Eco-friendly fibers, derived from renewable resources and produced through sustainable processes, significantly reduce environmental impact compared to conventional fibers, which often rely on synthetic materials and chemical-intensive methods. These sustainable fibers biodegrade more efficiently, minimizing pollution and resource depletion. Choosing eco-friendly fibers supports a circular economy by promoting reduced carbon emissions, water conservation, and healthier ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
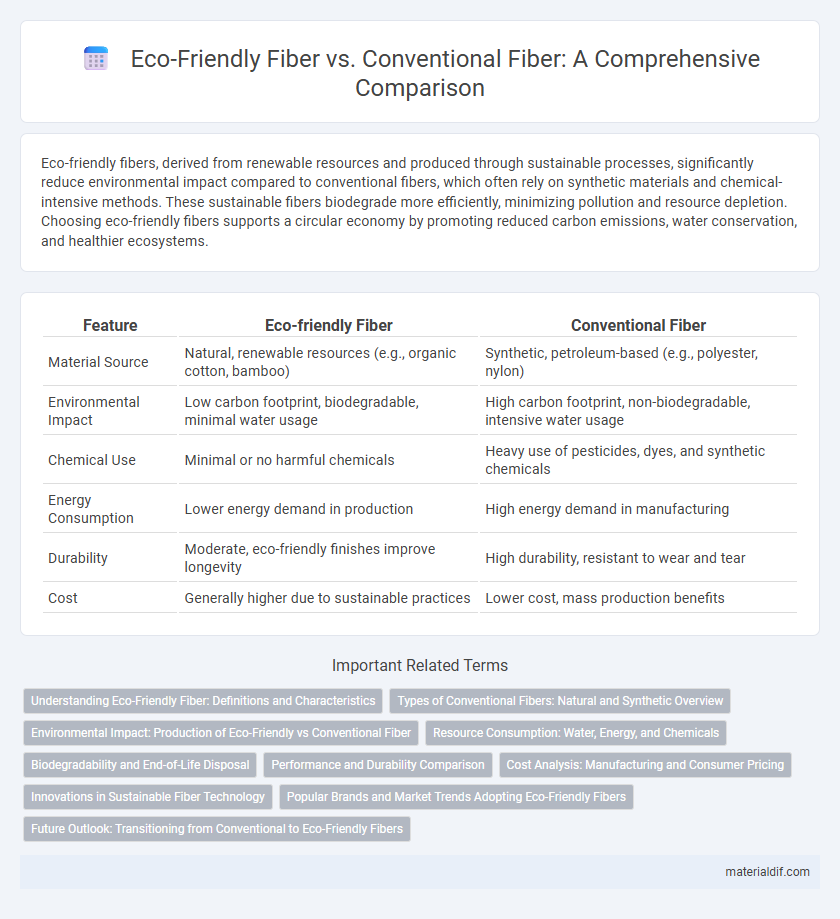
| Feature | Eco-friendly Fiber | Conventional Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, renewable resources (e.g., organic cotton, bamboo) | Synthetic, petroleum-based (e.g., polyester, nylon) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, minimal water usage | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable, intensive water usage |
| Chemical Use | Minimal or no harmful chemicals | Heavy use of pesticides, dyes, and synthetic chemicals |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy demand in production | High energy demand in manufacturing |
| Durability | Moderate, eco-friendly finishes improve longevity | High durability, resistant to wear and tear |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable practices | Lower cost, mass production benefits |
Understanding Eco-Friendly Fiber: Definitions and Characteristics
Eco-friendly fiber refers to textile fibers produced through sustainable processes that minimize environmental impact, such as organic cotton, bamboo, hemp, and recycled polyester. These fibers are characterized by reduced water usage, lower carbon emissions, and avoidance of harmful chemicals compared to conventional fibers like traditional cotton and synthetic polyester. Understanding eco-friendly fiber involves recognizing their biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and contribution to reducing textile industry pollution.
Types of Conventional Fibers: Natural and Synthetic Overview
Conventional fibers include natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk, which are biodegradable but often require significant water and pesticide use during cultivation. Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic are derived from petrochemicals, offering durability and cost-effectiveness but contributing to microplastic pollution and non-biodegradability. Evaluating these types highlights environmental challenges in water consumption, chemical use, and waste management compared to eco-friendly fiber alternatives.
Environmental Impact: Production of Eco-Friendly vs Conventional Fiber
Eco-friendly fibers such as organic cotton, hemp, and bamboo have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to conventional fibers like polyester and conventional cotton, which rely heavily on synthetic chemicals and pesticides. The production of eco-friendly fibers reduces water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions while promoting soil health and biodiversity. Conventional fiber manufacturing generates high levels of pollution, including toxic waste and microplastics, contributing to environmental degradation and climate change.
Resource Consumption: Water, Energy, and Chemicals
Eco-friendly fiber production significantly reduces resource consumption by using up to 90% less water compared to conventional fiber manufacturing, minimizing environmental impact. Energy use is also optimized through renewable sources and efficient processing technologies, leading to lower carbon emissions. Chemical inputs in eco-friendly fibers are drastically decreased or replaced with biodegradable alternatives, reducing pollution and promoting sustainability in the textile industry.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Disposal
Eco-friendly fibers demonstrate superior biodegradability compared to conventional fibers, breaking down naturally within months to years without leaving harmful residues. Conventional fibers, often synthetic, persist in the environment for decades, contributing to microplastic pollution and landfill accumulation. End-of-life disposal of eco-friendly fibers supports composting and reduces environmental impact, while conventional fibers require complex recycling processes or result in long-term waste.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Eco-friendly fibers, such as organic cotton and bamboo, exhibit comparable or superior performance and durability to conventional fibers by offering enhanced breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and resistance to wear and tear. Innovative bio-based fibers often achieve higher tensile strength and longer lifecycle under stress conditions, reducing frequent replacements and waste. These attributes make sustainable fibers a viable alternative without compromising fabric longevity or functional quality in textiles.
Cost Analysis: Manufacturing and Consumer Pricing
Eco-friendly fiber manufacturing involves higher initial costs due to sustainable raw materials and energy-efficient processes, resulting in production expenses approximately 15-25% above conventional fibers. Consumer pricing reflects these increased costs, with eco-friendly textiles typically retailing at a 20-30% premium compared to conventional fiber products. Long-term cost benefits include reduced environmental compliance fees and growing market demand for sustainable options, potentially offsetting higher upfront expenses.
Innovations in Sustainable Fiber Technology
Innovations in sustainable fiber technology are revolutionizing the textile industry by introducing eco-friendly fibers made from biodegradable materials, recycled plastics, and agricultural waste, significantly reducing environmental impact. Advanced processes such as enzymatic treatments and waterless dyeing techniques decrease chemical use and water consumption compared to conventional fiber production. These breakthroughs not only lower carbon emissions but also promote circular economy models through fiber recycling and upcycling, enhancing overall sustainability in fabric manufacturing.
Popular Brands and Market Trends Adopting Eco-Friendly Fibers
Popular brands such as Patagonia, Stella McCartney, and Adidas are leading the shift toward eco-friendly fibers like organic cotton, hemp, and recycled polyester, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable products. Market trends show a significant rise in the adoption of eco-friendly fibers, with global fiber production of sustainable materials expected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% through 2028. This shift aligns with corporate sustainability goals and environmental regulations pushing the textile industry toward reduced carbon footprints and less water-intensive manufacturing processes.
Future Outlook: Transitioning from Conventional to Eco-Friendly Fibers
The future outlook for fiber production emphasizes a significant shift from conventional fibers like polyester and nylon, which rely heavily on fossil fuels, toward eco-friendly fibers derived from renewable resources such as bamboo, organic cotton, and recycled materials. Innovations in sustainable fiber technologies, including biodegradable and low-water-impact fibers, are driving industry-wide adoption and regulatory support aimed at reducing carbon footprints and environmental degradation. As consumer demand grows for transparency and sustainability, investment in circular economy practices and eco-friendly fiber development is expected to accelerate, reshaping global textile supply chains.
Eco-friendly Fiber vs Conventional Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com