Wool fiber is known for its elasticity, warmth, and water resistance, making it a versatile choice for clothing and insulation. Alpaca fiber offers superior softness, hypoallergenic properties, and excellent thermal insulation, often preferred for luxury textiles and sensitive skin. Both fibers provide durability and breathability, but alpaca fibers tend to be lighter and less prickly compared to traditional wool.
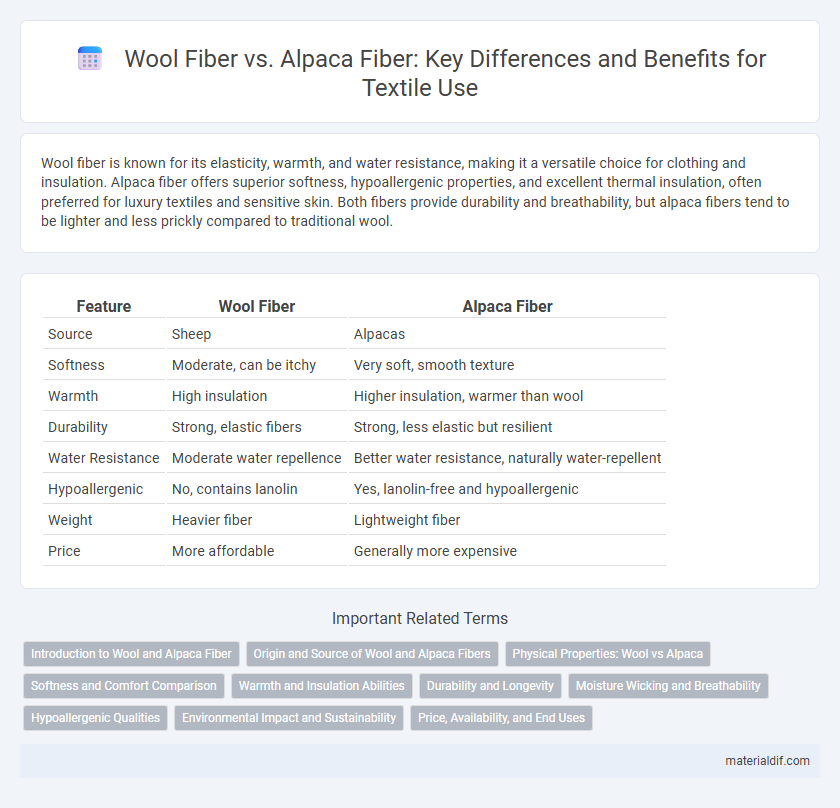
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool Fiber | Alpaca Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sheep | Alpacas |
| Softness | Moderate, can be itchy | Very soft, smooth texture |
| Warmth | High insulation | Higher insulation, warmer than wool |
| Durability | Strong, elastic fibers | Strong, less elastic but resilient |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water repellence | Better water resistance, naturally water-repellent |
| Hypoallergenic | No, contains lanolin | Yes, lanolin-free and hypoallergenic |
| Weight | Heavier fiber | Lightweight fiber |
| Price | More affordable | Generally more expensive |
Introduction to Wool and Alpaca Fiber
Wool fiber, derived primarily from sheep breeds such as Merino, is renowned for its elasticity, warmth, and moisture-wicking properties, making it a versatile choice for textiles and insulation. Alpaca fiber, harvested from the South American alpacas, is prized for its exceptional softness, hypoallergenic qualities, and superior thermal insulation due to its hollow fiber structure. Both fibers offer unique benefits for apparel and home goods, with wool excelling in durability and alpaca favored for luxury softness and lightweight warmth.
Origin and Source of Wool and Alpaca Fibers
Wool fiber primarily originates from sheep, with notable varieties like Merino sourced predominantly from Australia and New Zealand, revered for its fine texture and insulation properties. Alpaca fiber comes from the domesticated alpaca, native to the Andean regions of South America, especially Peru, where the fiber is prized for its softness, warmth, and hypoallergenic qualities. Both fibers derive from animals adapted to specific climates, influencing the distinct characteristics and uses of wool and alpaca in textile production.
Physical Properties: Wool vs Alpaca
Wool fiber is known for its crimp, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, offering excellent insulation and durability. Alpaca fiber, while softer and lighter, has a smoother, less elastic structure with superior thermal insulation and hypoallergenic qualities due to the absence of lanolin. Both fibers provide warmth but differ in texture and elasticity, making alpaca ideal for sensitive skin and wool preferred for resilience in rugged conditions.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Wool fiber offers a classic balance of softness and durability, making it ideal for everyday wear and insulation. Alpaca fiber exceeds wool in softness due to its finer, smoother structure, providing superior comfort without itching or irritation. Both fibers provide excellent warmth, but alpaca's hypoallergenic properties enhance comfort for sensitive skin.
Warmth and Insulation Abilities
Wool fiber, derived from sheep, possesses excellent warmth and moisture-wicking properties due to its crimped structure that traps air effectively for insulation. Alpaca fiber excels in insulation by providing superior thermal regulation with hollow core fibers, making it warmer and lighter than wool. Both fibers offer natural breathability, but alpaca's finer, smoother fibers enhance comfort while maintaining higher insulation efficiency.
Durability and Longevity
Wool fiber exhibits excellent durability due to its natural elasticity and resilience, maintaining shape and resisting wear over extended use. Alpaca fiber offers superior longevity with its smooth, strong fibers that are less prone to pilling, making it ideal for high-quality garments. Both fibers provide lasting performance, but alpaca's inherent toughness often surpasses traditional wool in maintaining fabric integrity.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Wool fiber excels in moisture wicking due to its natural lanolin content, which repels water while allowing sweat to evaporate, enhancing breathability in varied climates. Alpaca fiber, though less moisture-wicking than wool, offers superior breathability with its hollow core structure facilitating excellent air circulation and temperature regulation. Both fibers provide natural odor resistance, but wool's dynamic moisture management makes it ideal for high-performance activewear, whereas alpaca suits luxurious, breathable garments for milder conditions.
Hypoallergenic Qualities
Alpaca fiber is naturally hypoallergenic due to its lack of lanolin, making it less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to wool fiber, which contains lanolin and can irritate sensitive skin. Wool fibers tend to retain moisture and can harbor allergens, while alpaca fibers have a smoother cuticle that repels water and allergens more effectively. For individuals with allergies or sensitive skin, alpaca fiber offers a gentler and more comfortable alternative to traditional wool.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wool fiber production typically requires significant water, land use, and generates methane emissions from sheep, contributing to environmental concerns. Alpaca fiber is more sustainable due to alpacas' lower water consumption, minimal grazing impact, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to sheep. The biodegradability and renewable nature of both fibers support eco-friendly textile practices, but alpaca fiber's lower environmental footprint makes it a preferable choice for sustainable fashion.
Price, Availability, and End Uses
Wool fiber is generally more affordable and widely available than alpaca fiber, making it the preferred choice for mass-market textile production. Alpaca fiber, prized for its softness and hypoallergenic properties, commands a higher price and is less common due to limited supply from alpaca herds primarily in South America. Wool is predominantly used in durable, everyday clothing and blankets, while alpaca fiber is favored for luxury garments, scarves, and specialty items that require enhanced warmth and a silky texture.
Wool Fiber vs Alpaca Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com