Cork oak bark harvesting involves carefully stripping the outer bark of cork oak trees without damaging the inner layers, ensuring sustainability and allowing the bark to regenerate over time. Composite cork manufacturing, on the other hand, utilizes granulated cork waste combined with adhesives to create versatile products such as flooring and insulation, optimizing material efficiency and reducing waste. Both processes play critical roles in Cork's economy, balancing traditional methods with modern innovation to maximize resource use.
Table of Comparison
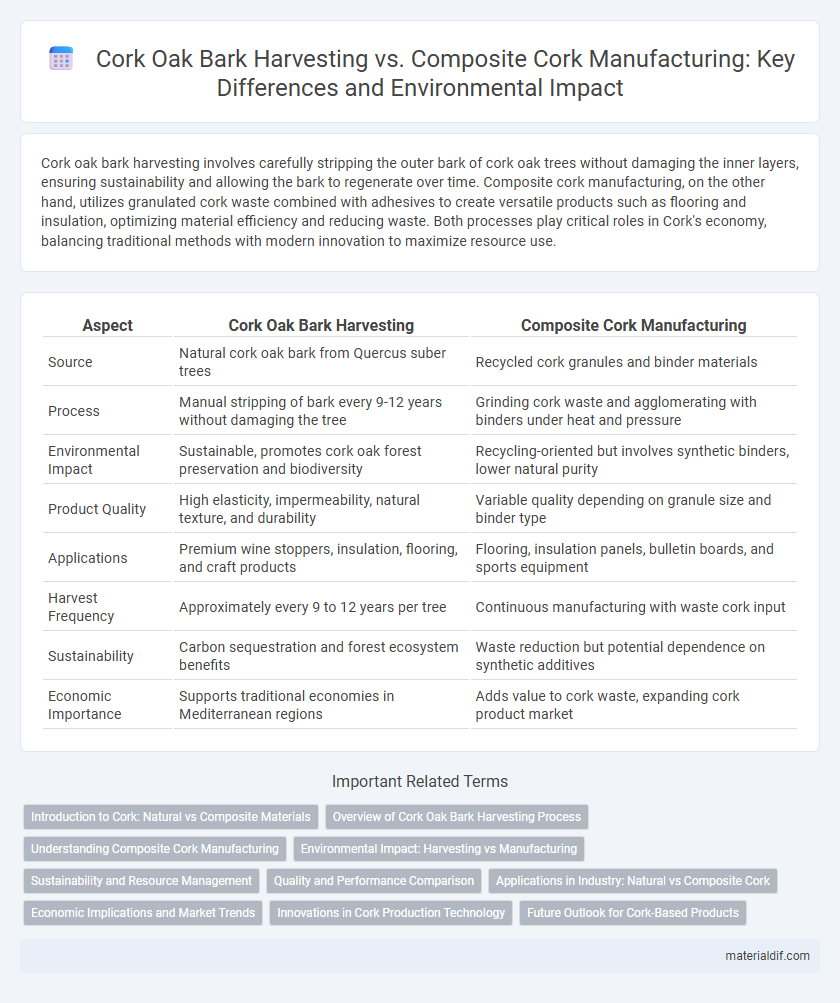
| Aspect | Cork Oak Bark Harvesting | Composite Cork Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural cork oak bark from Quercus suber trees | Recycled cork granules and binder materials |
| Process | Manual stripping of bark every 9-12 years without damaging the tree | Grinding cork waste and agglomerating with binders under heat and pressure |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable, promotes cork oak forest preservation and biodiversity | Recycling-oriented but involves synthetic binders, lower natural purity |
| Product Quality | High elasticity, impermeability, natural texture, and durability | Variable quality depending on granule size and binder type |
| Applications | Premium wine stoppers, insulation, flooring, and craft products | Flooring, insulation panels, bulletin boards, and sports equipment |
| Harvest Frequency | Approximately every 9 to 12 years per tree | Continuous manufacturing with waste cork input |
| Sustainability | Carbon sequestration and forest ecosystem benefits | Waste reduction but potential dependence on synthetic additives |
| Economic Importance | Supports traditional economies in Mediterranean regions | Adds value to cork waste, expanding cork product market |
Introduction to Cork: Natural vs Composite Materials
Cork oak bark harvesting involves carefully stripping the outer bark from cork oak trees every 9 to 12 years, preserving the tree's health while producing natural, renewable cork material. Composite cork manufacturing recycles cork granules bound with resins or adhesives to create versatile cork products that maintain some natural properties but offer enhanced flexibility and durability. Natural cork stands out for its sustainability and breathability, while composite cork provides cost-effective alternatives suited for diverse industrial applications.
Overview of Cork Oak Bark Harvesting Process
Cork oak bark harvesting involves carefully stripping the outer bark from mature Quercus suber trees every 9 to 12 years, ensuring the tree remains unharmed and continues to thrive. This sustainable process yields high-quality cork bark, which is then traditionally used for natural cork production or processed further into composite cork materials. The harvesting technique emphasizes manual skill and timing to maximize cork quality and maintain ecological balance in cork oak forests.
Understanding Composite Cork Manufacturing
Composite cork manufacturing involves the processing of cork granules derived from cork oak bark harvesting, which maximizes material utilization and reduces waste. This method blends granulated cork with resins or binders to create versatile products used in flooring, insulation, and fashion accessories. The innovation in composite cork manufacturing enhances durability and design flexibility compared to natural cork bark products.
Environmental Impact: Harvesting vs Manufacturing
Cork oak bark harvesting supports sustainable forestry by allowing bark to regrow every 9 to 12 years, promoting carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation. Composite cork manufacturing involves recycling cork granules, reducing waste but requiring energy-intensive processes with higher carbon emissions compared to natural bark harvesting. Overall, harvesting has a lower environmental impact due to its renewable nature and minimal processing, while composite manufacturing leverages waste reduction but incurs greater resource use.
Sustainability and Resource Management
Cork oak bark harvesting is a sustainable practice that promotes the health and regeneration of cork oak forests by allowing trees to live for over 200 years while continuously providing bark every 9-12 years. Composite cork manufacturing utilizes cork waste and by-products, reducing raw material consumption and minimizing environmental impact through circular resource management. Both methods contribute to biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration, positioning Cork's traditional harvesting and innovative manufacturing as complementary strategies in sustainable cork industry development.
Quality and Performance Comparison
Cork oak bark harvesting produces natural cork known for its superior elasticity, breathability, and long-term durability, essential qualities for premium wine stoppers and insulation materials. Composite cork manufacturing uses granulated cork bonded with synthetic resins, offering consistent density and enhanced dimensional stability but slightly reduced natural performance characteristics. Quality assessments reveal that natural cork excels in resilience and environmental sustainability, while composite cork provides improved uniformity and cost-effectiveness for industrial applications.
Applications in Industry: Natural vs Composite Cork
Natural cork from Cork Oak bark harvesting is predominantly used in premium wine stoppers, insulation panels, and acoustic dampening due to its renewable and biodegradable properties. Composite cork manufacturing combines granulated cork with agglomerants, enabling versatile applications in flooring, sports equipment, and automotive components where durability and cost efficiency are critical. Industry adoption depends on the balance between sustainability of natural cork and the enhanced mechanical properties offered by composite cork products.
Economic Implications and Market Trends
Cork oak bark harvesting remains a cornerstone of the Portuguese and Spanish economies, generating substantial revenue through sustainable forestry practices and supporting rural communities. In contrast, composite cork manufacturing, driven by increased demand for budget-friendly and versatile products, is expanding rapidly, influencing market dynamics by broadening application sectors such as construction and fashion. Economic implications highlight traditional cork's premium market positioning versus composite cork's cost-efficiency, signaling a diversification in global market trends and consumer preferences.
Innovations in Cork Production Technology
Innovations in cork production technology are revolutionizing both Cork Oak bark harvesting and composite cork manufacturing processes. Advanced mechanical debarking techniques enhance precision and sustainability during cork oak bark harvesting, reducing tree damage and increasing bark quality. Concurrently, new composites utilize eco-friendly binders and automated molding systems to produce high-performance cork products with consistent density and improved durability.
Future Outlook for Cork-Based Products
Cork oak bark harvesting remains a sustainable and renewable resource, supporting biodiversity and local economies in regions like southern Portugal and southwestern Spain. Advances in composite cork manufacturing enhance product versatility, reducing waste and enabling applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors. The future of cork-based products lies in combining traditional bark harvesting with innovative composite technologies to meet growing demand for eco-friendly, high-performance materials worldwide.
Cork Oak Bark Harvesting vs Composite Cork Manufacturing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com