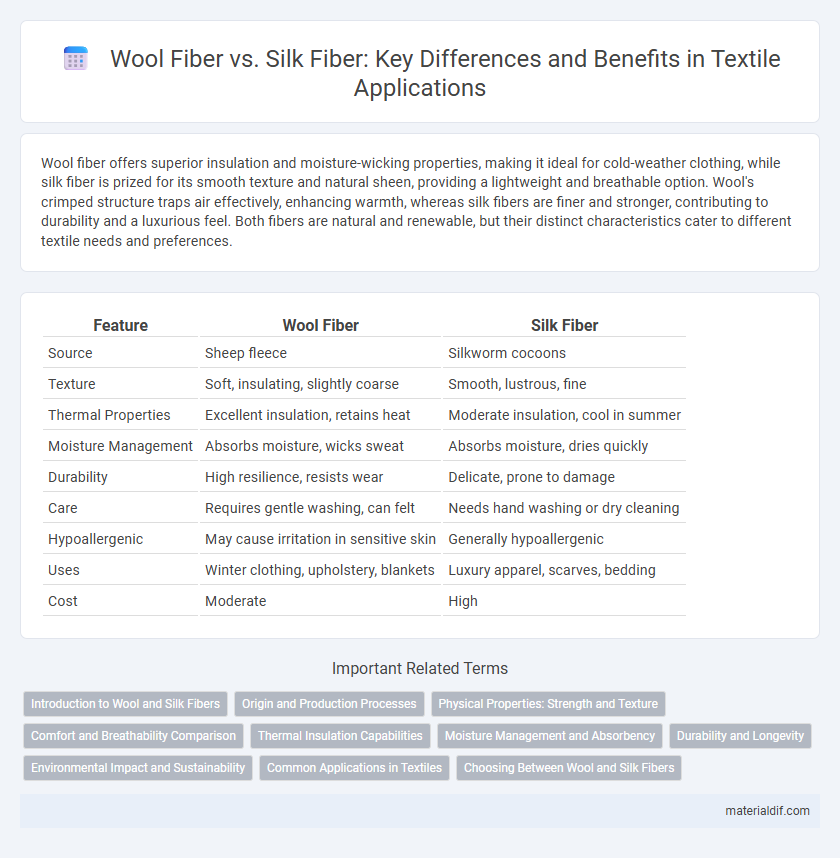
Wool fiber offers superior insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for cold-weather clothing, while silk fiber is prized for its smooth texture and natural sheen, providing a lightweight and breathable option. Wool's crimped structure traps air effectively, enhancing warmth, whereas silk fibers are finer and stronger, contributing to durability and a luxurious feel. Both fibers are natural and renewable, but their distinct characteristics cater to different textile needs and preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool Fiber | Silk Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sheep fleece | Silkworm cocoons |
| Texture | Soft, insulating, slightly coarse | Smooth, lustrous, fine |
| Thermal Properties | Excellent insulation, retains heat | Moderate insulation, cool in summer |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs moisture, wicks sweat | Absorbs moisture, dries quickly |
| Durability | High resilience, resists wear | Delicate, prone to damage |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, can felt | Needs hand washing or dry cleaning |
| Hypoallergenic | May cause irritation in sensitive skin | Generally hypoallergenic |
| Uses | Winter clothing, upholstery, blankets | Luxury apparel, scarves, bedding |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Wool and Silk Fibers
Wool fiber, derived from the fleece of sheep, is a natural protein fiber known for its excellent insulation, moisture-wicking, and elasticity properties, making it ideal for cold-weather garments. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, is a natural protein fiber prized for its smooth texture, high tensile strength, and luxurious sheen, commonly used in high-end textiles and apparel. Both fibers offer unique benefits in textile manufacturing, with wool excelling in warmth and durability, while silk provides softness and elegance.
Origin and Production Processes
Wool fiber originates from the fleece of sheep, primarily produced through shearing and subsequent cleaning, carding, and spinning processes. Silk fiber is derived from the cocoons of silkworms, obtained by carefully harvesting and unwinding the delicate protein filaments after boiling the cocoons. The production of wool emphasizes animal husbandry and mechanical processing, while silk production relies on sericulture and meticulous filament extraction.
Physical Properties: Strength and Texture
Wool fiber exhibits high elasticity and resilience, making it strong and durable with a coarse, crimped texture that provides warmth and insulation. Silk fiber is renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and smooth, lustrous texture, offering a soft, luxurious feel with natural sheen. While wool retains heat efficiently due to its structure, silk combines strength and softness but is less insulating than wool.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Wool fiber provides superior moisture-wicking and temperature regulation, making it highly breathable and comfortable in both cold and warm conditions. Silk fiber, while smooth and lightweight, offers excellent softness but less effective moisture management compared to wool. The natural crimp in wool enhances air circulation, contributing to better breathability and overall comfort during extended wear.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Wool fiber exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its natural crimp, creating air pockets that trap heat and regulate body temperature effectively. Silk fiber, though smooth and lightweight, provides moderate insulation by forming a thin layer that retains warmth while allowing breathability. The moisture-wicking ability of wool further enhances its thermal performance, making it preferable for cold and variable climates.
Moisture Management and Absorbency
Wool fiber excels in moisture management by efficiently wicking moisture away from the skin and retaining up to 30% of its weight in water without feeling wet, making it ideal for temperature regulation in varying climates. Silk fiber, while naturally absorbent, holds less moisture than wool and dries faster, offering a lightweight and breathable option for moisture-sensitive applications. Both fibers provide unique benefits, with wool preferred for high absorbency and sustained moisture control, and silk favored for its smooth texture and quick-drying properties.
Durability and Longevity
Wool fiber exhibits excellent durability due to its natural elasticity and resilience, making it resistant to wear and tear over time. Silk fiber, while luxurious and smooth, is less durable and more susceptible to weakening from exposure to sunlight and abrasion. Wool's ability to retain its shape and resist pilling ensures greater longevity compared to the delicate nature of silk fibers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wool fiber, derived from sheep, is renewable and biodegradable with a lower environmental footprint when managed sustainably, as it requires natural grazing and emits less pollution compared to synthetic fibers. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, is biodegradable but involves intensive water and energy consumption during cultivation and harvesting, often raising concerns about animal welfare and resource use. Choosing wool supports eco-friendly farming practices, while silk's environmental impact varies widely depending on production methods and scale.
Common Applications in Textiles
Wool fiber is widely used in warm clothing, blankets, and upholstery due to its excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties. Silk fiber is preferred in luxury garments, scarves, and bedding because of its smooth texture, natural sheen, and strength. Both fibers are integral to textile industries, with wool dominating winter wear and silk enhancing high-end fashion and home decor.
Choosing Between Wool and Silk Fibers
Wool fiber offers excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for colder climates and active wear, while silk fiber provides a smooth texture and natural sheen, preferred for lightweight, breathable garments. The decision between wool and silk fibers depends on the desired durability, warmth, and tactile experience, with wool being more resilient and silk offering luxurious softness. Consider factors such as climate, garment use, and maintenance requirements to choose the appropriate fiber for your textile needs.
Wool Fiber vs Silk Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com