Aramid fiber and para-aramid fiber both belong to the aromatic polyamide family, known for exceptional strength and heat resistance. Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit higher tensile strength and superior ballistic resistance compared to generic aramid fibers, making them ideal for body armor and aerospace applications. The molecular structure of para-aramid fibers aligns polymer chains more effectively, enhancing durability and impact performance.
Table of Comparison
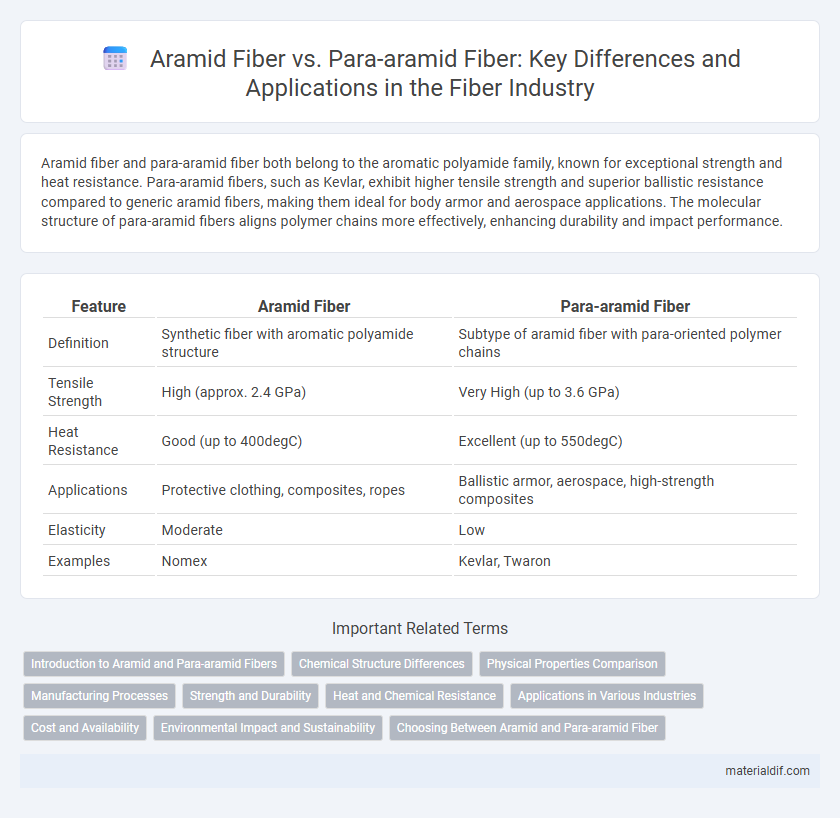
| Feature | Aramid Fiber | Para-aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic fiber with aromatic polyamide structure | Subtype of aramid fiber with para-oriented polymer chains |
| Tensile Strength | High (approx. 2.4 GPa) | Very High (up to 3.6 GPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Good (up to 400degC) | Excellent (up to 550degC) |
| Applications | Protective clothing, composites, ropes | Ballistic armor, aerospace, high-strength composites |
| Elasticity | Moderate | Low |
| Examples | Nomex | Kevlar, Twaron |
Introduction to Aramid and Para-aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers commonly used in aerospace, military, and automotive industries due to their high tensile strength and thermal stability. Para-aramid fibers, a subset of aramid fibers, differentiate themselves through their parallel molecular chain alignment, resulting in superior strength and impact resistance compared to meta-aramid fibers. Key examples include Kevlar and Twaron, which are widely utilized for body armor, ropes, and composites requiring exceptional durability and lightweight properties.
Chemical Structure Differences
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers with a molecular backbone composed of aromatic polyamides, whereas para-aramid fibers specifically refer to poly(paraphenylene terephthalamide) with rigid, linear molecular chains aligned along the fiber axis. The chemical structure of para-aramid fibers features para-oriented benzene rings directly opposite each other, which enhances tensile strength and stiffness, compared to meta-aramid fibers where benzene rings are attached at the meta position causing less chain alignment and lower strength. These differences in chemical structure influence mechanical properties, with para-aramids offering superior impact resistance and durability used notably in ballistic and aerospace applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Aramid fiber and para-aramid fiber differ significantly in their physical properties, with para-aramid fibers such as Kevlar exhibiting higher tensile strength and better thermal stability. Aramid fibers provide excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, making para-aramid particularly suitable for ballistic applications and protective gear. The molecular alignment of para-aramid fibers results in increased modulus and stiffness compared to meta-aramid fibers, optimizing performance in demanding engineering and industrial uses.
Manufacturing Processes
Aramid fiber manufacturing involves spinning aromatic polyamides from liquid crystal polymers through wet or dry spinning techniques, yielding fibers with high tensile strength and heat resistance. Para-aramid fiber, a subset of aramid fibers, is produced using a more refined spinning process that aligns polymer chains parallel to the fiber axis, enhancing its strength-to-weight ratio and thermal stability. The para-aramid production typically includes advanced solvent spinning with precise temperature control to achieve superior molecular orientation and crystallinity compared to standard aramid fiber manufacturing.
Strength and Durability
Aramid fiber and para-aramid fiber both exhibit exceptional strength and durability, but para-aramid fibers such as Kevlar typically offer higher tensile strength and better resistance to impact and abrasion. The molecular structure of para-aramid fibers aligns polymer chains more efficiently, enhancing load-bearing capacity and prolonging material lifespan under stress. This superior performance makes para-aramid fibers ideal for protective gear, aerospace applications, and high-performance composites where durability is critical.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Aramid fiber exhibits exceptional heat resistance, maintaining strength at temperatures up to 400degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Para-aramid fiber, a subtype of aramid, offers enhanced heat resistance combined with superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This chemical resilience makes para-aramid fibers preferred in protective gear and industrial environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is frequent.
Applications in Various Industries
Aramid fiber and para-aramid fiber are essential in aerospace, military, and automotive industries due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and thermal resistance. Para-aramid fiber, known for superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, is extensively used in ballistic protection, aerospace composites, and industrial fiber optics. Aramid fiber finds applications in flame-resistant clothing, ropes, and reinforcement materials across construction and marine sectors, highlighting its versatility and durability.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fiber generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to para-aramid fiber, which demands higher production complexity and raw material quality, leading to increased prices. Para-aramid fiber, known for superior strength and thermal resistance, tends to have limited availability due to specialized manufacturing processes and proprietary technologies. The cost and supply constraints of para-aramid fiber often make aramid fiber the preferred choice for applications balancing performance with budget considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fiber and para-aramid fiber both offer excellent strength and durability, but para-aramid fiber generally exhibits a lower environmental impact due to more efficient production processes and higher recyclability rates. The sustainable attributes of para-aramid fibers include reduced energy consumption during manufacturing and enhanced lifecycle performance, minimizing waste and resource depletion. Aramid fibers, while robust, tend to have a higher carbon footprint and limited recyclability, making para-aramid fiber a more eco-friendly choice in high-performance textile applications.
Choosing Between Aramid and Para-aramid Fiber
Choosing between aramid and para-aramid fibers depends on the application's strength and heat resistance requirements, as para-aramid fibers like Kevlar offer superior tensile strength and thermal stability compared to meta-aramid fibers. Aramid fibers are ideal for impact protection and ballistic applications due to their high durability and lightweight nature, while para-aramid fibers excel in aerospace, military, and industrial uses where consistent performance under extreme conditions is critical. Evaluating specific factors such as modulus, elongation, and chemical resistance helps optimize fiber selection for maximizing safety and efficiency in technical textiles.
Aramid Fiber vs Para-aramid Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com