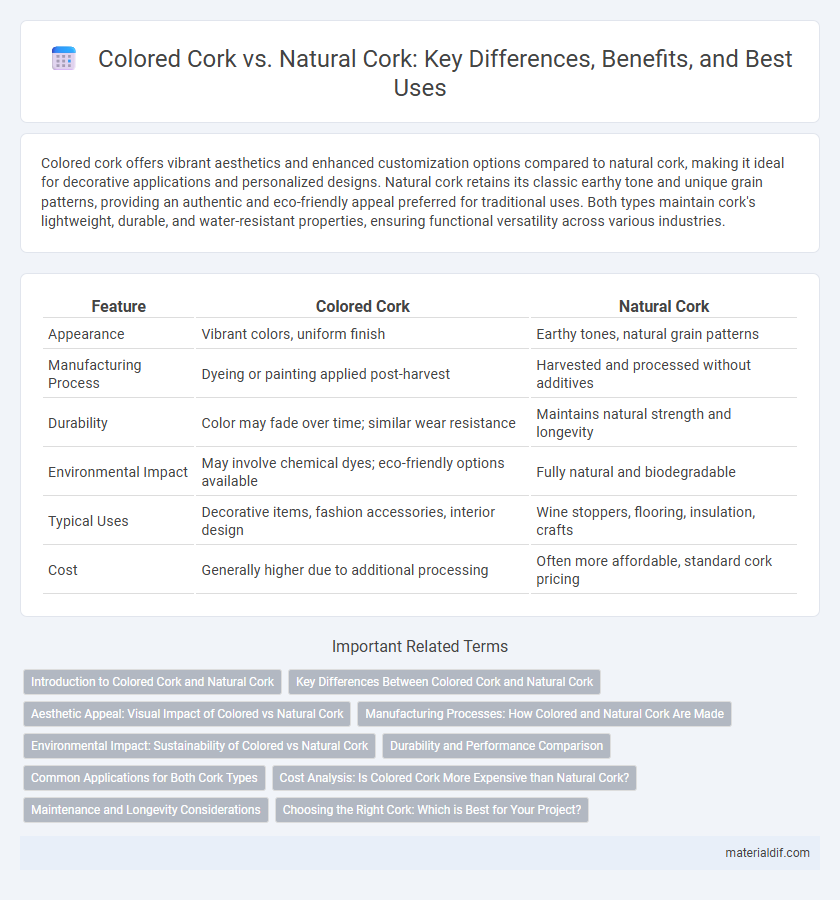
Colored cork offers vibrant aesthetics and enhanced customization options compared to natural cork, making it ideal for decorative applications and personalized designs. Natural cork retains its classic earthy tone and unique grain patterns, providing an authentic and eco-friendly appeal preferred for traditional uses. Both types maintain cork's lightweight, durable, and water-resistant properties, ensuring functional versatility across various industries.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Cork | Natural Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Vibrant colors, uniform finish | Earthy tones, natural grain patterns |
| Manufacturing Process | Dyeing or painting applied post-harvest | Harvested and processed without additives |
| Durability | Color may fade over time; similar wear resistance | Maintains natural strength and longevity |
| Environmental Impact | May involve chemical dyes; eco-friendly options available | Fully natural and biodegradable |
| Typical Uses | Decorative items, fashion accessories, interior design | Wine stoppers, flooring, insulation, crafts |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additional processing | Often more affordable, standard cork pricing |
Introduction to Colored Cork and Natural Cork
Colored cork offers versatile design options by infusing natural cork with pigments, enhancing aesthetic appeal while maintaining its lightweight and sustainable properties. Natural cork, harvested from the bark of cork oak trees primarily in Portugal and Spain, is prized for its elasticity, breathability, and eco-friendly characteristics. Both types serve diverse applications in flooring, wall coverings, and crafts, with colored cork providing a modern twist on traditional natural cork textures.
Key Differences Between Colored Cork and Natural Cork
Colored cork undergoes a dyeing or painting process that imparts vibrant hues, while natural cork retains its original earthy tones and grain patterns. The treatment used for colored cork can enhance its aesthetic versatility but may slightly reduce its natural breathability compared to untreated natural cork. Both types maintain cork's inherent properties like lightweight, resilience, and water resistance, making them suitable for flooring, crafts, and insulation.
Aesthetic Appeal: Visual Impact of Colored vs Natural Cork
Colored cork offers vibrant hues that enhance design versatility in interior and product applications, creating bold, modern aesthetics not achievable with natural cork. Natural cork's warm, organic tones provide a timeless, rustic charm that complements eco-friendly and minimalist styles. Selecting between colored and natural cork depends on desired visual impact, with colored cork emphasizing creativity and natural cork highlighting authenticity and texture.
Manufacturing Processes: How Colored and Natural Cork Are Made
Natural cork is harvested directly from the bark of cork oak trees and undergoes a traditional curing process involving boiling, drying, and sanding to maintain its organic properties. Colored cork is created by infusing natural cork with dyes or pigments during manufacturing, often combined with resin to enhance color saturation and durability. Both types require precise control of temperature and pressure during production to retain cork's elasticity and lightweight characteristics.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Colored vs Natural Cork
Natural cork is environmentally advantageous due to its renewable harvesting process and biodegradability, preserving cork oak forests and supporting biodiversity. Colored cork, often modified with synthetic dyes or coatings, may introduce chemicals that affect its compostability and increase environmental footprint. Opting for natural cork ensures lower ecological impact and promotes sustainable forest management.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Colored cork undergoes additional dyeing processes that may slightly reduce its natural elasticity and durability compared to natural cork, which retains its inherent resilience and compressibility. Natural cork typically offers superior performance in cushioning, moisture resistance, and longevity, making it ideal for applications requiring sustained durability. While colored cork can be used aesthetically, natural cork remains the preferred choice for high-performance uses due to its unmatched structural integrity and environmental adaptability.
Common Applications for Both Cork Types
Colored cork and natural cork are widely used in applications such as flooring, wall tiles, and bulletin boards due to their durability and insulation properties. Both types are popular in fashion accessories like wallets, handbags, and footwear, offering eco-friendly alternatives with different aesthetic appeals. Additionally, colored cork is often favored in decorative crafts and interior design projects where color customization is important, while natural cork remains preferred for wine stoppers and acoustic panels.
Cost Analysis: Is Colored Cork More Expensive than Natural Cork?
Colored cork generally incurs higher production costs due to added dyeing and finishing processes, making it more expensive than natural cork. Natural cork's cost benefits stem from its minimal processing and sustainable harvesting methods. Market prices vary depending on quality, but colored cork typically commands a premium in both retail and wholesale sectors.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Colored cork offers enhanced aesthetic options but may require more frequent maintenance due to potential color fading and surface wear compared to natural cork. Natural cork boasts superior durability and resilience, often lasting several decades with minimal upkeep, as its natural properties resist moisture and microbial growth effectively. Choosing between colored and natural cork depends on balancing visual appeal with long-term durability and maintenance efforts.
Choosing the Right Cork: Which is Best for Your Project?
Colored cork offers vibrant customization options ideal for decorative crafts and interior design, while natural cork provides a classic, eco-friendly material known for its durability and sustainability. Selecting the right cork depends on the project's aesthetic needs, environmental considerations, and functional requirements such as water resistance and flexibility. For sustainable architecture or sealing applications, natural cork is preferred, whereas colored cork suits creative projects demanding visual impact.
Colored cork vs Natural cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com