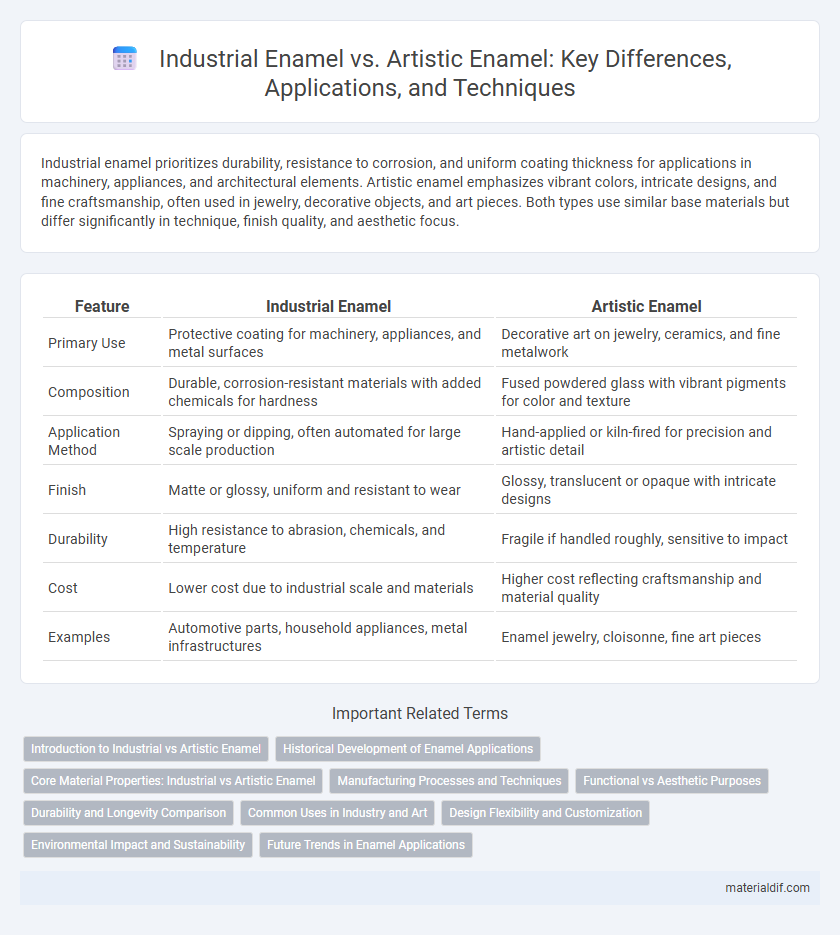
Industrial enamel prioritizes durability, resistance to corrosion, and uniform coating thickness for applications in machinery, appliances, and architectural elements. Artistic enamel emphasizes vibrant colors, intricate designs, and fine craftsmanship, often used in jewelry, decorative objects, and art pieces. Both types use similar base materials but differ significantly in technique, finish quality, and aesthetic focus.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Industrial Enamel | Artistic Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protective coating for machinery, appliances, and metal surfaces | Decorative art on jewelry, ceramics, and fine metalwork |
| Composition | Durable, corrosion-resistant materials with added chemicals for hardness | Fused powdered glass with vibrant pigments for color and texture |
| Application Method | Spraying or dipping, often automated for large scale production | Hand-applied or kiln-fired for precision and artistic detail |
| Finish | Matte or glossy, uniform and resistant to wear | Glossy, translucent or opaque with intricate designs |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and temperature | Fragile if handled roughly, sensitive to impact |
| Cost | Lower cost due to industrial scale and materials | Higher cost reflecting craftsmanship and material quality |
| Examples | Automotive parts, household appliances, metal infrastructures | Enamel jewelry, cloisonne, fine art pieces |
Introduction to Industrial vs Artistic Enamel
Industrial enamel is designed for durability and corrosion resistance, commonly used in automotive, appliance, and architectural applications where protective coatings are essential. Artistic enamel emphasizes aesthetic qualities, enabling vibrant colors and intricate designs on jewelry, decorative objects, and fine art pieces. Understanding the differences involves recognizing industrial enamel's focus on functionality and longevity versus artistic enamel's priority on color vibrancy and visual expression.
Historical Development of Enamel Applications
Industrial enamel evolved during the 19th century with advances in mass production techniques, enabling durable coatings for machinery, cookware, and architectural elements that resisted corrosion and wear. Artistic enamel, tracing back to ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Byzantines, developed through meticulous handcrafting methods to create vibrant, decorative jewelry and religious artifacts. Both types of enamel reflect significant technological and cultural milestones, with industrial enamel prioritizing functionality and artistic enamel emphasizing intricate design and color richness.
Core Material Properties: Industrial vs Artistic Enamel
Industrial enamel exhibits superior hardness, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for coatings on machinery, appliances, and automotive parts. Artistic enamel prioritizes vivid color retention, translucency, and flexibility to support intricate designs on jewelry, decorative objects, and fine art. Both types use a glassy vitreous substance fused to metal, but industrial enamel emphasizes protective performance, while artistic enamel focuses on aesthetic qualities.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Industrial enamel manufacturing involves controlled processes such as continuous coating, kiln firing at high temperatures, and automated application to ensure durability and uniformity on metal surfaces. Artistic enamel techniques emphasize manual skill, including cloisonne, champleve, and painted enamel, with multiple layers of glass powder fused by precise kiln firing to create intricate designs. Both methods require specific temperature control, but industrial enamel prioritizes consistency and corrosion resistance, while artistic enamel focuses on aesthetic detail and color vibrancy.
Functional vs Aesthetic Purposes
Industrial enamel serves primarily functional purposes, offering durability, corrosion resistance, and heat protection for machinery, appliances, and automotive parts. Artistic enamel focuses on aesthetic appeal, emphasizing vibrant colors, intricate designs, and smooth finishes used in jewelry, decorative art, and fine crafts. Both types utilize similar enamel materials but differ significantly in application techniques and intended outcomes.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Industrial enamel offers superior durability with resistance to high temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Artistic enamel prioritizes aesthetic qualities, often incorporating delicate colors and intricate designs, which may reduce its longevity under harsh conditions. While industrial enamel typically achieves longer service life due to robust formulation, artistic enamel requires careful maintenance to preserve its visual appeal and structural integrity.
Common Uses in Industry and Art
Industrial enamel is primarily used for coating metal surfaces to provide corrosion resistance, durability, and heat resistance in applications such as automotive parts, machinery, and appliances. Artistic enamel is favored for decorative purposes, applied in jewelry, fine art, and ornamental objects to create vibrant, long-lasting color and intricate designs. Both types leverage the unique properties of enamel but serve distinct functions based on their formulation and application techniques.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Industrial enamel offers high durability and consistent finishes with limited design flexibility, primarily suited for large-scale applications requiring uniform results. Artistic enamel provides extensive customization options, enabling intricate designs, varied color palettes, and personal expression through handcrafting techniques. This versatility makes artistic enamel ideal for unique, detailed artworks and bespoke decorative projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Industrial enamel coatings often utilize synthetic chemicals and heavy metals, leading to higher environmental pollution and waste generation compared to artistic enamel. Artistic enamel typically employs natural minerals and traditional techniques, resulting in lower carbon footprints and enhanced sustainability. Choosing artistic enamel promotes eco-friendly practices by minimizing toxic emissions and supporting resource conservation.
Future Trends in Enamel Applications
Industrial enamel applications increasingly integrate advanced ceramic coatings that enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, targeting sectors like automotive and aerospace for long-term performance. Artistic enamel trends emphasize nano-pigments and customizable textures, enabling more vibrant and diverse creative expressions with improved longevity. Emerging smart enamel technologies combine functionality with aesthetics, promising innovations in heat regulation and self-cleaning surfaces across both industrial and artistic domains.
Industrial enamel vs artistic enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com