Acrylic fiber is lightweight, soft, and resistant to wrinkles and UV rays, making it ideal for apparel and upholstery. Modacrylic fiber, a modified form of acrylic, offers enhanced flame retardancy and chemical resistance, commonly used in protective clothing and wigs. Both fibers provide excellent durability and colorfastness, but modacrylic's specialty properties suit safety-focused applications.
Table of Comparison
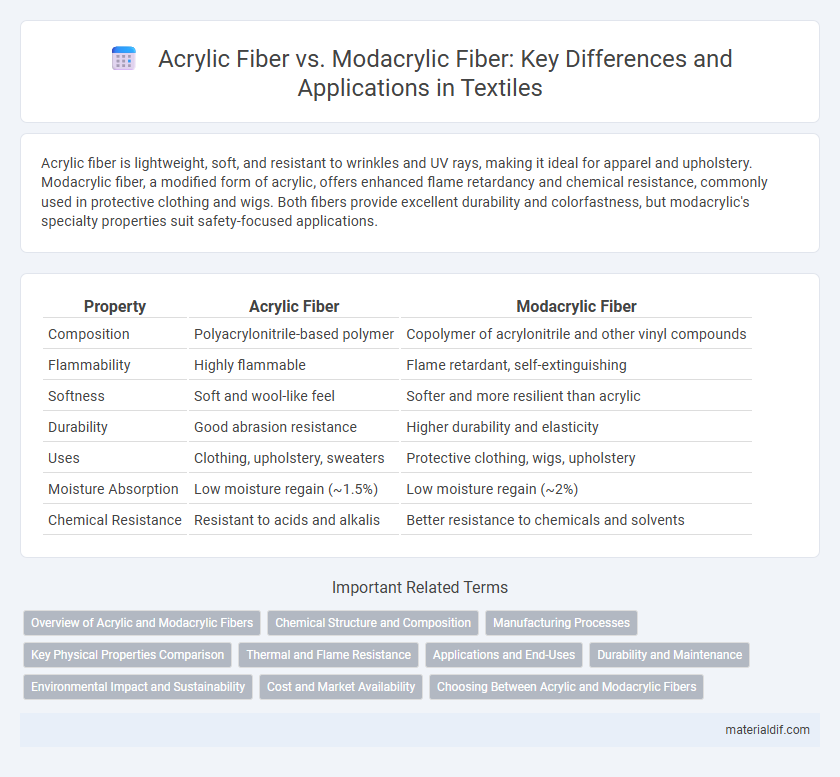
| Property | Acrylic Fiber | Modacrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polyacrylonitrile-based polymer | Copolymer of acrylonitrile and other vinyl compounds |
| Flammability | Highly flammable | Flame retardant, self-extinguishing |
| Softness | Soft and wool-like feel | Softer and more resilient than acrylic |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Higher durability and elasticity |
| Uses | Clothing, upholstery, sweaters | Protective clothing, wigs, upholstery |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture regain (~1.5%) | Low moisture regain (~2%) |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Better resistance to chemicals and solvents |
Overview of Acrylic and Modacrylic Fibers
Acrylic fibers are synthetic fibers made from polyacrylonitrile, known for their wool-like feel, lightweight nature, and excellent resistance to moisture, UV rays, and chemicals. Modacrylic fibers, derived from modified acrylic polymers containing acrylonitrile copolymers, offer enhanced flame resistance, durability, and softness, making them ideal for protective clothing and upholstery. Both fibers are widely used in textiles, with acrylic favored for general apparel and modacrylic preferred in applications requiring flame retardancy and resilience.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Acrylic fiber is primarily composed of polyacrylonitrile with at least 85% acrylonitrile units, providing high strength and durability due to its linear polymer chains. Modacrylic fiber contains a copolymer with 35-85% acrylonitrile units combined with other monomers like vinyl chloride, giving it enhanced flame resistance and softness compared to acrylic. The chemical variation between acrylic and modacrylic fibers directly influences properties such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and application suitability in textiles.
Manufacturing Processes
Acrylic fiber is produced through a wet-spinning or dry-spinning process using polyacrylonitrile as the primary polymer, which undergoes polymerization, spinning, and stretching to enhance fiber strength. Modacrylic fiber manufacturing involves copolymerizing acrylonitrile with other monomers, resulting in fibers with inherent flame-retardant properties, typically processed through dry-spinning techniques followed by drawing and finishing. Both fibers demand precise control of temperature and solvent recovery systems during spinning to ensure fiber quality and optimize production efficiency.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Acrylic fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and excellent resistance to sunlight and chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor textiles, while modacrylic fiber offers superior flame resistance and softness, widely used in protective clothing and upholstery. The density of acrylic fibers ranges from 1.16 to 1.18 g/cm3, slightly lighter than modacrylic fibers, which have a density around 1.29 g/cm3. Moisture regain for acrylic fiber averages 1.5 to 2%, whereas modacrylic fiber absorbs more moisture, about 2.5 to 3%, enhancing comfort in wear applications.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Acrylic fiber exhibits moderate thermal resistance, melting at approximately 255degC, but it is highly flammable and tends to ignite quickly. Modacrylic fiber offers superior flame resistance, self-extinguishing when the heat source is removed, and char formation reduces flame spread. The enhanced thermal stability and inherent flame-retardant properties of modacrylic fiber make it ideal for protective clothing and upholstery applications requiring fire safety.
Applications and End-Uses
Acrylic fiber is widely used in clothing, home textiles, and upholstery due to its softness, warmth, and colorfastness, making it ideal for sweaters, blankets, and outdoor fabrics. Modacrylic fiber excels in flame-resistant applications such as protective apparel, wigs, and hairpieces because of its inherent flame retardant properties and durability. Both fibers serve distinct markets where comfort and safety are prioritized, with modacrylic dominating specialized safety gear and acrylic favored for everyday textiles.
Durability and Maintenance
Acrylic fiber offers good durability with resistance to sunlight and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor applications, while modacrylic fiber provides enhanced flame retardancy and better resistance to chemicals and heat. Maintenance of acrylic fiber is easier as it resists mildew and shrinking, whereas modacrylic fiber requires careful handling during washing to avoid damage from high temperatures. Both fibers are low-maintenance but selecting the right type depends on the specific durability needs and intended use environment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylic fibers are petroleum-based synthetic fibers with significant environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradability and high energy consumption during production, leading to substantial carbon emissions. Modacrylic fibers, although also synthetic and partially derived from acrylonitrile, tend to have slightly lower environmental impact because of their flame-retardant properties that reduce the need for additional chemical treatments. Both fibers pose challenges for sustainability, but advancements in recycling technologies and the development of bio-based alternatives are critical for mitigating their ecological footprint.
Cost and Market Availability
Acrylic fiber generally costs less than modacrylic fiber, making it more accessible for large-scale textile production and budget-conscious markets. Modacrylic fiber, known for its flame resistance and durability, is priced higher due to specialized manufacturing processes and is less widely available. Market availability favors acrylic fibers with extensive global distribution channels, while modacrylic fibers are niche products primarily supplied to industries requiring specific safety standards.
Choosing Between Acrylic and Modacrylic Fibers
Acrylic fibers offer lightweight, soft, and wool-like texture, making them suitable for sweaters and blankets, while modacrylic fibers provide enhanced flame resistance and durability, ideal for protective clothing and wigs. Choosing between acrylic and modacrylic fibers depends on the required properties such as flame retardancy, resilience, and comfort. Modacrylic fibers combine synthetic polymer properties with superior chemical stability, whereas acrylic fibers excel in cost-effectiveness and moisture-wicking capabilities.
Acrylic fiber vs Modacrylic fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com