Cork is a natural, renewable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, valued for its lightweight, insulating, and moisture-resistant properties. Rubber, derived either naturally from latex sap or synthetically from petrochemicals, offers high elasticity, durability, and water resistance. While cork excels in sustainability and breathability, rubber outperforms in flexibility and impact absorption, making each ideal for different applications.
Table of Comparison
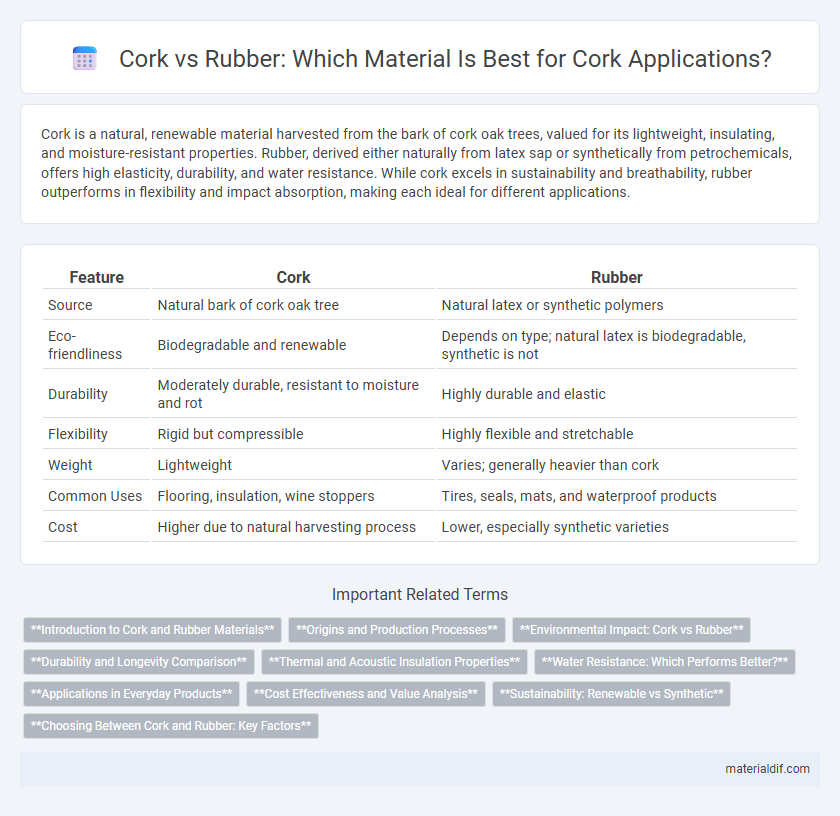
| Feature | Cork | Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural bark of cork oak tree | Natural latex or synthetic polymers |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable and renewable | Depends on type; natural latex is biodegradable, synthetic is not |
| Durability | Moderately durable, resistant to moisture and rot | Highly durable and elastic |
| Flexibility | Rigid but compressible | Highly flexible and stretchable |
| Weight | Lightweight | Varies; generally heavier than cork |
| Common Uses | Flooring, insulation, wine stoppers | Tires, seals, mats, and waterproof products |
| Cost | Higher due to natural harvesting process | Lower, especially synthetic varieties |
Introduction to Cork and Rubber Materials
Cork, harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, is a natural, renewable material prized for its lightweight, buoyant, and insulating properties. Rubber, derived either naturally from latex of rubber trees or synthetically produced, offers elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for diverse applications. Both materials serve distinct purposes with cork excelling in eco-friendly insulation and cushioning, while rubber is favored in flexible, resilient products such as tires and seals.
Origins and Production Processes
Cork is harvested from the bark of the cork oak tree (Quercus suber), primarily found in Mediterranean regions, with Portugal and Spain leading production due to their favorable climates and sustainable harvesting methods that allow bark regrowth every nine years. Rubber, derived from the latex sap of the Hevea brasiliensis tree native to the Amazon rainforest, undergoes a different production process involving tapping the trees and coagulating the sap into solid rubber sheets or synthetic alternatives manufactured through chemical polymerization. The distinct biological sources and extraction techniques define cork as a natural, renewable material and rubber as both a natural and synthetic polymer widely used in industrial applications.
Environmental Impact: Cork vs Rubber
Cork, harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, is a renewable and biodegradable material that supports biodiversity and reduces carbon emissions through sustainable forestry practices. Rubber, especially synthetic rubber derived from petroleum, has a higher environmental footprint due to non-renewable resource extraction, chemical processing, and lower biodegradability. Natural rubber, while renewable, involves deforestation and habitat loss in tropical regions, making cork a more eco-friendly choice overall.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cork offers exceptional durability due to its natural resilience, resisting wear, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, which contributes to its long-lasting performance in flooring and insulation applications. Rubber, while flexible and shock-absorbent, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV rays and heavy mechanical stress, reducing its effective lifespan compared to cork. Cork's cellular structure provides superior longevity, often outlasting rubber products in environments demanding consistent durability.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Cork offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.04 W/m*K, making it highly effective at maintaining temperature stability compared to rubber, whose thermal conductivity varies between 0.13 and 0.18 W/m*K. In terms of acoustic insulation, cork excels by absorbing sound waves due to its cellular structure, reducing noise transmission significantly more than rubber, which primarily reflects sound rather than absorbing it. These properties make cork a preferred choice for building applications requiring energy efficiency and soundproofing.
Water Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Rubber outperforms cork in water resistance due to its non-porous structure that prevents water absorption, making it highly effective for waterproof applications. Cork, while naturally water-repellent because of its cellular structure filled with suberin, tends to absorb some water over extended exposure. This makes rubber the preferred material for environments requiring consistent and long-term water resistance.
Applications in Everyday Products
Cork is widely used in everyday products such as wine stoppers, bulletin boards, and coasters due to its lightweight, buoyant, and sustainable properties. Rubber finds applications in tires, footwear soles, and seals because of its elasticity, durability, and water resistance. Both materials serve distinct functional purposes, with cork excelling in insulation and aesthetics while rubber prioritizes flexibility and impact absorption.
Cost Effectiveness and Value Analysis
Cork offers superior cost effectiveness compared to rubber due to its renewable sourcing and longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. While rubber may have a lower initial price, cork's natural insulation properties and durability provide better long-term value in applications such as flooring and insulation. Investment in cork materials ultimately results in lower total ownership costs and enhanced sustainability benefits.
Sustainability: Renewable vs Synthetic
Cork is a renewable and biodegradable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without harming them, making it a highly sustainable option. Rubber, often synthetic, is derived from petrochemicals, contributing to resource depletion and environmental pollution. Using cork helps reduce carbon footprints due to its natural regeneration and lower energy consumption in production compared to synthetic rubber.
Choosing Between Cork and Rubber: Key Factors
When choosing between cork and rubber, consider durability, environmental impact, and application suitability. Cork offers natural sustainability, lightweight properties, and excellent insulation, ideal for flooring and wine stoppers. Rubber provides superior elasticity, water resistance, and shock absorption, making it preferable for industrial uses and footwear.
Cork vs Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com