Hemp fiber offers superior strength and durability compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty textiles and industrial applications. Hemp fibers are naturally resistant to pests and mold, requiring fewer pesticides and less water during cultivation, which enhances its environmental sustainability. While jute fiber is more cost-effective and widely used for packaging and burlap products, hemp's versatility and eco-friendly properties provide a valuable alternative for sustainable fiber production.
Table of Comparison
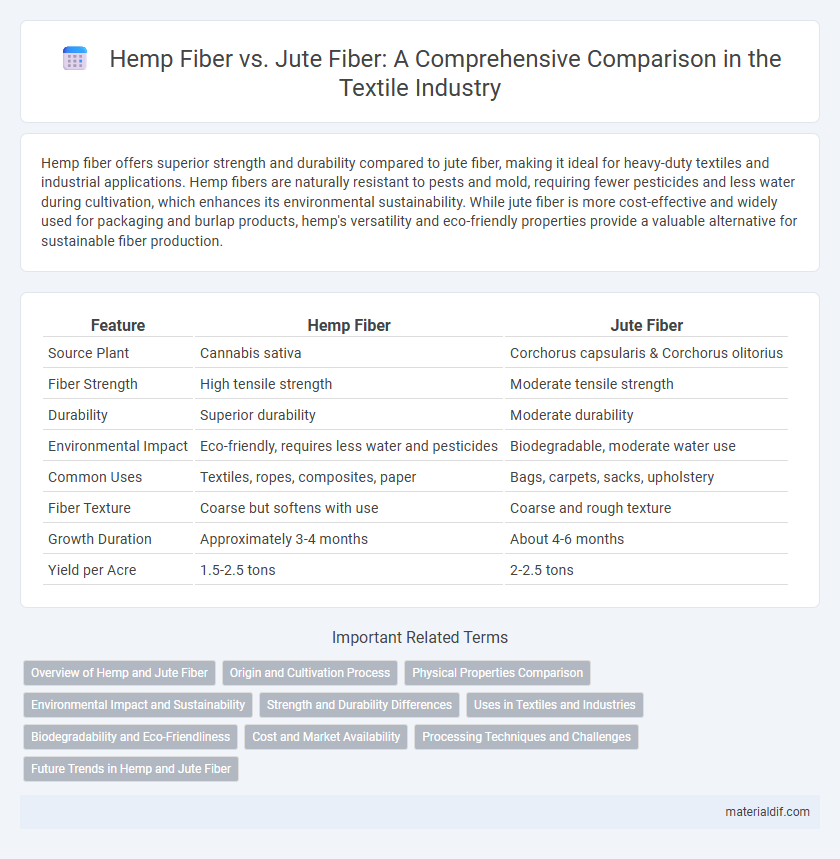
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Cannabis sativa | Corchorus capsularis & Corchorus olitorius |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Durability | Superior durability | Moderate durability |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, requires less water and pesticides | Biodegradable, moderate water use |
| Common Uses | Textiles, ropes, composites, paper | Bags, carpets, sacks, upholstery |
| Fiber Texture | Coarse but softens with use | Coarse and rough texture |
| Growth Duration | Approximately 3-4 months | About 4-6 months |
| Yield per Acre | 1.5-2.5 tons | 2-2.5 tons |
Overview of Hemp and Jute Fiber
Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to mold, making it ideal for textiles, ropes, and composite materials. Jute fiber, obtained from the Corchorus plants, is valued for its affordability, biodegradability, and breathability, commonly used in sacks, mats, and upholstery. Both fibers are sustainable natural materials but differ significantly in texture, tensile strength, and applications within the fiber industry.
Origin and Cultivation Process
Hemp fiber originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, primarily cultivated in temperate regions with fast growth cycles lasting about 3 to 4 months, requiring minimal pesticides and thriving in diverse soil types. Jute fiber is derived from the outer bast of plants in the Corchorus genus, predominantly grown in warm, humid climates like India and Bangladesh, with a cultivation period of 4 to 6 months relying heavily on monsoon rains for optimal growth. Both fibers involve retting processes to separate fibers, but hemp tends to offer higher yields per acre and is more versatile in sustainable agricultural practices.
Physical Properties Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and greater durability compared to jute fiber, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications. Hemp fibers are longer and coarser, which enhances their resistance to wear and tear, while jute fibers are shorter and softer, providing better flexibility but lower mechanical strength. Moisture absorption rates are higher in jute fiber, resulting in greater susceptibility to mold and degradation than the more moisture-resistant hemp fiber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber boasts a lower environmental footprint than jute fiber due to its rapid growth rate, minimal pesticide requirements, and ability to improve soil health through phytoremediation. Jute cultivation demands significant water resources and is more vulnerable to deforestation, impacting biodiversity and soil erosion. Hemp's high yield per acre and carbon sequestration properties position it as a more sustainable and eco-friendly option in natural fiber production.
Strength and Durability Differences
Hemp fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength compared to jute fiber, making it more resistant to wear and tear under stress. It also demonstrates superior durability in harsh environmental conditions due to its natural resistance to UV light, mold, and rot. Jute fiber, while less strong, offers adequate durability for lightweight applications but degrades faster when exposed to moisture and abrasion.
Uses in Textiles and Industries
Hemp fiber offers superior durability and breathability, making it ideal for high-quality textiles such as clothing, upholstery, and eco-friendly fabrics. Jute fiber is extensively used in coarse textiles like sacks, bags, and carpet backing due to its affordability and strong tensile strength. Both fibers find applications in industries including automotive composites, geotextiles, and home furnishings, with hemp favored for premium, sustainable materials and jute for cost-effective, heavy-duty products.
Biodegradability and Eco-Friendliness
Hemp fiber exhibits superior biodegradability compared to jute fiber, breaking down naturally within a shorter timeframe and leaving minimal environmental impact. Both fibers are eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic materials, but hemp requires less water and fewer pesticides during cultivation, enhancing its sustainability profile. The higher tensile strength and durability of hemp fiber also contribute to longer product life cycles, reducing waste overall.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber generally commands a higher cost than jute fiber due to its superior durability and processing requirements, making it a premium option in textile and industrial applications. Jute fiber benefits from widespread cultivation in regions like India and Bangladesh, resulting in greater market availability and lower prices driven by abundant supply and established production infrastructure. The price variance and availability directly influence their selection in eco-friendly packaging, ropes, and composite materials manufacturing.
Processing Techniques and Challenges
Hemp fiber processing involves decortication, where the stalk is crushed and fibers are separated from the woody core, demanding careful retting to avoid fiber damage, which poses significant challenges in uniform quality. Jute fiber processing primarily uses water retting, submerging stalks in water to soften and separate fibers, but this method faces environmental concerns and longer processing times. Both fibers require efficient drying to prevent microbial growth, with hemp offering stronger durability while jute remains more affordable and easier to process at scale.
Future Trends in Hemp and Jute Fiber
Hemp fiber is gaining momentum in sustainable industries due to its superior strength, faster growth cycle, and lower environmental impact compared to jute fiber. Innovations in biodegradable composites and textile technologies are driving future market expansion for hemp fiber, especially in automotive and fashion sectors. Meanwhile, jute fiber maintains steady demand through eco-friendly packaging and home decor, with emerging trends focusing on enhanced fiber processing and blending techniques to improve durability and versatility.
Hemp Fiber vs Jute Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com