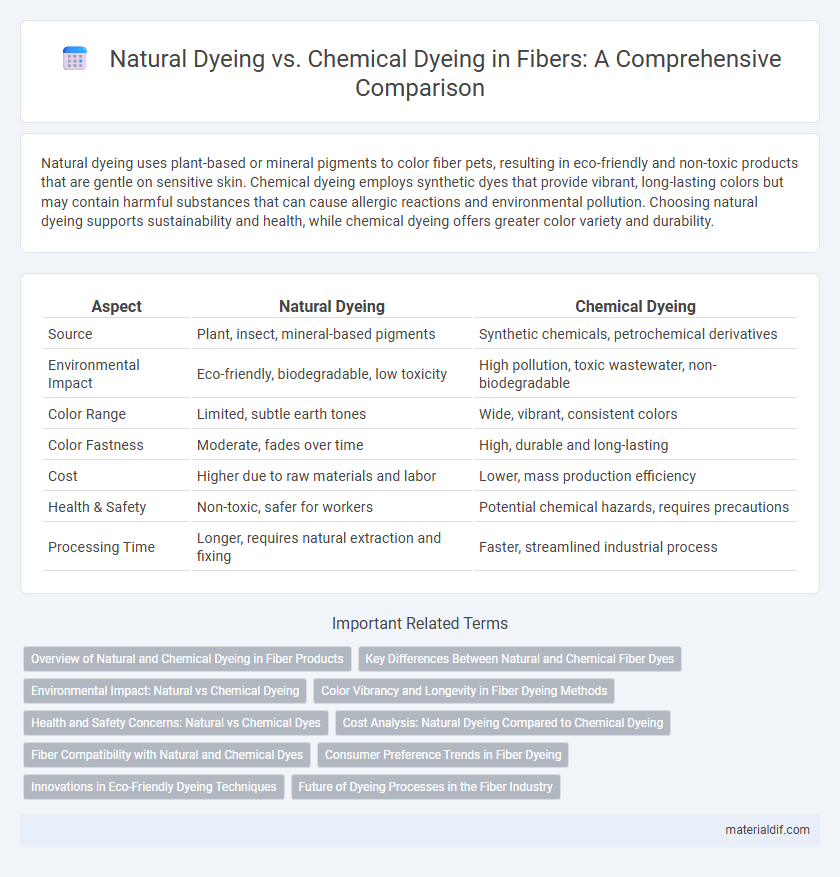
Natural dyeing uses plant-based or mineral pigments to color fiber pets, resulting in eco-friendly and non-toxic products that are gentle on sensitive skin. Chemical dyeing employs synthetic dyes that provide vibrant, long-lasting colors but may contain harmful substances that can cause allergic reactions and environmental pollution. Choosing natural dyeing supports sustainability and health, while chemical dyeing offers greater color variety and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Dyeing | Chemical Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant, insect, mineral-based pigments | Synthetic chemicals, petrochemical derivatives |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, low toxicity | High pollution, toxic wastewater, non-biodegradable |
| Color Range | Limited, subtle earth tones | Wide, vibrant, consistent colors |
| Color Fastness | Moderate, fades over time | High, durable and long-lasting |
| Cost | Higher due to raw materials and labor | Lower, mass production efficiency |
| Health & Safety | Non-toxic, safer for workers | Potential chemical hazards, requires precautions |
| Processing Time | Longer, requires natural extraction and fixing | Faster, streamlined industrial process |
Overview of Natural and Chemical Dyeing in Fiber Products
Natural dyeing in fiber products utilizes pigments extracted from plants, minerals, and insects, offering eco-friendly and biodegradable coloring options with limited colorfastness and a narrower range of hues. Chemical dyeing employs synthetic dyes derived from petrochemicals, providing vibrant, consistent colors with high durability and fastness but posing environmental and health concerns due to toxic effluents and non-biodegradable waste. The choice between natural and chemical dyeing significantly impacts the sustainability, cost, and quality of fiber products in the textile industry.
Key Differences Between Natural and Chemical Fiber Dyes
Natural fiber dyes use pigments derived from plants, minerals, and insects, offering eco-friendly, biodegradable options with lower toxicity and limited colorfastness compared to chemical dyes. Chemical fiber dyes are synthetic compounds engineered for vibrant, consistent colors and superior colorfastness but often involve toxic substances and environmental pollutants. The key differences between natural and chemical fiber dyes lie in their origin, environmental impact, color durability, and application processes.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Chemical Dyeing
Natural dyeing minimizes environmental impact by using biodegradable, non-toxic materials derived from plants, insects, or minerals, reducing water pollution and chemical runoff. Chemical dyeing relies on synthetic dyes containing harmful substances like heavy metals and azo compounds, which contribute significantly to water contamination and pose risks to aquatic ecosystems. Wastewater treatment challenges and high energy consumption further exacerbate the ecological footprint of chemical dyeing processes compared to sustainable natural dye alternatives.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity in Fiber Dyeing Methods
Natural dyeing imparts subtle, earthy tones to fibers, with color vibrancy that often softens over time due to light and washing exposure. Chemical dyeing produces intense, vivid hues that maintain brightness and resist fading longer, enhancing the longevity of dyed fibers. The molecular bonding in chemical dyes offers superior colorfastness compared to the weaker attachment found in most natural dyes.
Health and Safety Concerns: Natural vs Chemical Dyes
Natural dyes, derived from plants and minerals, offer a safer alternative with minimal toxicity and reduced risk of skin irritation or respiratory issues compared to chemical dyes. Chemical dyes often contain synthetic compounds and heavy metals that can cause allergic reactions, environmental pollution, and long-term health hazards for workers handling the substances. Prioritizing natural dyes supports healthier production environments and safer textile products, aligning with sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
Cost Analysis: Natural Dyeing Compared to Chemical Dyeing
Natural dyeing typically incurs higher costs due to the labor-intensive extraction process and the need for large quantities of plant materials, limiting scalability. Chemical dyeing offers cost efficiency through synthetic pigments and optimized manufacturing, reducing both time and resource expenses. However, natural dyes provide eco-friendly benefits that may justify their premium in sustainable textile markets.
Fiber Compatibility with Natural and Chemical Dyes
Natural dyeing is highly compatible with protein fibers like wool, silk, and cotton due to their ability to absorb plant-based pigments effectively, resulting in rich, earthy tones. Chemical dyeing offers broader compatibility across synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, enabling vibrant, consistent coloration through reactive, acid, or disperse dyes. Fiber type significantly influences dye uptake, with natural fibers favoring mordant-dependent dyes and synthetic fibers requiring specialized chemical formulations for optimal colorfastness.
Consumer Preference Trends in Fiber Dyeing
Consumer preference trends in fiber dyeing show a growing demand for natural dyeing due to increased awareness of environmental sustainability and health safety concerns. Natural dyes, derived from plant-based sources such as indigo, madder, and turmeric, offer biodegradable and non-toxic alternatives to synthetic chemicals commonly used in chemical dyeing. Market research indicates a rising consumer inclination toward eco-friendly textile products, driving brands to adopt natural dyeing techniques that align with green fashion initiatives and reduce harmful ecological impacts.
Innovations in Eco-Friendly Dyeing Techniques
Innovations in eco-friendly dyeing techniques highlight the use of natural dyes extracted from plants, fruits, and insects, which significantly reduce water pollution and chemical waste compared to traditional chemical dyeing processes. Advancements in enzyme-based mordants and microbial fermentation improve colorfastness and fabric compatibility while minimizing environmental impact. Emerging technologies like supercritical CO2 dyeing further eliminate water usage and toxic effluents, promoting sustainable textile production in the fiber industry.
Future of Dyeing Processes in the Fiber Industry
Natural dyeing uses plant and mineral-based colorants offering eco-friendly, biodegradable alternatives that reduce water pollution and energy consumption. Chemical dyeing, while efficient and vibrant, faces increasing regulatory pressure due to toxic effluents and environmental concerns, prompting research into sustainable synthetic dyes and closed-loop systems. The future of dyeing in the fiber industry relies on innovative technologies blending natural dye extraction with advanced chemical methods to achieve sustainable, high-performance color solutions.
Natural Dyeing vs Chemical Dyeing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com