Kevlar fiber and Twaron fiber are both high-performance aramid fibers known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, commonly used in ballistic protection and composite materials. Kevlar offers superior tensile strength, making it ideal for body armor and aerospace applications, while Twaron provides enhanced flexibility and moisture resistance, which benefits automotive and industrial uses. Selecting between Kevlar and Twaron depends on specific requirements such as environmental exposure, weight constraints, and mechanical properties needed for the end application.
Table of Comparison
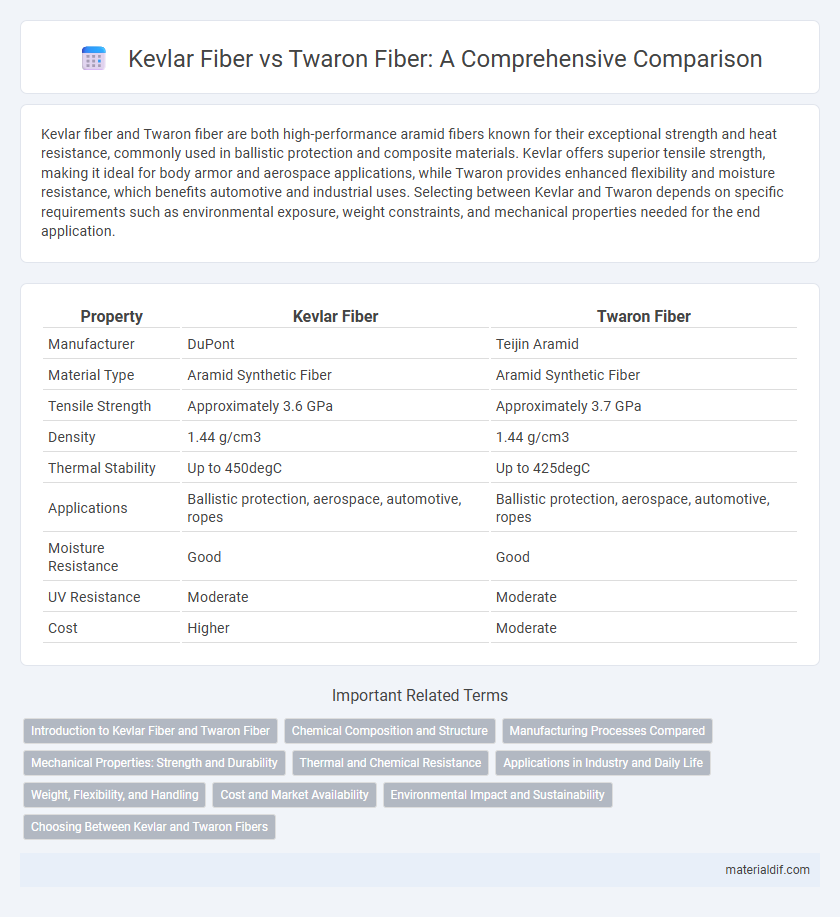
| Property | Kevlar Fiber | Twaron Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | DuPont | Teijin Aramid |
| Material Type | Aramid Synthetic Fiber | Aramid Synthetic Fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Approximately 3.6 GPa | Approximately 3.7 GPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 425degC |
| Applications | Ballistic protection, aerospace, automotive, ropes | Ballistic protection, aerospace, automotive, ropes |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Good |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Kevlar Fiber and Twaron Fiber
Kevlar fiber, developed by DuPont, is a high-strength aramid fiber known for its excellent thermal stability, lightweight properties, and superior tensile strength, widely used in ballistic and protective applications. Twaron fiber, produced by Teijin, offers similar aramid fiber performance with enhanced flexibility and chemical resistance, making it suitable for automotive, industrial, and safety equipment. Both fibers belong to the aramid family and provide exceptional durability and impact resistance, with Kevlar favored for extreme strength and Twaron recognized for its versatile handling characteristics.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Kevlar fiber is composed of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, featuring rigid, rod-like polymer chains oriented parallel to each other, which enhances its tensile strength. Twaron fiber shares a similar chemical composition as it is also an aramid fiber made from poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide), but slight variations in polymerization and processing methods result in differences in molecular weight and crystallinity. Both fibers exhibit a highly ordered, crystalline structure contributing to their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation in high-performance applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Kevlar fiber is primarily produced using a sulfonation process involving poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, resulting in high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability through a spinning method in sulfuric acid. Twaron fiber, a para-aramid similar to Kevlar, employs a proprietary wet spinning process also using polyamide polymer dissolved in sulfuric acid but differs slightly in polymer chain orientation and molecular weight control to enhance heat resistance and flexibility. Both manufacturing processes emphasize controlled polymerization and spinning techniques to optimize fiber strength, durability, and moisture resistance for applications in ballistic protection and aerospace.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Kevlar fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, typically around 3,620 MPa, and outstanding durability due to its aromatic polyamide structure, making it highly resistant to impact and abrasion. Twaron fiber, with tensile strength close to 3,600 MPa, offers comparable mechanical performance but excels in heat resistance and chemical stability, slightly enhancing durability in extreme conditions. Both fibers provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and are widely used in ballistic protection and composite materials requiring high mechanical resilience.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar fiber exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining stability up to temperatures around 450degC, while Twaron fiber offers similar heat resistance but with slightly better performance in prolonged high-temperature exposure. Chemically, Kevlar resists most organic solvents and chemicals but can degrade when exposed to strong acids and bases; Twaron fiber demonstrates superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons. Both fibers are engineered for demanding environments, but Twaron's enhanced chemical stability makes it a preferred choice in harsh industrial applications requiring prolonged chemical exposure.
Applications in Industry and Daily Life
Kevlar fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, is widely used in aerospace, military armor, and automotive components, providing enhanced protection and durability. Twaron fiber, a para-aramid fiber similar to Kevlar, excels in ballistic reinforcement, ropes, and composites, commonly employed in protective clothing, tires, and cables. Both fibers contribute significantly to industrial safety equipment and everyday products requiring lightweight, high-strength materials.
Weight, Flexibility, and Handling
Kevlar fiber offers a lighter weight compared to Twaron fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring reduced mass. Twaron fiber provides superior flexibility, enhancing its performance in dynamic environments where material adaptability is critical. Handling Kevlar can be more challenging due to its stiffness, whereas Twaron's easier manipulation improves manufacturing efficiency.
Cost and Market Availability
Kevlar fiber generally offers a lower cost compared to Twaron fiber, making it more accessible for large-scale industrial applications. Twaron fiber, produced primarily by Teijin Aramid, commands a higher price but is valued for its consistent quality and availability in Europe and Asia markets. Market availability of Kevlar is broader globally due to its long-established presence and multiple manufacturers, whereas Twaron's supply is more regionally concentrated, influencing procurement decisions in specialized sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kevlar fiber and Twaron fiber both offer high strength-to-weight ratios, but their environmental impact differs due to variations in production processes. Kevlar manufacturing involves more energy-intensive steps and generates higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to Twaron, which utilizes a more eco-efficient process with lower carbon footprints. Twaron fiber's enhanced recyclability and reduced chemical usage contribute to greater sustainability in high-performance applications.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Twaron Fibers
Kevlar fiber and Twaron fiber both offer high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, ideal for applications in ballistic protection and aerospace. Kevlar's superior thermal stability and widespread industry acceptance make it favorable for environments with extreme heat, while Twaron provides better moisture resistance and flexibility for dynamic stress conditions. Selecting between Kevlar and Twaron fibers depends on specific performance requirements such as thermal exposure, mechanical durability, and environmental factors.
Kevlar Fiber vs Twaron Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com