Aramid fiber offers superior strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and protective clothing. Polyester fiber excels in affordability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, which suit everyday apparel and home textiles. Choosing between aramid and polyester fibers depends on the balance of performance requirements versus cost-effectiveness for the intended use.
Table of Comparison
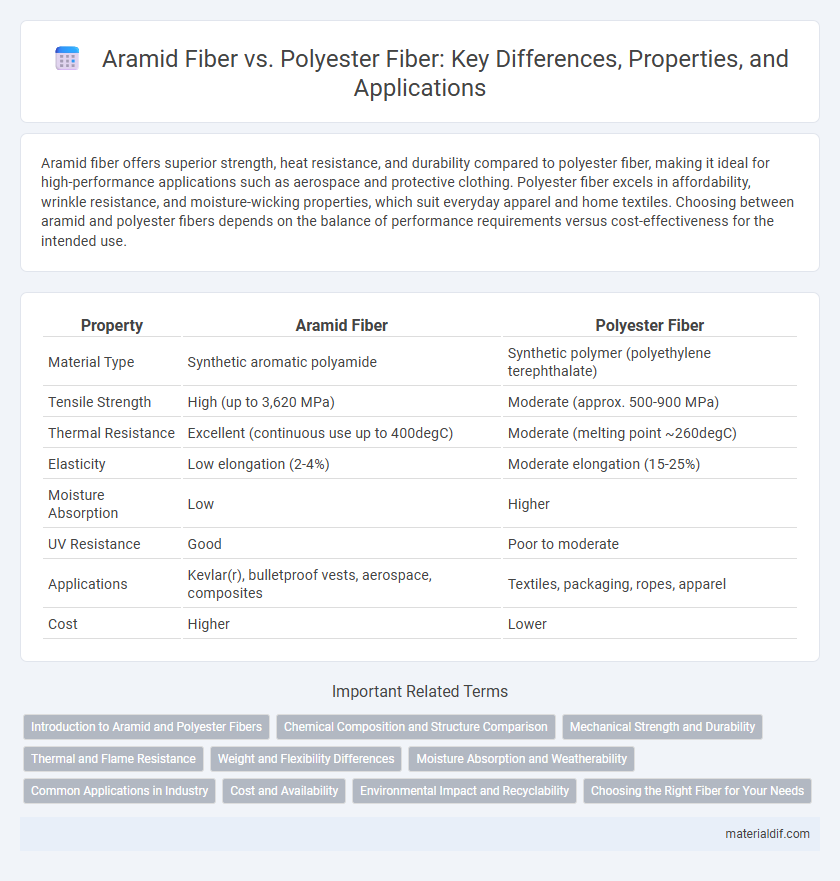
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide | Synthetic polymer (polyethylene terephthalate) |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (approx. 500-900 MPa) |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent (continuous use up to 400degC) | Moderate (melting point ~260degC) |
| Elasticity | Low elongation (2-4%) | Moderate elongation (15-25%) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Higher |
| UV Resistance | Good | Poor to moderate |
| Applications | Kevlar(r), bulletproof vests, aerospace, composites | Textiles, packaging, ropes, apparel |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Aramid and Polyester Fibers
Aramid fibers are synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, commonly used in aerospace and ballistic applications. Polyester fibers, made from polyethylene terephthalate, offer high tensile strength, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties widely utilized in textiles and industrial fabrics. Both fibers provide distinct advantages in performance and application, with aramid fibers excelling in protective gear and polyester fibers favored for versatile, everyday fabric use.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Aramid fiber is composed of aromatic polyamides with rigid molecular chains, providing high tensile strength and thermal resistance due to its para-oriented molecular structure. Polyester fiber consists of long-chain synthetic polymers derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, characterized by flexible ester linkages that offer moderate strength and elasticity. The difference in chemical composition and molecular alignment results in aramid's superior mechanical properties compared to polyester's versatile but less durable structure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aramid fiber offers superior mechanical strength compared to polyester fiber, with tensile strength reaching up to 3,620 MPa, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Its exceptional durability includes high resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure, maintaining performance in extreme environments. Polyester fiber, while less strong with tensile strength around 500 MPa, provides good durability and flexibility but degrades faster under UV and chemical stress.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Aramid fiber exhibits superior thermal and flame resistance compared to polyester fiber, withstanding temperatures up to 500degC without melting or degrading. Polyester fiber ignites at lower temperatures around 260degC and tends to melt, making it less suitable for high-heat applications. Aramid's inherent flame retardant properties make it ideal for protective clothing, aerospace, and industrial uses where fire resistance is critical.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Aramid fiber is significantly lighter than polyester fiber, with a density around 1.44 g/cm3 compared to polyester's 1.38 g/cm3, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio ideal for high-performance applications. Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional flexibility and resistance to stretching, maintaining structural integrity under stress, whereas polyester fibers are less flexible and prone to deformation under prolonged tension. These properties make aramid fiber preferred for aerospace, military, and protective gear, while polyester is commonly used in textiles and industrial fabrics.
Moisture Absorption and Weatherability
Aramid fiber exhibits low moisture absorption, maintaining strength and dimensional stability in humid or wet conditions, whereas polyester fiber absorbs more moisture, which can reduce its mechanical properties over time. In terms of weatherability, aramid fiber resists UV degradation and chemical exposure more effectively than polyester, making it suitable for long-term outdoor applications. Polyester fiber may degrade faster under prolonged sunlight and harsh environmental conditions, impacting durability and performance.
Common Applications in Industry
Aramid fiber is widely used in aerospace, military armor, and high-performance automotive components due to its exceptional strength, heat resistance, and impact protection. Polyester fiber finds common applications in textiles, packaging, and home furnishings, valued for its durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Industries select aramid fiber for safety-critical and high-stress environments, while polyester fiber is favored for everyday products requiring flexibility and ease of care.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fiber typically costs significantly more than polyester fiber due to its high-performance characteristics and complex manufacturing process. Polyester fiber is widely available and mass-produced, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications where budget constraints are critical. The widespread availability of polyester fiber ensures consistent supply for various industries, while aramid fiber remains specialized and less accessible.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Aramid fiber offers superior environmental benefits due to its high durability and resistance to degradation, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste. Polyester fiber, while widely recyclable through chemical and mechanical processes, often involves energy-intensive production and contributes to microplastic pollution during washing. Choosing aramid fiber supports sustainability goals by extending product lifespan, whereas polyester's recyclability benefits depend heavily on the availability of efficient recycling infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Aramid fiber offers exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it ideal for protective gear, aerospace, and automotive applications where safety and performance are critical. Polyester fiber excels in flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suited for textiles, packaging, and everyday consumer products requiring durability with affordability. Selecting between aramid and polyester fibers depends on specific application demands such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, budget constraints, and environmental exposure.
Aramid Fiber vs Polyester Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com