Nylon fiber offers superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and durability compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-performance textiles and activewear. Polyester fiber excels in moisture-wicking properties, UV resistance, and retains color better after repeated washing, making it well-suited for outdoor and everyday garments. Choosing between nylon and polyester fibers depends on specific requirements such as stretch, strength, moisture management, and exposure to environmental elements.
Table of Comparison
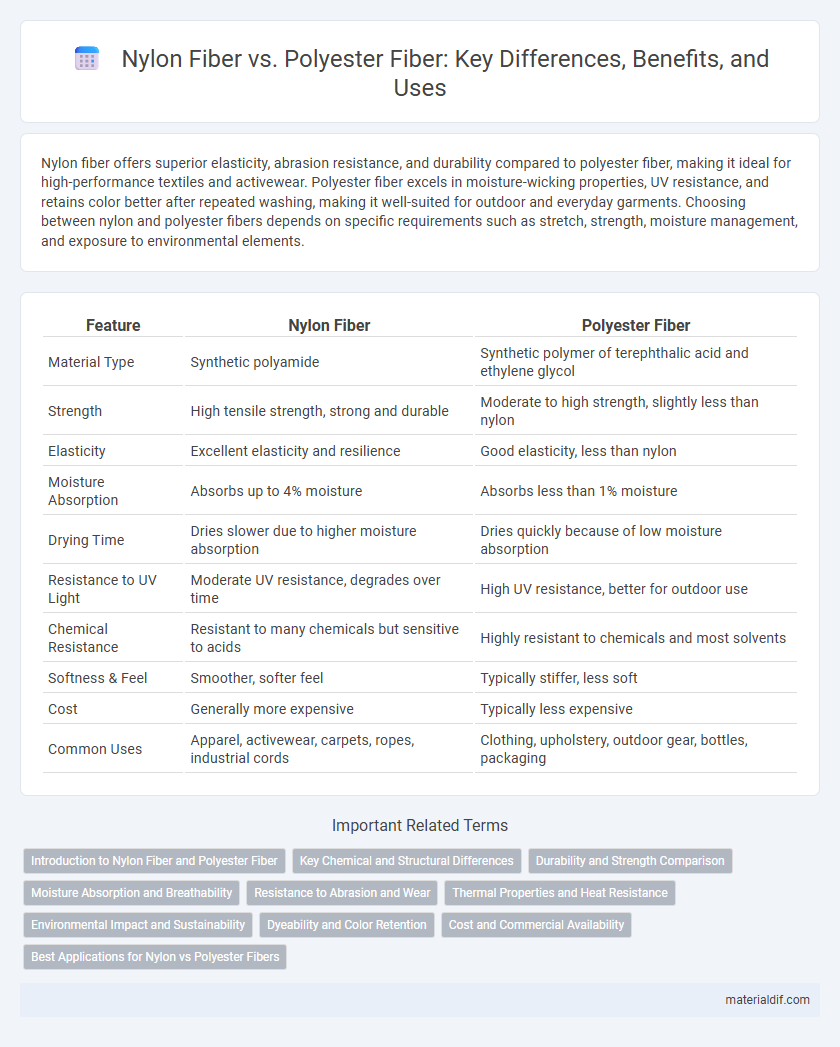
| Feature | Nylon Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polyamide | Synthetic polymer of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol |
| Strength | High tensile strength, strong and durable | Moderate to high strength, slightly less than nylon |
| Elasticity | Excellent elasticity and resilience | Good elasticity, less than nylon |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs up to 4% moisture | Absorbs less than 1% moisture |
| Drying Time | Dries slower due to higher moisture absorption | Dries quickly because of low moisture absorption |
| Resistance to UV Light | Moderate UV resistance, degrades over time | High UV resistance, better for outdoor use |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals but sensitive to acids | Highly resistant to chemicals and most solvents |
| Softness & Feel | Smoother, softer feel | Typically stiffer, less soft |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically less expensive |
| Common Uses | Apparel, activewear, carpets, ropes, industrial cords | Clothing, upholstery, outdoor gear, bottles, packaging |
Introduction to Nylon Fiber and Polyester Fiber
Nylon fiber is a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, commonly used in textiles, carpets, and industrial applications. Polyester fiber, also a synthetic polymer, offers excellent durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, making it popular in clothing, home furnishings, and outdoor fabrics. Both fibers are thermoplastic, enabling heat molding and recycling, but nylon generally provides higher tensile strength while polyester excels in UV and chemical resistance.
Key Chemical and Structural Differences
Nylon fiber is a polyamide composed of repeating amide linkages, characterized by its strong hydrogen bonding which leads to high tensile strength and elasticity, whereas polyester fiber is primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET) consisting of ester functional groups that provide superior resistance to UV degradation and moisture absorption. Structurally, nylon exhibits a semi-crystalline arrangement with a higher degree of crystallinity contributing to its toughness, while polyester fibers have a more rigid molecular backbone with aromatic rings, enhancing dimensional stability and wrinkle resistance. These chemical and structural distinctions dictate their divergent performance in applications such as textiles, with nylon favored for durability and elasticity and polyester preferred for moisture management and resistance to environmental factors.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Nylon fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to polyester fiber, making it highly resistant to wear and tear in demanding applications. Polyester fiber offers excellent durability with enhanced resistance to UV rays and moisture, contributing to longer lifespan in outdoor environments. The combination of nylon's strength and polyester's weather resistance determines the optimal choice based on the specific durability requirements of textiles and industrial products.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Nylon fiber exhibits lower moisture absorption, retaining less water and drying faster compared to polyester fiber, which absorbs more moisture but offers better moisture-wicking properties. Polyester fiber's enhanced breathability is due to its hydrophobic nature, allowing moisture vapor to escape more efficiently, improving comfort during physical activities. Both fibers are durable, but nylon's quick-drying ability suits humid environments, while polyester excels in moisture management and ventilation.
Resistance to Abrasion and Wear
Nylon fiber exhibits superior resistance to abrasion and wear compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-friction applications such as industrial textiles and activewear. Its molecular structure provides enhanced durability and elasticity, allowing it to withstand repeated stress without significant degradation. Polyester fiber, while still durable, tends to show more surface wear and fiber breakage under intense abrasion conditions, limiting its lifespan in demanding environments.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Nylon fiber exhibits higher melting points ranging from 215degC to 265degC, providing superior heat resistance compared to polyester fiber, which melts between 250degC and 265degC but begins to degrade thermally at around 200degC. Nylon fibers have excellent thermal stability, maintaining strength and flexibility under elevated temperatures, making them suitable for high-heat applications such as industrial fabrics and protective clothing. Polyester fiber, while slightly more prone to heat-induced deformation, offers better thermal insulation and moisture resistance, balancing heat resistance with comfort in textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon fiber production consumes significantly more energy and releases higher greenhouse gases compared to polyester, posing greater environmental challenges. Polyester fiber, often derived from recycled PET bottles, offers more sustainable options by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting circular economy practices. Both fibers contribute to microplastic pollution, but advancements in recycling technologies are enhancing the eco-friendliness of polyester more rapidly than nylon.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Nylon fiber exhibits superior dyeability compared to polyester fiber due to its higher absorbency, allowing it to achieve vibrant and rich colors with ease. Polyester fiber typically requires high-temperature dyeing processes or disperse dyes, resulting in moderate color depth but excellent color retention over time and resistance to fading. While nylon offers a broader range of shades and sharper hues, polyester excels in maintaining colorfastness through repeated washing and exposure to sunlight.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Nylon fiber generally costs more than polyester fiber due to its superior strength and elasticity, making it a premium choice in various applications. Polyester fiber is widely available commercially, benefiting from large-scale production and versatility across industries, which makes it a cost-effective option. Both fibers are extensively used, but polyester dominates the market because of its lower price point and broad accessibility.
Best Applications for Nylon vs Polyester Fibers
Nylon fiber excels in applications requiring high strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for activewear, hosiery, and industrial uses such as ropes and fishing nets. Polyester fiber is preferred for its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and resistance to shrinking and stretching, commonly used in outerwear, upholstery, and home textiles. Selecting nylon or polyester fibers depends on specific needs like stretchability for sportswear or weather resistance for outdoor gear.
Nylon Fiber vs Polyester Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com