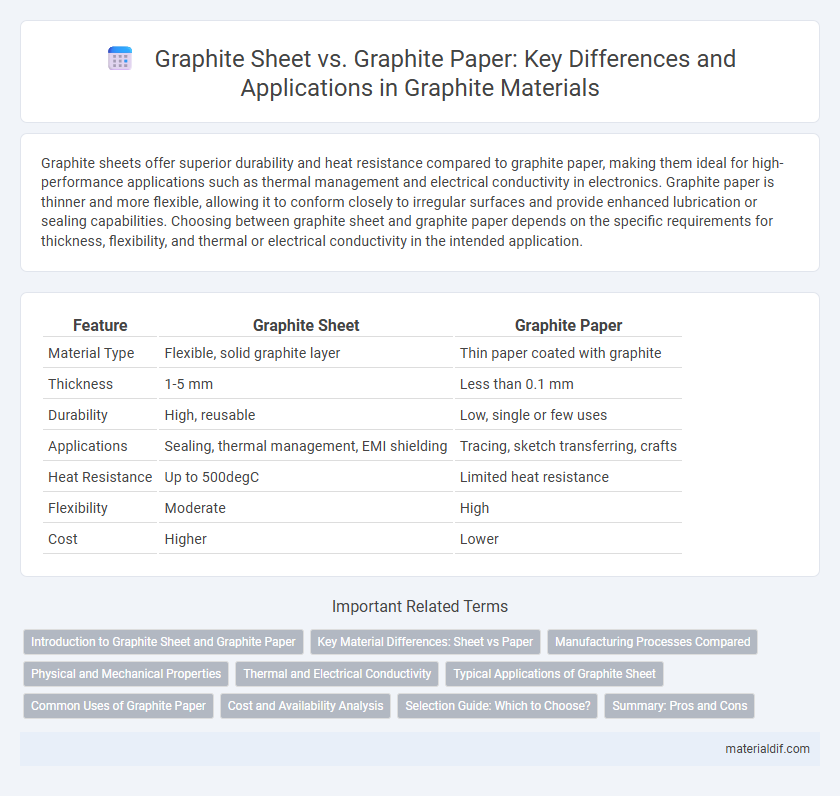
Graphite sheets offer superior durability and heat resistance compared to graphite paper, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as thermal management and electrical conductivity in electronics. Graphite paper is thinner and more flexible, allowing it to conform closely to irregular surfaces and provide enhanced lubrication or sealing capabilities. Choosing between graphite sheet and graphite paper depends on the specific requirements for thickness, flexibility, and thermal or electrical conductivity in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Sheet | Graphite Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Flexible, solid graphite layer | Thin paper coated with graphite |
| Thickness | 1-5 mm | Less than 0.1 mm |
| Durability | High, reusable | Low, single or few uses |
| Applications | Sealing, thermal management, EMI shielding | Tracing, sketch transferring, crafts |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 500degC | Limited heat resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Graphite Sheet and Graphite Paper
Graphite sheets are thin, flexible layers composed of pure graphite, known for their excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-temperature sealing and heat dissipation applications. Graphite paper, on the other hand, consists of a softer, fibrous material impregnated with graphite, primarily used as a lubricant or writing medium due to its unique ability to transfer graphite marks onto surfaces. Both graphite sheets and graphite paper leverage the intrinsic properties of graphite but serve distinct industrial and artistic purposes based on their structural differences.
Key Material Differences: Sheet vs Paper
Graphite sheets are composed of compressed graphite flakes that provide high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them ideal for heat dissipation and EMI shielding applications. Graphite paper, on the other hand, is a thin, flexible material made by depositing graphite particles onto a substrate, offering excellent electrical conductivity and conformability for use in battery electrodes and sensors. The primary material difference lies in the structure and density, with sheets being thicker and more robust while papers are thinner and more flexible.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Graphite sheets are manufactured through a complex process involving the compression and baking of exfoliated graphite flakes into dense, uniform sheets, ensuring high thermal conductivity and durability. In contrast, graphite paper is produced by coating a thin substrate with a layer of fine graphite particles, resulting in a flexible, lightweight material suitable for lubrication and electrical applications. The manufacturing process of graphite sheets emphasizes structural integrity and thickness control, while graphite paper focuses on surface smoothness and particle distribution.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Graphite sheets exhibit higher tensile strength and better flexibility compared to graphite paper, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and mechanical resilience. Graphite paper offers superior electrical conductivity and conformability, useful in precision coating and battery electrode manufacturing. Both materials share excellent thermal stability and lubricity, but sheets typically provide enhanced structural integrity.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Graphite sheets provide superior thermal conductivity, typically around 150-200 W/mK, making them ideal for efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices. In contrast, graphite paper offers moderate thermal conductivity but excels in electrical conductivity due to its thin, flexible structure that allows for uniform current distribution. Both materials leverage graphite's intrinsic conductivity properties, but sheets are preferred in applications demanding robust thermal management, while paper is suited for electrical contacts and flexible circuit designs.
Typical Applications of Graphite Sheet
Graphite sheets are commonly used in thermal management applications such as heat spreaders and thermal interface materials in electronics due to their excellent thermal conductivity and flexibility. They also serve as EMI (electromagnetic interference) shielding and gasketing materials in automotive and aerospace industries. Unlike graphite paper, which is mainly used for drafting or artistic purposes, graphite sheets provide structural stability and durability in industrial settings.
Common Uses of Graphite Paper
Graphite paper is commonly used for transferring detailed designs or sketches onto various surfaces, making it essential in art, drafting, and technical drawing. Its thin, flexible nature allows for precise replication of images on wood, fabric, or metal, supporting artisans, architects, and engineers. Unlike graphite sheets, which primarily serve as thermal management solutions, graphite paper excels in creative and technical tracing applications due to its superior transfer capabilities.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Graphite sheets typically cost more due to their thicker, durable structure but offer longer lifespan and better thermal conductivity compared to graphite paper. Graphite paper is more widely available and cheaper, making it ideal for short-term or disposable applications despite its lower durability. Availability for both materials can vary by region, with graphite paper commonly found in art supply and industrial stores, while graphite sheets are often sourced from specialized suppliers.
Selection Guide: Which to Choose?
Graphite sheets offer superior durability and heat resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring high-temperature insulation and thermal management. Graphite paper provides greater flexibility and is better suited for electronic shielding and precision stamping due to its thin, lightweight properties. Select graphite sheets for mechanical strength and long-term use, while graphite paper is preferable when flexibility and fine detail are essential.
Summary: Pros and Cons
Graphite sheets offer superior heat resistance, durability, and thermal conductivity compared to graphite paper, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring repeated use and stability under high temperatures. Graphite paper is thinner, more flexible, and cost-effective, suitable for single-use tasks like sketching or transferring designs but less durable and prone to tearing. Choosing between graphite sheets and paper depends on the need for longevity and heat tolerance versus affordability and disposability.
Graphite Sheet vs Graphite Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com