Electrostatic enamel application uses charged particles to improve coating adhesion and reduce overspray, resulting in a more uniform and efficient finish. Wet spray application involves spraying liquid enamel directly onto surfaces, which can lead to thicker coats but often requires more drying time and increased material waste. Choosing between these methods depends on factors like surface complexity, desired finish quality, and production efficiency.
Table of Comparison
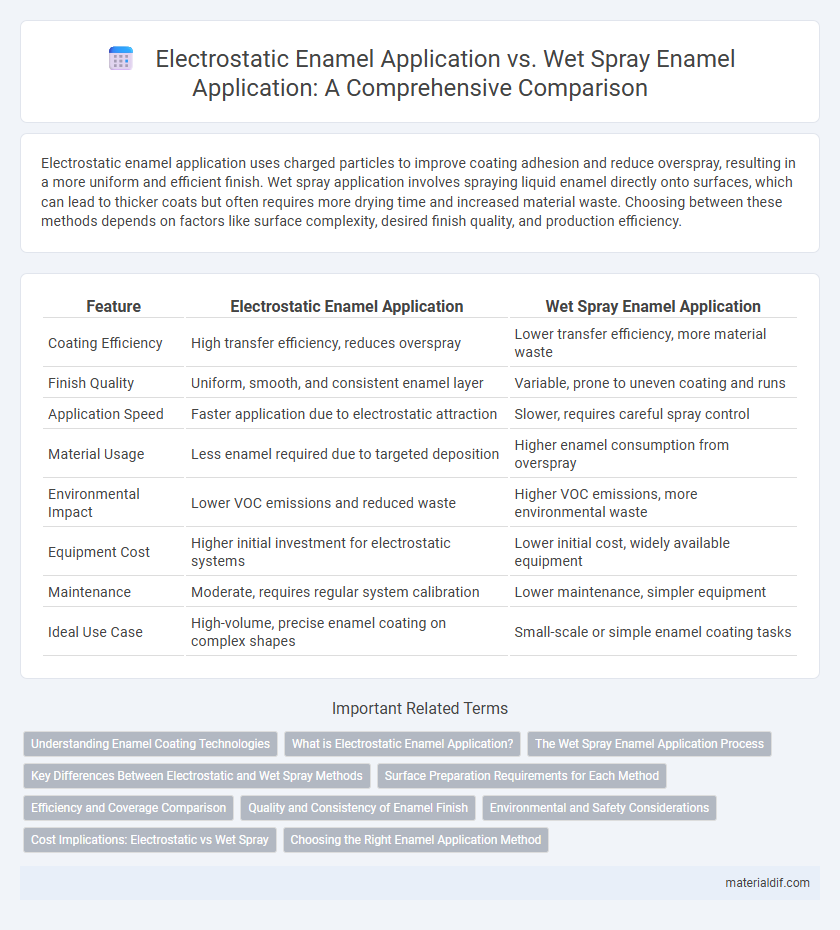
| Feature | Electrostatic Enamel Application | Wet Spray Enamel Application |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Efficiency | High transfer efficiency, reduces overspray | Lower transfer efficiency, more material waste |
| Finish Quality | Uniform, smooth, and consistent enamel layer | Variable, prone to uneven coating and runs |
| Application Speed | Faster application due to electrostatic attraction | Slower, requires careful spray control |
| Material Usage | Less enamel required due to targeted deposition | Higher enamel consumption from overspray |
| Environmental Impact | Lower VOC emissions and reduced waste | Higher VOC emissions, more environmental waste |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for electrostatic systems | Lower initial cost, widely available equipment |
| Maintenance | Moderate, requires regular system calibration | Lower maintenance, simpler equipment |
| Ideal Use Case | High-volume, precise enamel coating on complex shapes | Small-scale or simple enamel coating tasks |
Understanding Enamel Coating Technologies
Electrostatic enamel application utilizes charged particles to enhance paint adhesion, resulting in a uniform, durable coat with minimal overspray and waste. Wet spray application involves applying enamel in liquid form, requiring precise control to avoid drips and achieve even coverage, but it typically results in higher material usage and longer drying times. Understanding these enamel coating technologies helps optimize surface protection and finish quality based on project requirements and environmental considerations.
What is Electrostatic Enamel Application?
Electrostatic enamel application is a coating process that uses electrically charged particles to achieve a uniform enamel finish on metal surfaces. This method enhances adhesion and reduces overspray by attracting the enamel particles directly to the grounded substrate. The resulting coating is more durable, consistent, and environmentally friendly compared to traditional wet spray application.
The Wet Spray Enamel Application Process
The wet spray enamel application process involves atomizing enamel into fine droplets and spraying them onto the substrate, ensuring uniform coverage and strong adhesion. This method allows for precise control over film thickness and is ideal for complex geometries or large surface areas where consistent coating quality is critical. Compared to electrostatic enamel application, wet spray provides better compatibility with various enamel viscosities and reduces issues related to electrostatic interference or grounding.
Key Differences Between Electrostatic and Wet Spray Methods
Electrostatic enamel application utilizes charged particles that are attracted to the grounded metal surface, resulting in a uniform and high-transfer efficiency coating with minimal overspray. Wet spray application involves atomizing enamel into fine droplets sprayed onto the surface, allowing for versatile thickness control but often leading to higher material waste and lower transfer efficiency. The electrostatic method excels in precision and environmental impact reduction, while wet spray provides adaptability for complex shapes and larger surfaces.
Surface Preparation Requirements for Each Method
Electrostatic enamel application requires a meticulously clean and dry surface to ensure optimal adhesion and uniform coating, often involving degreasing and thorough abrasion to enhance surface energy. Wet spray application demands a similarly clean surface but is more tolerant of slight contaminants since the enamel's solvents aid in substrate bonding. Both methods prioritize rust removal and surface profile development, but electrostatic techniques necessitate stricter control to maximize the electrostatic forces enabling enamel particle attraction.
Efficiency and Coverage Comparison
Electrostatic enamel application delivers superior efficiency by using electrically charged particles that adhere uniformly to metal surfaces, minimizing overspray and material waste. Wet spray application often results in uneven coverage and higher consumption of enamel due to gravity-driven deposition and overspray losses. Overall, electrostatic application achieves better coverage with less enamel usage, making it more cost-effective and environmentally friendly for industrial coating processes.
Quality and Consistency of Enamel Finish
Electrostatic enamel application delivers a highly uniform and durable finish by using charged particles that adhere evenly to surfaces, minimizing overspray and ensuring consistent enamel thickness. Wet spray application can result in variable enamel coverage and potential runs or drips due to manual control, affecting the overall quality and smoothness of the finish. The precision of electrostatic technology significantly enhances the enamel's appearance and longevity compared to traditional wet spray methods.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Electrostatic enamel application significantly reduces overspray and material waste, minimizing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to wet spray methods, leading to a lower environmental impact. The electrostatic process also improves worker safety by reducing airborne enamel particles and exposure to hazardous solvents common in wet spray application. Enhanced transfer efficiency in electrostatic systems supports compliance with stringent environmental regulations and occupational health standards.
Cost Implications: Electrostatic vs Wet Spray
Electrostatic enamel application reduces paint wastage by up to 30% compared to wet spray, leading to significant material cost savings. Wet spray application often requires higher solvent use and generates more overspray, increasing environmental disposal expenses and overall operational costs. Although electrostatic systems demand higher initial investment, their efficiency and reduced waste contribute to lower long-term application costs.
Choosing the Right Enamel Application Method
Electrostatic enamel application provides superior adhesion and uniform coating thickness by using charged particles that attract enamel powders to the substrate, reducing overspray and material waste. Wet spray application offers versatility for complex shapes and larger surfaces by spraying liquid enamel, ensuring smooth finishes and quick drying times. Selecting the right enamel application method depends on factors like part geometry, production volume, and desired finish quality, with electrostatic being ideal for precision and efficiency, while wet spray suits diverse shapes and larger batches.
Electrostatic enamel application vs Wet spray application Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com