Vitreous enamel offers a durable, glass-like coating created by fusing powdered glass to metal at high temperatures, providing exceptional resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemicals. Powder coating, a dry finishing process using electrostatically applied polyester or epoxy powders, delivers a flexible, uniform layer that is easier to apply and repair but generally less resistant to extreme conditions. Choosing between vitreous enamel and powder coating depends on the desired durability, application environment, and aesthetic requirements of the project.
Table of Comparison
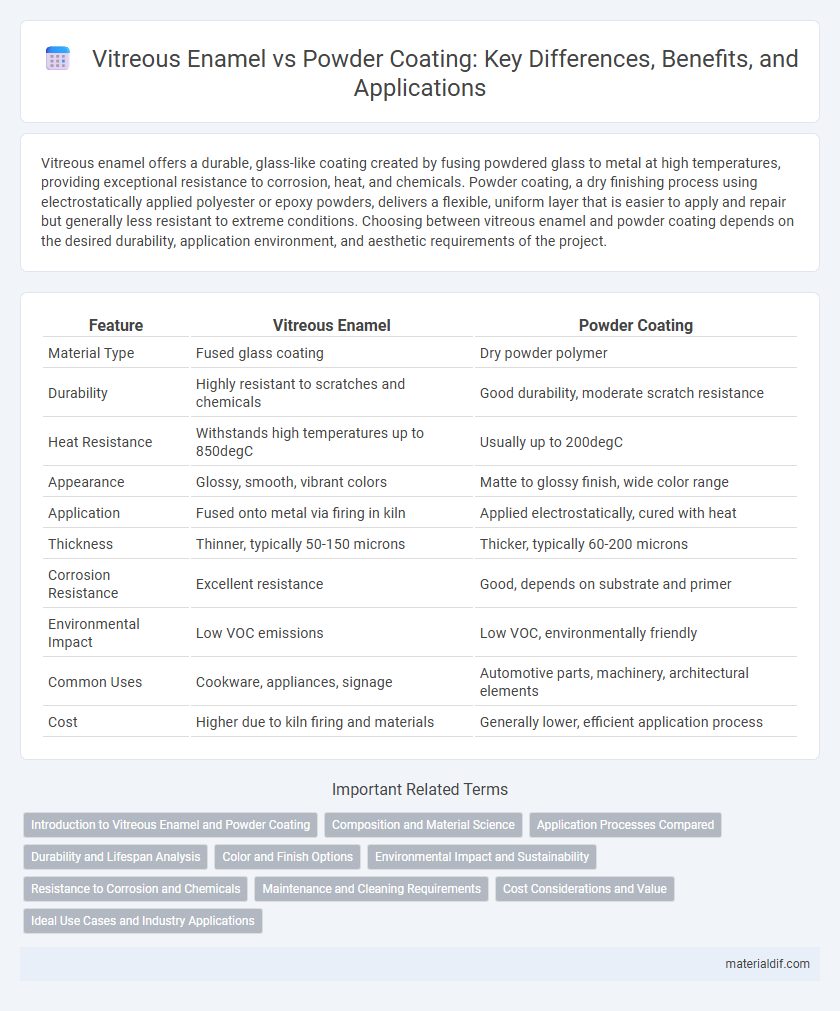
| Feature | Vitreous Enamel | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fused glass coating | Dry powder polymer |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches and chemicals | Good durability, moderate scratch resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures up to 850degC | Usually up to 200degC |
| Appearance | Glossy, smooth, vibrant colors | Matte to glossy finish, wide color range |
| Application | Fused onto metal via firing in kiln | Applied electrostatically, cured with heat |
| Thickness | Thinner, typically 50-150 microns | Thicker, typically 60-200 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance | Good, depends on substrate and primer |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions | Low VOC, environmentally friendly |
| Common Uses | Cookware, appliances, signage | Automotive parts, machinery, architectural elements |
| Cost | Higher due to kiln firing and materials | Generally lower, efficient application process |
Introduction to Vitreous Enamel and Powder Coating
Vitreous enamel is a smooth, durable coating created by fusing powdered glass to a substrate through high-temperature firing, offering superior resistance to heat, corrosion, and UV radiation. Powder coating involves applying a dry powder, typically thermoplastic or thermoset polymer, which is then cured under heat to form a protective, flexible finish ideal for metals exposed to outdoor environments. Both finishes enhance surface protection, but vitreous enamel provides a glass-like, chemically inert layer, while powder coating offers thicker, impact-resistant coverage with a broader color range.
Composition and Material Science
Vitreous enamel is composed of finely ground glass fused to a metal substrate at high temperatures, creating a durable, inert, and smooth glassy coating that resists corrosion and heat. In contrast, powder coating consists of thermoplastic or thermoset polymer powders that melt and cure to form a protective and decorative layer, relying on polymer chemistry rather than inorganic glass composition. The fundamental material science distinction lies in vitreous enamel's inorganic vitreous nature versus powder coating's organic polymer matrix, affecting their thermal stability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties.
Application Processes Compared
Vitreous enamel application involves fusing powdered glass onto metal at high temperatures, creating a durable, smooth, and chemically resistant coating ideal for cookware, appliances, and architectural panels. In contrast, powder coating applies thermoplastic or thermoset polymer powders that are electrostatically sprayed and cured under heat, offering a wide range of colors and textures primarily used for automotive, industrial, and outdoor furniture finishes. Vitreous enamel requires precise temperature control and longer curing times, while powder coating allows faster production cycles with lower application temperatures.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Vitreous enamel provides superior durability compared to powder coating due to its glass-like ceramic composition, which resists scratches, corrosion, and UV damage over extended periods. Its lifespan often exceeds 20 to 50 years, maintaining color vibrancy and structural integrity under harsh environmental conditions. Powder coating typically offers 10 to 15 years of protection but may chip or fade faster when exposed to extreme weather or mechanical wear.
Color and Finish Options
Vitreous enamel offers a vibrant, glossy finish with exceptional color depth and durability, resistant to fading and scratching over time. Powder coating provides a broader range of matte and textured finishes but may lack the high-gloss brilliance and chemical resistance characteristic of enamel. Both options deliver strong adhesion and corrosion protection, yet vitreous enamel's color palette remains unmatched for long-lasting brightness and smooth, glass-like surface.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vitreous enamel offers superior environmental benefits compared to powder coating due to its long-lasting durability and resistance to corrosion, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. Its raw materials are primarily natural minerals, and the vitrification process produces fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Powder coating, while efficient in application, relies on synthetic resins and often requires energy-intensive curing, contributing to higher environmental impact over the product lifecycle.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemicals
Vitreous enamel offers superior resistance to corrosion and chemicals compared to powder coating due to its glass-like, non-porous surface that forms a durable barrier against acids, alkalis, and moisture. Powder coating, while providing good protection against physical abrasion, is more susceptible to degradation from harsh chemicals and prolonged exposure to corrosive environments. This makes vitreous enamel the preferred choice for applications requiring long-term chemical resistance and durability.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Vitreous enamel offers superior resistance to scratches, UV rays, and chemical exposure, making its maintenance requirements minimal and cleaning straightforward with mild detergents and soft cloths. Powder coating, while durable, is more susceptible to chipping and fading over time, necessitating more frequent touch-ups and careful cleaning to prevent surface degradation. The long-lasting nature of vitreous enamel reduces the frequency and intensity of maintenance compared to powder coating, preserving aesthetic and functional qualities with less effort.
Cost Considerations and Value
Vitreous enamel offers superior durability and longevity compared to powder coating, often justifying its higher initial cost through reduced maintenance and replacement expenses. Powder coating generally provides a lower upfront investment with faster application times but may require more frequent touch-ups or recoating, impacting long-term value. When evaluating cost considerations, vitreous enamel's resistance to corrosion, heat, and UV exposure enhances its overall value despite a steeper price point.
Ideal Use Cases and Industry Applications
Vitreous enamel provides a durable, heat-resistant finish ideal for cookware, architectural panels, and industrial equipment exposed to high temperatures and corrosive environments. Powder coating suits applications requiring cost-effective, abrasion-resistant surfaces such as automotive parts, household appliances, and outdoor furniture. Industries like construction, manufacturing, and kitchenware benefit from selecting vitreous enamel for longevity and chemical resistance, while powder coating is preferred for versatile, aesthetic surface protection.
vitreous enamel vs powder coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com