Cork granules consist of larger, irregular pieces of cork that provide excellent insulation and drainage properties, making them ideal for construction and horticultural applications. Cork powder, on the other hand, is finely ground cork used primarily as a filler material or in producing lightweight composites and cork-based adhesives. The choice between cork granules and cork powder depends on the desired texture, application, and performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
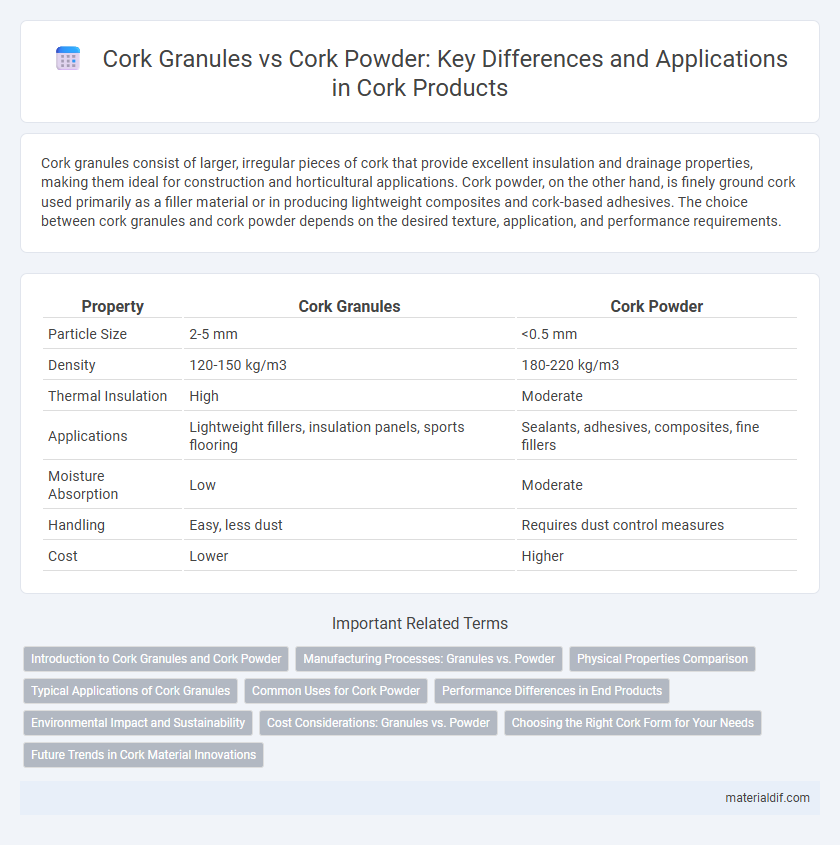
| Property | Cork Granules | Cork Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 2-5 mm | <0.5 mm |
| Density | 120-150 kg/m3 | 180-220 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | High | Moderate |
| Applications | Lightweight fillers, insulation panels, sports flooring | Sealants, adhesives, composites, fine fillers |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Handling | Easy, less dust | Requires dust control measures |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cork Granules and Cork Powder
Cork granules and cork powder are two processed forms of natural cork derived from the bark of the cork oak tree. Cork granules consist of small, irregularly shaped particles typically used in insulation, flooring, and composite materials, offering durability and thermal resistance. Cork powder, which is a finer, dust-like material, is often utilized in adhesives, sealants, and cosmetics due to its smooth texture and binding properties.
Manufacturing Processes: Granules vs. Powder
Cork granules are produced by mechanically shredding whole cork bark into coarse particles, retaining irregular shapes ideal for insulation and composite materials. Cork powder results from further grinding or milling these granules into fine, uniform particles, primarily used in binders and sealants. The manufacturing process for granules emphasizes controlled size reduction to preserve structural integrity, while powder production involves milling that increases surface area for enhanced binding properties.
Physical Properties Comparison
Cork granules exhibit larger particle sizes ranging from 1 to 4 mm, providing better insulation and vibration absorption compared to cork powder, which consists of fine particles below 0.5 mm. Granules maintain higher porosity and elasticity, enhancing durability and cushioning performance in flooring and composite materials. Conversely, cork powder offers smoother texture and higher surface area, ideal for adhesives and fillers but with reduced mechanical strength relative to granules.
Typical Applications of Cork Granules
Cork granules, with their coarse texture, are primarily used in applications such as insulation panels, decorative aggregates, and as fillers in composites for enhanced durability and thermal efficiency. Unlike cork powder, which is finer and often utilized in adhesives, sealants, or as a raw material in agglomerated cork production, cork granules provide superior structural support and water resistance in construction and flooring materials. Typical industries employing cork granules include building construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing, where their natural elasticity and lightweight properties improve product performance.
Common Uses for Cork Powder
Cork powder is commonly used in agriculture as a soil conditioner to improve aeration and water retention, enhancing plant growth. In the textile industry, cork powder is incorporated into fabrics to create lightweight, durable, and water-resistant materials. Additionally, cork powder serves as an eco-friendly filler in the manufacturing of composite materials and cosmetics, leveraging its fine granularity and natural properties.
Performance Differences in End Products
Cork granules provide superior insulation and durability in end products compared to cork powder, which tends to offer finer texture but lower structural strength. Products made with cork granules exhibit enhanced thermal and acoustic performance, making them ideal for flooring and wall panels. Meanwhile, cork powder is preferred in composite materials where smooth surface finish and moldability are prioritized over mechanical resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cork granules offer superior environmental benefits over cork powder due to their reduced processing requirements and higher recyclability, contributing to lower carbon emissions in production. The use of cork granules supports sustainable harvesting practices, preserving cork oak forests and promoting biodiversity. Compared to cork powder, cork granules provide enhanced durability and longer lifecycle, minimizing waste and reinforcing cork's reputation as an eco-friendly material.
Cost Considerations: Granules vs. Powder
Cork granules generally command a higher price than cork powder due to their larger particle size and enhanced durability, making them ideal for applications requiring structural integrity. Cork powder offers a cost-effective alternative for filler and insulation purposes where fine texture is preferable, enabling more economical production processes. Choosing between cork granules and powder depends on balancing performance requirements against budget constraints in specific industrial or construction uses.
Choosing the Right Cork Form for Your Needs
Cork granules provide superior drainage and cushioning, making them ideal for applications such as flooring underlays and horticultural mulch, while cork powder offers finer texture suited for adhesives, fillers, and composite materials. Selecting the right cork form depends on the specific project requirements, including particle size impact on durability and flexibility. Evaluating granule size versus powder fineness ensures optimized performance and cost-effectiveness in construction, packaging, or craft uses.
Future Trends in Cork Material Innovations
Cork granules offer superior thermal and acoustic insulation properties compared to cork powder, driving increased adoption in sustainable construction and automotive industries. Advances in nano-structuring cork granules are enhancing their durability and functional versatility, positioning them as key components in next-generation eco-friendly composites. Research into biodegradable binders combined with cork powder aims to expand applications in packaging and filtration, indicating a promising future for diverse cork material innovations.
cork granules vs cork powder Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com