Raw cork features a natural, untreated texture that retains its original porous structure, making it highly breathable but more prone to wear and staining. Treated cork undergoes processes such as sealing or coating, enhancing its durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal while maintaining its lightweight and eco-friendly qualities. Choosing between raw and treated cork depends on the specific application requirements, balancing natural authenticity against enhanced performance.
Table of Comparison
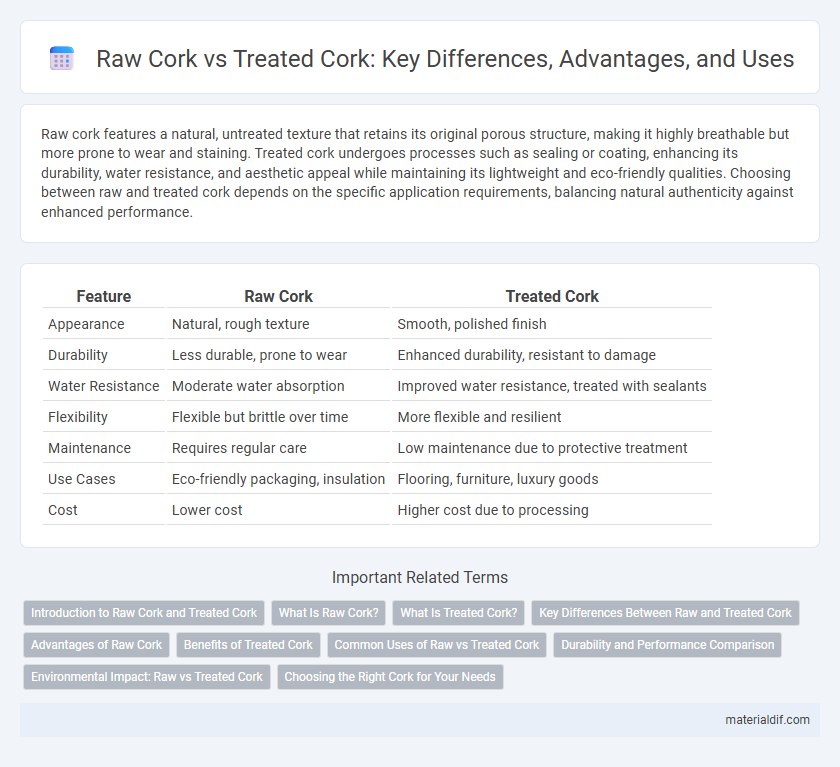
| Feature | Raw Cork | Treated Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Natural, rough texture | Smooth, polished finish |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to wear | Enhanced durability, resistant to damage |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water absorption | Improved water resistance, treated with sealants |
| Flexibility | Flexible but brittle over time | More flexible and resilient |
| Maintenance | Requires regular care | Low maintenance due to protective treatment |
| Use Cases | Eco-friendly packaging, insulation | Flooring, furniture, luxury goods |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Raw Cork and Treated Cork
Raw cork is the natural bark stripped directly from cork oak trees, characterized by its porous texture and high elasticity, making it ideal for eco-friendly applications. Treated cork undergoes various processes such as grinding, boiling, and bonding to enhance durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal for use in flooring, insulation, and fashion products. Understanding the differences between raw and treated cork is essential for selecting the right material based on performance requirements and sustainability goals.
What Is Raw Cork?
Raw cork is the natural bark harvested from the cork oak tree without undergoing any chemical or mechanical treatments, preserving its original texture and properties. It offers excellent breathability, natural insulation, and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for sustainable packaging and craft projects. Unlike treated cork, raw cork retains its organic composition, enhancing its biodegradability and eco-friendly appeal.
What Is Treated Cork?
Treated cork is raw cork that has undergone processes such as washing, boiling, or coating to enhance durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal. This treatment removes impurities and improves the cork's texture, making it suitable for various applications like flooring, insulation, and crafts. Unlike raw cork, treated cork offers increased longevity and performance in both indoor and outdoor environments.
Key Differences Between Raw and Treated Cork
Raw cork is harvested directly from the cork oak tree, maintaining its natural, porous structure and moisture content, which makes it lightweight and flexible but more susceptible to damage and decay. Treated cork undergoes processes such as boiling, drying, and surface treatments that enhance its durability, resistance to moisture, and stability while preserving its eco-friendly and insulating properties. Key differences include treated cork's improved longevity and performance in construction and design applications compared to the more vulnerable, untreated raw cork.
Advantages of Raw Cork
Raw cork offers superior breathability and natural insulation, making it an ideal choice for eco-friendly building materials and sustainable fashion. Its untreated state preserves the cork's inherent elasticity and moisture resistance, enhancing durability in various applications. Compared to treated cork, raw cork maintains a chemical-free composition, promoting healthier indoor air quality and environmental safety.
Benefits of Treated Cork
Treated cork offers enhanced durability and resistance to moisture compared to raw cork, making it ideal for flooring and insulation in humid environments. Its improved structural integrity reduces susceptibility to cracking and insect damage, extending the lifespan of cork products. The treatment process also allows for better adhesion in composite materials, increasing versatility in construction and design applications in Cork.
Common Uses of Raw vs Treated Cork
Raw cork, known for its natural texture and flexibility, is commonly used in insulation, bulletin boards, and flooring underlayment due to its soundproofing and cushioning properties. Treated cork undergoes processes like bleaching or lacquering, making it ideal for wine stoppers, decorative wall tiles, and fashion accessories where durability and aesthetic appeal are important. Both forms harness cork's lightweight, water-resistant qualities, but treated cork offers enhanced protection and longevity for more refined applications.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Raw cork, harvested directly from the cork oak tree, retains its natural properties including high elasticity and water resistance but is more susceptible to wear and environmental damage over time. Treated cork undergoes processes such as thermal stabilization, chemical treatment, or lamination, significantly enhancing its durability, resistance to moisture, and overall performance in applications like flooring and insulation. The treatment improves cork's mechanical strength and lifespan, making it a superior choice for products requiring long-term resilience and consistent aesthetic quality.
Environmental Impact: Raw vs Treated Cork
Raw cork is harvested directly from the cork oak tree's bark, preserving natural properties and requiring minimal processing, which results in a lower carbon footprint and less water consumption. Treated cork undergoes chemical or physical modifications to enhance durability and appearance, often involving solvents or additives that can introduce pollutants and increase energy use during production. The environmental impact of raw cork remains significantly lower due to its biodegradability and minimal processing compared to treated cork products.
Choosing the Right Cork for Your Needs
Raw cork maintains its natural, porous texture ideal for sound insulation and breathability, while treated cork undergoes processes like sealing or dyeing to enhance durability and resistance to moisture. Selecting the right cork depends on application requirements; raw cork suits eco-friendly interior designs and craft projects, whereas treated cork is preferred for high-traffic flooring and exterior use due to its improved longevity. Understanding the differences in maintenance and performance ensures optimal functionality and aesthetic appeal for your cork-based solutions.
Raw Cork vs Treated Cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com