A Cork Gasket offers excellent compressibility and conforms well to irregular surfaces, making it ideal for sealing applications with low to moderate pressure and temperature. Rubber Gaskets provide superior elasticity and chemical resistance, suitable for environments with dynamic movement and exposure to oils or chemicals. Choosing between Cork and Rubber Gaskets depends on the specific sealing requirements, including pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
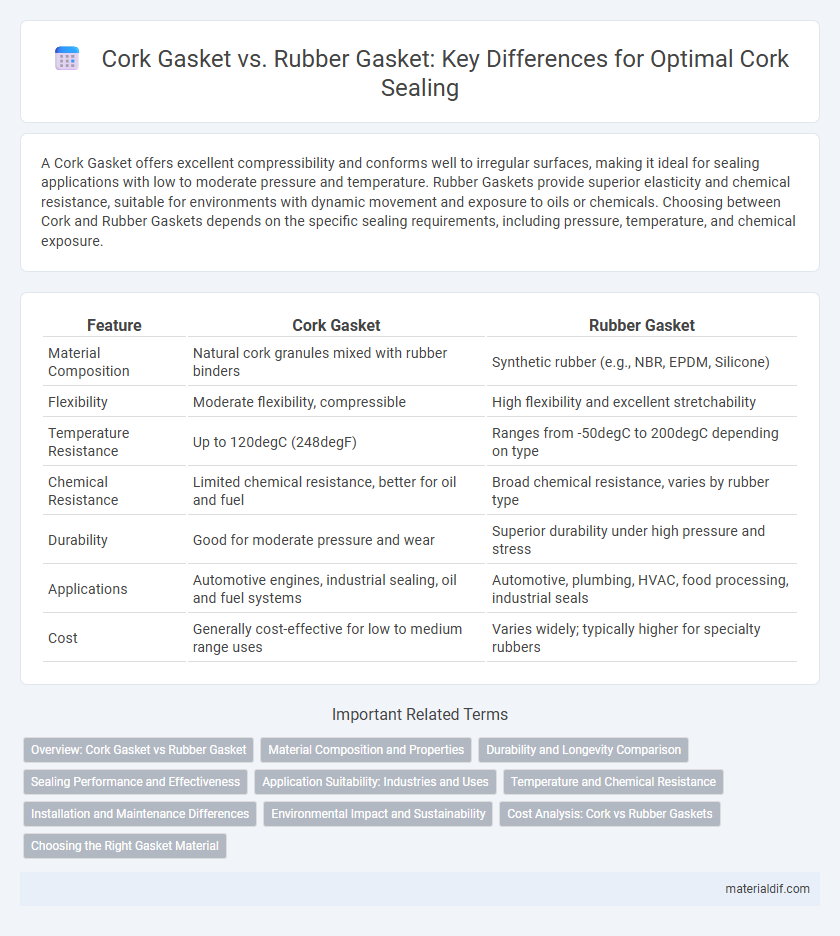
| Feature | Cork Gasket | Rubber Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural cork granules mixed with rubber binders | Synthetic rubber (e.g., NBR, EPDM, Silicone) |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, compressible | High flexibility and excellent stretchability |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Ranges from -50degC to 200degC depending on type |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited chemical resistance, better for oil and fuel | Broad chemical resistance, varies by rubber type |
| Durability | Good for moderate pressure and wear | Superior durability under high pressure and stress |
| Applications | Automotive engines, industrial sealing, oil and fuel systems | Automotive, plumbing, HVAC, food processing, industrial seals |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for low to medium range uses | Varies widely; typically higher for specialty rubbers |
Overview: Cork Gasket vs Rubber Gasket
Cork gaskets offer natural compressibility and excellent sealing properties under low to moderate pressure, making them ideal for applications involving oils and fuels. Rubber gaskets provide superior flexibility, resistance to weathering, and durability under high-pressure conditions, commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery. The choice between cork and rubber gaskets depends on specific requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress in sealing applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Cork gaskets are made from natural cork granules combined with a binder, offering excellent compressibility, flexibility, and resistance to oils and solvents, making them ideal for sealing applications requiring conformability and vibration dampening. Rubber gaskets, typically composed of synthetic elastomers such as Nitrile, EPDM, or Neoprene, provide superior elastic recovery, chemical resistance, and durability under pressure and temperature variations. The choice between cork and rubber gaskets depends on specific material properties like compressibility, chemical compatibility, and environmental resistance essential for sealing performance in automotive, industrial, or plumbing systems.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cork gaskets offer excellent compressibility and resistance to oils, making them ideal for sealing applications with moderate pressure and temperature but tend to degrade faster under continuous exposure to heat and chemicals compared to rubber gaskets. Rubber gaskets provide superior durability and longevity, with enhanced resistance to extreme temperatures, weathering, and chemical exposure, ensuring a longer service life in demanding environments. Selecting between cork and rubber gaskets depends on the specific application requirements, where rubber gaskets generally outperform cork gaskets in terms of extended durability and lifespan.
Sealing Performance and Effectiveness
Cork gaskets offer excellent compressibility and conform well to irregular surfaces, making them highly effective for sealing applications involving low to moderate pressure and temperatures up to 150degC. Rubber gaskets, particularly those made from materials like EPDM or Nitrile, provide superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, excelling in sealing performance under dynamic conditions and higher pressure environments. Selecting cork versus rubber gaskets depends on the sealing requirements, where cork is ideal for static, low-pressure seals, and rubber ensures enhanced effectiveness for dynamic, high-pressure, and chemically aggressive applications.
Application Suitability: Industries and Uses
Cork gaskets excel in applications requiring compressibility and flexibility, commonly found in automotive, plumbing, and HVAC industries due to their ability to conform to irregular surfaces and resist oil and gasoline. Rubber gaskets offer superior chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for chemical processing, food and beverage, and water treatment industries where exposure to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures is frequent. Selecting between cork and rubber gaskets depends on specific operational conditions, with cork preferred for sealing in static applications and rubber favored for dynamic environments requiring elasticity and longevity.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
Cork gaskets offer moderate temperature resistance, typically up to 250degF (121degC), making them suitable for low to medium-heat applications, but they degrade when exposed to harsh chemicals. Rubber gaskets withstand higher temperatures, often up to 400degF (204degC), and provide superior chemical resistance against oils, solvents, and acids, making them essential in industrial settings. Choosing between cork and rubber gaskets depends on the specific temperature range and chemical exposure needed for the sealing task.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Cork gaskets offer easier installation due to their flexibility and compressibility, allowing them to conform well to irregular surfaces without requiring additional adhesives. Rubber gaskets, while slightly more rigid, require careful alignment and sometimes the use of lubricants or sealants to ensure a proper fit and prevent leaks. Maintenance-wise, cork gaskets tend to degrade faster under heat and oil exposure, necessitating more frequent replacement, whereas rubber gaskets provide longer-lasting durability and resistance to various chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cork gaskets, derived from natural cork oak bark, offer a sustainable alternative to rubber gaskets due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, reducing landfill waste and environmental toxins. Rubber gaskets, often made from synthetic elastomers, contribute to higher carbon emissions and waste disposal challenges due to their non-biodegradable nature and reliance on petroleum-based materials. Cork's low environmental footprint and recyclability make it a preferable choice for eco-conscious industries seeking to minimize ecological impact.
Cost Analysis: Cork vs Rubber Gaskets
Cork gaskets typically offer a lower initial cost compared to rubber gaskets, making them a budget-friendly option for many applications. However, rubber gaskets provide better durability and resistance to chemicals and temperature variations, potentially reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Evaluating overall cost effectiveness involves balancing cork's affordability against rubber's extended lifespan and performance reliability in industrial settings.
Choosing the Right Gasket Material
Choosing the right gasket material between cork gasket and rubber gasket depends on the application's temperature resistance, compressibility, and chemical exposure. Cork gaskets excel in low to medium pressure sealing with excellent compressibility and flexibility, making them ideal for oil and fuel-resistant applications. Rubber gaskets offer superior durability, higher temperature tolerance, and better chemical resistance for demanding industrial settings in Cork's manufacturing and automotive sectors.
Cork Gasket vs Rubber Gasket Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com