compaction. Additionally, gypsum sand's higher porosity enhances water retention, whereas silica sand's lower porosity and angular grain shape provide better drainage and structural stability.
Geological Formation and Occurrence
Gypsum sand primarily forms through the evaporation of sulfate-rich waters in sedimentary basins, resulting in extensive beds of evaporite minerals often found in arid regions. In contrast, silica sand originates from the mechanical weathering and erosion of quartz-rich igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, accumulating in fluvial, beach, and dune environments. Gypsum sand occurs in evaporitic basins such as those in the Great Salt Lake Desert, while silica sand is abundant globally in riverbeds, beaches, and deserts due to its resistance to weathering.
Industrial Applications of Gypsum and Silica Sand
Gypsum sand is primarily used in the construction industry for wallboard manufacture, cement production, and soil conditioning due to its calcium sulfate content which improves material workability and strength. Silica sand, composed mainly of silicon dioxide, is essential in glassmaking, foundry molds, and hydraulic fracturing because of its high melting point and mechanical durability. Industrial applications leverage gypsum sand's chemical properties for moisture control and sulfate addition, while silica sand is prized for its abrasion resistance and thermal stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum sand offers a lower environmental impact compared to silica sand due to its natural abundance and lower energy requirements for extraction and processing. Unlike silica sand, which often involves habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions during mining and transportation, gypsum sand can be sustainably sourced as a byproduct of industrial processes such as flue gas desulfurization. Utilizing gypsum sand promotes circular economy principles by repurposing waste material, reducing landfill pressure, and minimizing resource depletion.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Sand vs Silica Sand
Gypsum sand generally offers a lower cost per ton compared to silica sand, making it a more economical choice for large-scale applications. The extraction and processing of gypsum sand require less energy, reducing overall production expenses and transportation costs due to its lighter weight and bulk density. Silica sand, while more expensive, provides superior hardness and durability essential for specific industrial uses, justifying the higher price in performance-critical projects.
Handling and Safety Considerations
Gypsum sand offers lower dust generation compared to silica sand, reducing respiratory risks during handling and minimizing the need for extensive protective equipment. Silica sand, containing crystalline silica, poses significant inhalation hazards that require stringent safety protocols, including respirators and dust control measures to prevent silicosis. Proper ventilation and protective gear are essential for silica sand, while gypsum sand allows for safer, less restrictive handling conditions in construction and industrial applications.
Performance in Construction and Manufacturing
Gypsum sand offers superior sulfate resistance and moisture regulation in construction materials, enhancing durability in plaster, drywall, and cement applications compared to silica sand. Silica sand, known for its high silica content and hardness, provides excellent strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for concrete, glass manufacturing, and foundry molds. The choice between gypsum sand and silica sand depends on specific performance requirements such as fire resistance, workability, and chemical properties in construction and manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right Sand for Specific Uses
Gypsum sand provides excellent moisture retention and nutrient release, making it ideal for agricultural applications and soil conditioning, while silica sand offers superior abrasion resistance and thermal stability, suited for industrial uses such as glass manufacturing and filtration systems. The choice between gypsum and silica sand depends on desired properties like solubility, particle size, and chemical composition, affecting performance in construction, landscaping, or water treatment. Understanding the specific requirements of each project ensures optimal results by selecting the sand type with the appropriate mineral content and granulometry.
Gypsum sand vs Silica sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com