Kevlar fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and is widely used in ballistic and protective applications due to its superior cut and abrasion resistance. Nomex fiber provides excellent thermal stability and flame resistance, making it ideal for use in fire-retardant clothing and equipment. While Kevlar excels in impact protection, Nomex is preferred for high-temperature environments requiring durable heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
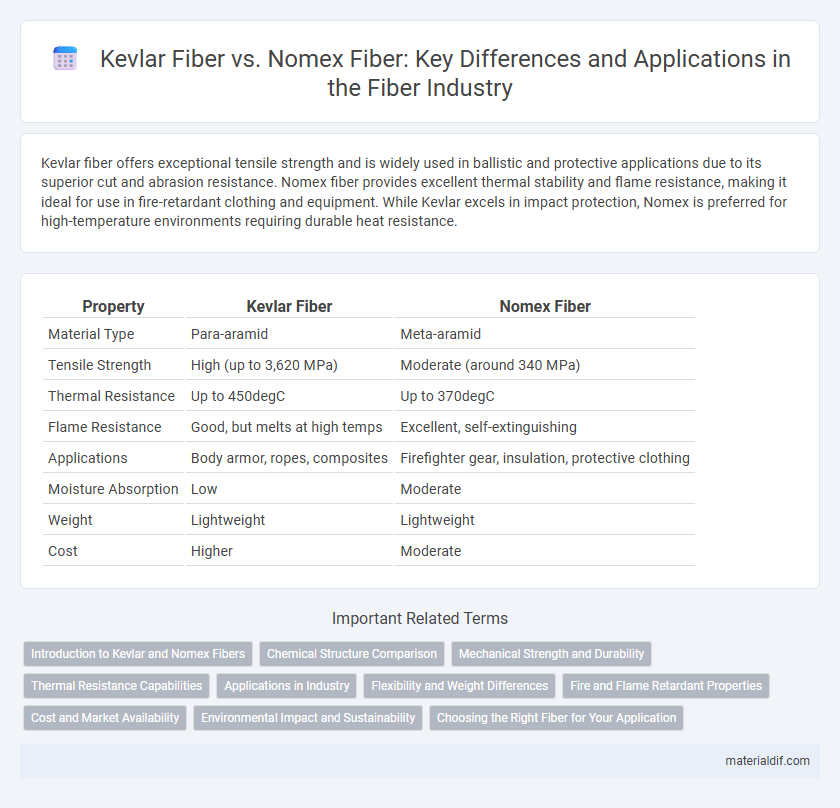
| Property | Kevlar Fiber | Nomex Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Para-aramid | Meta-aramid |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (around 340 MPa) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 450degC | Up to 370degC |
| Flame Resistance | Good, but melts at high temps | Excellent, self-extinguishing |
| Applications | Body armor, ropes, composites | Firefighter gear, insulation, protective clothing |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Kevlar and Nomex Fibers
Kevlar fiber, a high-strength aramid material, is renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for ballistic protection and aerospace applications. Nomex fiber, another aramid fiber, excels in heat and flame resistance, commonly used in firefighting gear and industrial protective clothing. Both fibers are synthetic, lightweight, and possess unique chemical structures that contribute to their specific performance benefits in safety and defense industries.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Kevlar fiber consists of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, characterized by rigid para-phenylene benzene rings linked by amide bonds, providing exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability. Nomex fiber is made from meta-aramid polymer, with benzene rings connected at the meta position, resulting in a more flexible molecular chain that offers superior flame resistance and thermal insulation. The structural difference between Kevlar's para-orientation and Nomex's meta-orientation significantly influences their respective mechanical properties and applications in high-performance textiles.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Kevlar fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength with a tensile strength of approximately 3,620 MPa, making it highly resistant to impact and abrasion, while Nomex fiber provides excellent thermal stability and moderate mechanical strength around 300 MPa. Kevlar's durability under high-stress conditions surpasses Nomex, which excels more in flame resistance and insulation rather than load-bearing applications. The choice between Kevlar and Nomex fibers hinges on the required balance between mechanical robustness and thermal protection in demanding environments.
Thermal Resistance Capabilities
Kevlar fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance with a decomposition temperature around 450degC, making it highly suitable for applications requiring extreme heat endurance and cut resistance. Nomex fiber offers excellent flame resistance and thermal stability up to approximately 370degC, commonly used in protective clothing for firefighters and industrial workers. While Kevlar provides higher heat resistance, Nomex excels in maintaining structural integrity under prolonged flame exposure, emphasizing their complementary roles in thermal protection.
Applications in Industry
Kevlar fiber is predominantly used in ballistic and protective gear, including bulletproof vests, helmets, and aerospace components, owing to its exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance. Nomex fiber finds extensive application in flame-resistant clothing for firefighters, industrial workers, and race car drivers due to its excellent thermal and fire-retardant properties. Both fibers serve critical roles in safety and defense industries, with Kevlar excelling in mechanical protection and Nomex specializing in heat and fire resistance.
Flexibility and Weight Differences
Kevlar fiber offers superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to Nomex fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and mobility. Nomex fiber is lighter in weight but less flexible, providing excellent thermal resistance and flame retardancy suited for protective gear. The weight difference typically sees Kevlar at approximately 1.44 g/cm3, while Nomex weighs around 1.38 g/cm3, influencing material choice based on the balance of flexibility and lightness needed.
Fire and Flame Retardant Properties
Kevlar fiber exhibits superior flame resistance with a high decomposition temperature around 450degC, maintaining structural integrity under intense heat and resisting ignition. Nomex fiber enhances fire retardancy through its inherent aromatic polyamide structure, providing excellent thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties without melting or dripping. Both fibers are widely used in protective clothing, but Kevlar's higher tensile strength complements Nomex's advanced flame resistance for optimal fire safety.
Cost and Market Availability
Kevlar fiber generally costs more than Nomex fiber due to its higher tensile strength and specialized production processes, making it a premium choice in protective gear and aerospace applications. Nomex fiber, while slightly less expensive, is widely available on the market and favored for fire-resistant clothing and insulation because of its excellent thermal stability and cost-effectiveness. Market availability of Nomex is broader globally, supported by steady demand in industrial and military sectors, whereas Kevlar's supply is more niche, concentrated in high-performance and safety-certified products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kevlar fiber, made from poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, exhibits high strength and durability but relies on petroleum-based resources, contributing to a larger carbon footprint during production. Nomex fiber, derived from meta-aramid polymers with inherent flame-resistant properties, also depends on non-renewable petrochemical inputs but offers longer lifespan and reduced waste in flame-retardant applications. Both fibers present challenges in biodegradability and recycling, emphasizing the need for advancements in sustainable fiber synthesis and lifecycle management to minimize environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Application
Kevlar fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for bulletproof vests, aerospace components, and high-performance sporting goods. Nomex fiber excels in thermal stability and flame resistance, commonly used in firefighter suits, electrical insulation, and protective apparel. Selecting the right fiber depends on whether your application prioritizes mechanical durability or heat and flame protection.
Kevlar Fiber vs Nomex Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com