Graphite coating provides a thin, protective layer that enhances the durability and scratches resistance of a surface without altering its structural integrity. Graphite laminate, however, involves bonding multiple layers of graphite material to create a thicker, more robust composite with improved strength and thermal conductivity. Choosing between graphite coating and laminate depends on the specific application requirements, such as wear resistance versus mechanical reinforcement.
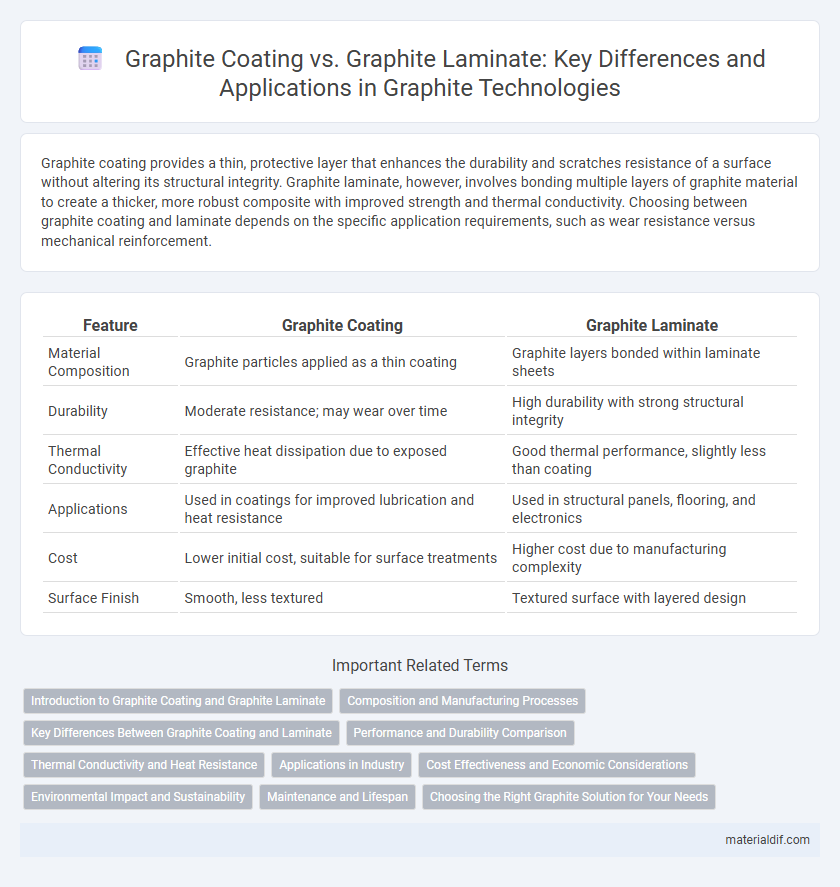
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Coating | Graphite Laminate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Graphite particles applied as a thin coating | Graphite layers bonded within laminate sheets |
| Durability | Moderate resistance; may wear over time | High durability with strong structural integrity |
| Thermal Conductivity | Effective heat dissipation due to exposed graphite | Good thermal performance, slightly less than coating |
| Applications | Used in coatings for improved lubrication and heat resistance | Used in structural panels, flooring, and electronics |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, suitable for surface treatments | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, less textured | Textured surface with layered design |
Introduction to Graphite Coating and Graphite Laminate
Graphite coating involves applying a thin layer of graphite to surfaces to enhance lubrication, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity, commonly used in industrial machinery and electronics. Graphite laminate consists of multiple layers of graphite sheets bonded together to create a solid composite material with high strength, thermal stability, and electrical properties, ideal for structural and electronic applications. Both materials leverage the unique characteristics of graphite, but coatings offer surface-level benefits while laminates provide bulk material advantages.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Graphite coating consists of a thin layer of graphite applied through processes such as vapor deposition or spraying, enhancing surface conductivity and lubrication properties. Graphite laminate involves layering graphite sheets bonded with resin, created through pressing and curing under heat, resulting in a thicker, structurally integrated material with higher mechanical strength. The coating focuses on surface modification, while laminates provide bulk material properties tailored for specific industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Graphite Coating and Laminate
Graphite coating involves applying a thin layer of graphite directly onto a surface to enhance lubricity and corrosion resistance, whereas graphite laminate consists of multiple layers of material bonded together with graphite to provide structural strength and thermal stability. The coating is typically used for improving surface properties without altering the substrate's bulk characteristics, while laminates are engineered composites designed for high mechanical performance in demanding applications. Graphite laminates offer better durability and heat resistance compared to coatings, which mainly serve as surface treatments.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Graphite coating enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance, improving overall durability in harsh environments, while graphite laminate offers superior structural integrity and impact resistance due to its layered composition. Performance-wise, graphite coating provides a smoother, low-friction surface ideal for reducing wear in mechanical applications, whereas graphite laminate excels in load-bearing capacities and stiffness, making it suitable for high-stress components. Both materials contribute to extending product lifespan, but graphite laminate generally outperforms coating in durability under repeated mechanical stress.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Resistance
Graphite coating offers superior thermal conductivity compared to graphite laminate, enabling faster heat dissipation in high-temperature applications. Heat resistance is enhanced in graphite coating due to its uniform layer, which provides consistent protection against thermal degradation. In contrast, graphite laminate's layered structure may introduce thermal barriers, resulting in lower overall heat resistance and conductivity.
Applications in Industry
Graphite coating offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and electronic industries requiring lightweight and durable materials. Graphite laminate provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, commonly used in industrial machinery, sports equipment, and high-performance composites. Both materials serve critical roles in manufacturing processes where heat dissipation and structural integrity are essential.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Graphite coating offers a cost-effective solution by providing durable protection and enhanced corrosion resistance at a lower initial expense compared to graphite laminate. Graphite laminate involves higher production costs due to complex manufacturing processes and thicker material usage, impacting overall budget allocations. For economic considerations, graphite coating is preferable in large-scale applications where reducing maintenance and replacement costs is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphite coatings typically have a lower environmental impact than graphite laminates due to their reduced material usage and simpler manufacturing process, which minimizes energy consumption and waste generation. Graphite laminates often involve combining graphite with polymers or resins that may contain non-recyclable or hazardous components, posing challenges for sustainability and end-of-life disposal. The choice between coating and laminate should prioritize lifecycle assessments highlighting carbon footprint, recyclability, and the potential for material recovery to achieve more sustainable graphite-based applications.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Graphite coatings offer enhanced durability with easy maintenance, as their protective layer resists scratches and corrosion, extending the lifespan of the underlying material. Graphite laminates, while cost-effective and aesthetically versatile, require more frequent upkeep due to their susceptibility to delamination and surface wear over time. Choosing graphite coatings is optimal for high-performance applications demanding long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
Choosing the Right Graphite Solution for Your Needs
Graphite coating offers superior surface protection and enhanced thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and efficient heat dissipation. Graphite laminate provides excellent mechanical strength and electrical insulation, suited for structural components and electronic devices. Selecting between graphite coating and laminate depends on your need for surface treatment versus bulk material properties, balancing factors like wear resistance, flexibility, and thermal management.
Graphite Coating vs Graphite Laminate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com