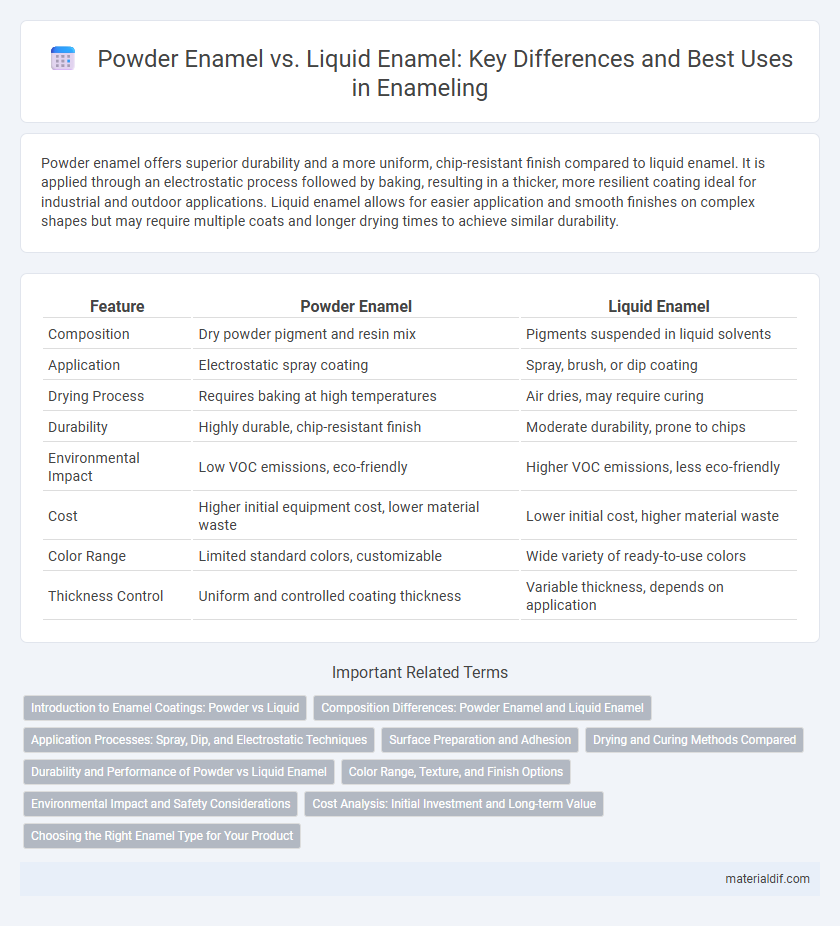
Powder enamel offers superior durability and a more uniform, chip-resistant finish compared to liquid enamel. It is applied through an electrostatic process followed by baking, resulting in a thicker, more resilient coating ideal for industrial and outdoor applications. Liquid enamel allows for easier application and smooth finishes on complex shapes but may require multiple coats and longer drying times to achieve similar durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Powder Enamel | Liquid Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Dry powder pigment and resin mix | Pigments suspended in liquid solvents |
| Application | Electrostatic spray coating | Spray, brush, or dip coating |
| Drying Process | Requires baking at high temperatures | Air dries, may require curing |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant finish | Moderate durability, prone to chips |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, eco-friendly | Higher VOC emissions, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost, lower material waste | Lower initial cost, higher material waste |
| Color Range | Limited standard colors, customizable | Wide variety of ready-to-use colors |
| Thickness Control | Uniform and controlled coating thickness | Variable thickness, depends on application |
Introduction to Enamel Coatings: Powder vs Liquid
Powder enamel coatings consist of finely ground particles that are electrostatically applied and cured under heat to form a durable, corrosion-resistant layer, offering superior thickness and environmental benefits compared to liquid enamel. Liquid enamel, available in solvent-based or water-based formulations, is applied via brush, spray, or dip, providing excellent adhesion and a smooth finish but often requires solvents and longer drying times. Choosing between powder and liquid enamel depends on application methods, substrate compatibility, performance requirements, and environmental considerations.
Composition Differences: Powder Enamel and Liquid Enamel
Powder enamel consists primarily of finely ground glass particles combined with pigments and resins, which are melted onto surfaces through high-temperature curing. Liquid enamel, on the other hand, is composed of suspended enamel powders in a solvent base, allowing for easier application but requiring solvent evaporation during drying. The key compositional difference lies in powder enamel's solid particulate form versus liquid enamel's solvent-based suspension, affecting their application methods and curing processes.
Application Processes: Spray, Dip, and Electrostatic Techniques
Powder enamel and liquid enamel differ significantly in application processes such as spray, dip, and electrostatic techniques. Powder enamel is commonly applied using electrostatic spray methods, which provide uniform coating thickness and reduce waste, while liquid enamel is often applied via dipping or traditional spray painting for smoother finishes on complex shapes. The choice of application technique impacts adhesion, durability, and aesthetic quality in industrial and artistic enamel coatings.
Surface Preparation and Adhesion
Powder enamel requires thorough surface preparation, often involving sandblasting or grinding, to achieve optimal adhesion and durability. Liquid enamel, on the other hand, demands a clean, rust-free surface typically prepared by degreasing and light sanding to ensure proper bonding. Both types rely heavily on meticulous surface treatment to enhance coating performance and longevity.
Drying and Curing Methods Compared
Powder enamel requires curing through baking at high temperatures typically between 160-200degC, ensuring a hard, durable finish that seals the coated surface effectively. Liquid enamel dries at ambient conditions or with low heat, relying on solvent evaporation, which results in longer drying times but allows for touch-up and easier application on intricate surfaces. The high-heat curing of powder enamel provides superior adhesion and chemical resistance, while liquid enamel's air-drying offers flexibility and simplicity in repair or layered applications.
Durability and Performance of Powder vs Liquid Enamel
Powder enamel offers superior durability compared to liquid enamel due to its thicker coating and resistance to chipping, scratching, and fading under high temperatures. Liquid enamel provides excellent adhesion and smooth finishes but may require multiple layers to achieve the robustness of powder enamel. Performance-wise, powder enamel excels in industrial applications requiring long-lasting protection, while liquid enamel is preferable for detailed or artistic work demanding fine control and color variability.
Color Range, Texture, and Finish Options
Powder enamel offers a broader color range with vibrant, durable pigments ideal for industrial applications, while liquid enamel provides more nuanced shades suitable for artistic and detailed work. Texture in powder enamel is typically smooth and uniform due to electrostatic application, whereas liquid enamel allows varied textures from glossy to matte depending on the layering and drying process. Finish options for powder enamel include high-gloss, satin, and textured surfaces, while liquid enamel excels in achieving intricate finishes with effects like crackle, speckled, or translucent coatings.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Powder enamel offers a lower environmental impact due to its solvent-free formulation, reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to liquid enamel, which often contains harmful solvents. Safety considerations favor powder enamel as it minimizes exposure to toxic fumes and flammable substances during application, enhancing workplace safety. Liquid enamel requires careful handling and ventilation to mitigate health risks, making powder enamel a more eco-friendly and safer alternative.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Value
Powder enamel typically demands a higher initial investment due to specialized equipment costs, but its durability and minimal waste contribute to lower long-term expenses. Liquid enamel requires less upfront capital and simpler application methods, making it cost-effective for small-scale projects despite higher material and maintenance costs over time. Analyzing production volume and longevity needs helps determine the most economical choice between powder and liquid enamel options.
Choosing the Right Enamel Type for Your Product
Powder enamel offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications where longevity and strength are crucial. Liquid enamel provides greater versatility and ease of application, suitable for intricate designs and smaller-scale production. Selecting the right enamel type depends on factors such as substrate compatibility, desired finish quality, and production volume requirements.
Powder enamel vs liquid enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com