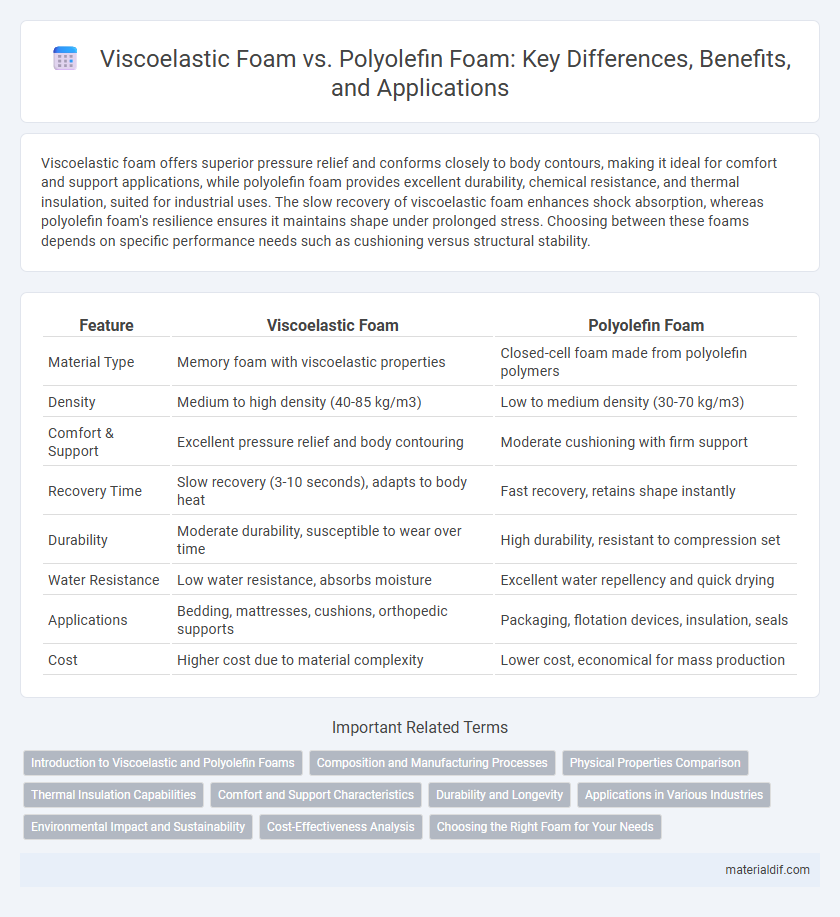
Viscoelastic foam offers superior pressure relief and conforms closely to body contours, making it ideal for comfort and support applications, while polyolefin foam provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and thermal insulation, suited for industrial uses. The slow recovery of viscoelastic foam enhances shock absorption, whereas polyolefin foam's resilience ensures it maintains shape under prolonged stress. Choosing between these foams depends on specific performance needs such as cushioning versus structural stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Viscoelastic Foam | Polyolefin Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Memory foam with viscoelastic properties | Closed-cell foam made from polyolefin polymers |
| Density | Medium to high density (40-85 kg/m3) | Low to medium density (30-70 kg/m3) |
| Comfort & Support | Excellent pressure relief and body contouring | Moderate cushioning with firm support |
| Recovery Time | Slow recovery (3-10 seconds), adapts to body heat | Fast recovery, retains shape instantly |
| Durability | Moderate durability, susceptible to wear over time | High durability, resistant to compression set |
| Water Resistance | Low water resistance, absorbs moisture | Excellent water repellency and quick drying |
| Applications | Bedding, mattresses, cushions, orthopedic supports | Packaging, flotation devices, insulation, seals |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material complexity | Lower cost, economical for mass production |
Introduction to Viscoelastic and Polyolefin Foams
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, exhibits unique pressure-sensitive properties that allow it to conform to body shape while providing superior support and comfort. Polyolefin foam, derived from polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, offers lightweight cushioning with excellent chemical resistance and durability. These distinct compositions influence their applications, with viscoelastic foam preferred in mattresses and medical devices, while polyolefin foam is widely used in packaging and insulation.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Viscoelastic foam, also known as memory foam, is primarily composed of polyurethane with added viscoelastic chemicals that enhance its slow-response and pressure-relieving properties, produced through a controlled reaction of polyols and isocyanates involving precise temperature and humidity conditions. Polyolefin foam, typically made from polyethylene or polypropylene, utilizes a polymerization process followed by physical or chemical foaming methods, resulting in a lightweight, durable material with excellent chemical resistance and cushioning qualities. The manufacturing of viscoelastic foam involves careful curing to achieve its characteristic viscoelastic behavior, while polyolefin foam production emphasizes extrusion and expansion techniques to create cellular structures with varying densities.
Physical Properties Comparison
Viscoelastic foam exhibits high density and slow recovery time, providing superior pressure distribution and comfort compared to polyolefin foam, which is lighter and more resilient with rapid return to its original shape. The viscoelastic foam's open-cell structure enhances breathability and thermal sensitivity, while polyolefin foam's closed-cell composition offers better moisture resistance and durability. Viscoelastic foam typically has higher indentation force deflection (IFD) values, indicating greater firmness and support, whereas polyolefin foam is noted for its impact absorption and chemical resistance in various applications.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Viscoelastic foam exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities due to its dense cellular structure, which traps air effectively and reduces heat transfer. Polyolefin foam, while having lower thermal resistance, provides moderate insulation combined with lightweight and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring balance between insulation and cushioning. The choice between viscoelastic and polyolefin foam depends on the specific thermal insulation requirements and environmental conditions of the intended use.
Comfort and Support Characteristics
Viscoelastic foam offers superior comfort with its slow-response, pressure-relieving properties that conform closely to the body's contours, enhancing support by evenly distributing weight. Polyolefin foam provides firmer support and faster recovery, maintaining structural integrity under prolonged use while delivering moderate comfort. The choice depends on the desired balance between cushioning softness and resilient support in applications such as mattresses and seating.
Durability and Longevity
Viscoelastic foam exhibits superior durability due to its high density and slow recovery rate, which allows it to maintain shape and support over extended periods. Polyolefin foam, while more resistant to moisture and chemicals, tends to degrade faster under continuous compression and environmental stress. The longevity of viscoelastic foam often surpasses polyolefin foam in applications requiring sustained comfort and pressure relief.
Applications in Various Industries
Viscoelastic foam, known for its exceptional pressure-relieving properties and slow recovery, is widely used in healthcare for mattresses and orthopedic cushions, as well as in automotive seating to enhance comfort and reduce fatigue. Polyolefin foam, characterized by its lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant nature, finds extensive applications in packaging, automotive insulation, and sports equipment for impact absorption and vibration damping. Both foams serve critical roles across industries by optimizing comfort, protection, and energy absorption tailored to specific operational demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Viscoelastic foam, often derived from petroleum-based polyols, typically shows lower biodegradability and contributes more to environmental pollution compared to polyolefin foam, which is made from thermoplastic resins like polyethylene or polypropylene and is more recyclable. Polyolefin foam's closed-cell structure enhances durability and resistance to moisture, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation, supporting sustainable material use. Lifecycle assessments indicate polyolefin foam generally has a smaller carbon footprint and higher potential for reuse and recycling, aligning better with green building certifications and circular economy principles.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Viscoelastic foam typically incurs higher initial costs due to its advanced material properties and superior comfort, making it ideal for premium applications such as mattresses and medical supports. Polyolefin foam offers a more cost-effective solution for large-scale industrial uses, balancing durability and affordability in packaging and insulation. Analyzing total cost of ownership, including longevity and performance, positions viscoelastic foam as a higher upfront investment with potentially greater long-term value, whereas polyolefin foam delivers budget-conscious efficiency with broad utility.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Viscoelastic foam offers superior pressure relief and contouring, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and support, such as mattresses and orthopedic cushions. Polyolefin foam provides excellent durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, well-suited for packaging, automotive components, and construction insulation. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors like softness, resilience, environmental exposure, and specific performance requirements to match your intended use.
Viscoelastic foam vs Polyolefin foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com